Syllabus: GS3/Space
In News
- ISRO has successfully demonstrated the bootstrap-mode start of its CE20 cryogenic engine at the Mahendragiri High-Altitude Test facility engine.
- Bootstrap-mode is a self-sustaining start-up sequence where the engine uses its own propellant flow and turbopump dynamics to initiate ignition.
- This will increase engine efficiency, restart capability, and reduce weight.
About CE20 Cryogenic Engine
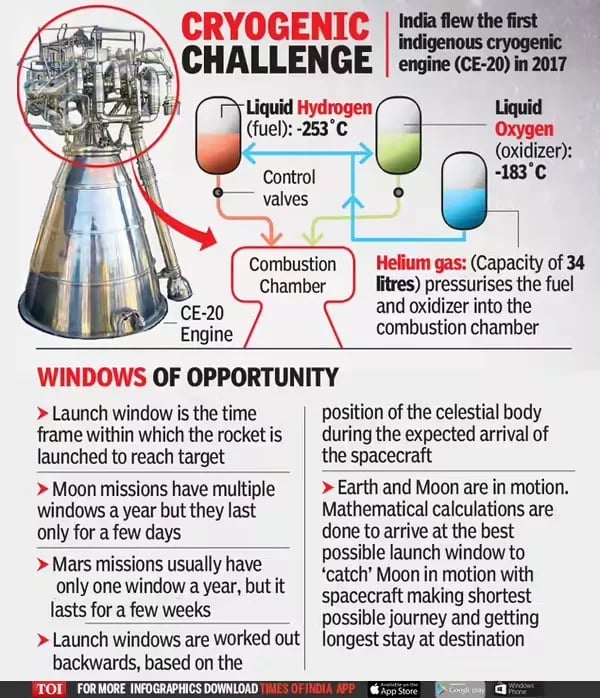
- Cryogenic engines use extremely low-temperature propellants — liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen (below -150°C).
- These engines are the last stage in space launch vehicles and provide higher efficiency and thrust per kilogram of propellant compared to earth-storable liquid or solid propellants.
- ISRO’s CE20 is India’s largest cryogenic engine developed by the Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre in Valiamala, Kerala.
- The CE20 engine powers the LVM3 upper stage and is also qualified for the ambitious Gaganyaan human spaceflight missions.
LVM3 (GSLV Mk III)
- LVM3 is ISRO’s new heavy-lift launch vehicle designed to carry payloads of up to 4000 kg to the Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit (GTO).
- It has three stages: two solid propellant S200 strap-ons, the liquid L110 core stage with two high thrust Vikas engines (human-rated Vikas engine supplied by Godrej Enterprises for Gaganyaan), and the C25 cryogenic upper stage powered by CE20 engines.
Significance
- Strengthens Gaganyaan readiness.
- Positions India competitively in global heavy-lift and commercial launch markets.
- Advances India’s cryogenic engine ecosystem toward reusable vehicles.
Source :ET
Previous article
SC Strikes Down Some Provisions of Tribunals Reforms Act
Next article
India Becoming A Hub of Natural Farming