BRICS Plus Naval Exercise
Syllabus: GS2/ International Relation
In News
- India skipped the BRICS Plus naval exercise “Will for Peace 2026” hosted by South Africa, opting out entirely despite holding the BRICS chair this year.
- India clarified that such naval drills are not institutionalised activities of BRICS, but ad-hoc initiatives, and therefore participation is not automatic or obligatory.
What are BRICS Plus Naval Exercises?
- BRICS Plus naval exercises are ad-hoc maritime drills involving BRICS members and selected non-BRICS partner countries.
- They are not mandated under the BRICS framework and do not form part of official BRICS mechanisms.
- Led by China, the exercise features active naval participation from Russia, Iran, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), and South Africa.
What is BRICS?
- Definition: BRICS is an informal, non-institutionalized group of eleven countries from the Global South.
- Origin: The term “BRIC” was coined in 2001 by a Goldman Sachs economist. The group formally launched as a diplomatic forum in 2006, with the first Summit of Heads of State held in 2009 in Russia.
- Member Countries: The group includes the five original members (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) and six members admitted during the 2024-25 expansion (Egypt, Ethiopia, Indonesia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates).
- Core Objectives: The group aims to increase the influence of emerging economies in international governance. It seeks to reform global institutions like the UN, IMF, and World Bank to make them more equitable and representative.
- Financial Arm: The New Development Bank (NDB) acts as the group’s primary international financial organization to support infrastructure and sustainable projects.
Source: TH
India’s First-ever Open-sea Marine Fish Farming Project
Syllabus: GS3/Aquaculture
Context
- The government launched India’s first-ever open-sea Marine Fish Farming project from the Andaman Sea.
About
- The project is a collaboration between the Ministry of Earth Sciences, the National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT), and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- The pilot initiative focuses on open-sea cultivation of marine finfish and seaweed in natural ocean conditions, integrating scientific innovation with livelihood generation.
- The project aims to boost seafood production and reduce pressure on coastal fishing.
Open-sea Fish Farming
- Open-sea marine fish farming refers to the cultivation of marine fish species in offshore waters, away from the coastline.
- It is done using cages, or submersible systems designed to withstand high waves, currents, and wind conditions.
- Open-sea marine fish farming holds significant potential for sustainable fisheries, livelihood security, and blue economy expansion.
Source: PIB
80 Years of Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)
Syllabus: GS2/ International Groupings
In News
- The United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) completed 80 years of its functioning.
About
- It is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations, acting as the central forum for international economic, social and environmental policy coordination.
- It was established in 1945 under the UN Charter.
- ECOSOC functions as a unique bridge between governments and non-state actors, with over 6,500 NGOs having consultative status, enabling civil society, youth and other stakeholders to participate in global policymaking.
- During the 2000s, ECOSOC emerged as a key forum to review progress on the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) and, since 2015, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) through mechanisms like the High-Level Political Forum (HLPF).
Source: UN
Tariff Threat Over Greenland May Imperil EU Trade Deal
Syllabus:GS2/IR
In News
- EU lawmakers are moving to delay or block approval of the EU–US trade deal after US President Donald Trump threatened tariffs on countries supporting Greenland’s sovereignty.
Greenland
- It is located in the Northern Hemisphere and is surrounded by the Arctic Ocean in the north, the North Atlantic Ocean in the south, Baffin Bay in the west and the Greenland Sea in the east.
- It lies closer to North America, but culturally and politically it is tied to Denmark.
- Resources: It is mineral-rich with large deposits of traditional resources such as gold, nickel, and cobalt.
- It also has some of the biggest reserves of rare earth minerals such as dysprosium, praseodymium, neodymium, and terbium.
- Governance : Greenland gained home rule in 1979 and expanded self-government in 2009, giving it authority over domestic affairs like healthcare and education.
- Denmark retains control over defense, foreign policy and monetary policy.
Major powers are eyeing Greenland
- Greenland, part of North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) through the membership of Denmark, has strategic significance for the US military and for its ballistic missile early-warning system since the shortest route from Europe to North America runs via the Arctic island.
- China has shown strong interest in Greenland’s rare mineral resources, and infrastructural projects.
- As part of its “Polar Silk Road” plan, China aims to develop Arctic shipping routes that could significantly reduce maritime travel times.
- Climate change has intensified the global interest in Greenland. Global warming has made the Arctic warm quicker, which means melting of ice happens faster and there is easier access to natural resources.
Various Developments
- Donald Trump announced new tariffs of 10% from February 1, rising to 25%, unless the EU agrees to a deal over Greenland, prompting strong backlash from EU leaders.
- Critics argue the trade deal already favors the US, especially after Washington expanded 50% tariffs on steel and aluminium.
- As tensions rise, EU lawmakers are considering suspending the agreement and potentially using the EU’s anti-coercion instrument in response to US pressure, making passage of the trade deal increasingly uncertain.
Source :IE
Chips to Start-up (C2S) Programme
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- Over 1 lakh individuals have enrolled in chip design training, with approximately 67,000 trained so far under the C2S programme.
About
- The C2S Programme is an umbrella capacity-building initiative launched by the MeitY in 2022, with a total outlay of ₹250 crore over five years.
- The C2S Programme targets the development of 85,000 industry-ready professionals across undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral levels. This includes:
- 200 PhD scholars engaged in advanced research in chip design,
- 7000 M. Tech graduates specializing in VLSI or Embedded Systems,
- 8800 M. Tech graduates from computer, communication, or electronic systems programmes with focused VLSI exposure,
- 69,000 B. Tech students trained through VLSI-oriented coursework.
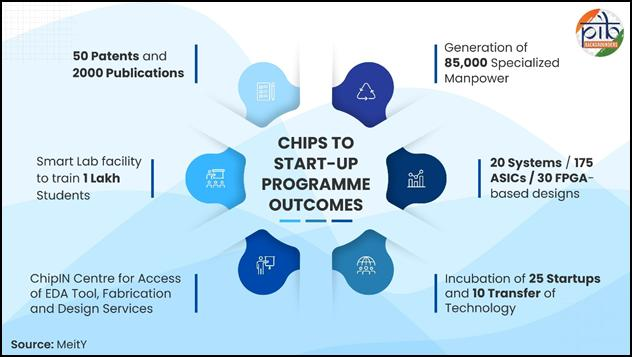
- Need for the Program: With rising demand for advanced electronics and AI, the semiconductor industry is expected to reach nearly USD 1 trillion by 2030.
- A global talent shortage of over 1 million professionals by 2032 positions India as a key contributor to the semiconductor ecosystem through focused initiatives.
- Significance: The C2S Programme democratises access to advanced design capabilities.
- It empowers students, researchers, and entrepreneurs irrespective of institution or location to develop innovative semiconductor solutions.
- It accelerates indigenous innovation in line with the vision of technological self-reliance and global competitiveness.
Source: PIB
Green Aluminium
Syllabus: GS3/Economy/Environment
In News
- NALCO CMD said India’s aluminium sector is not yet ready for green aluminium under the EU’s CBAM due to high power costs and dependence on thermal energy.
| Do you know? – India is the 2nd largest Aluminium producer after China, and top-10 producer in refined copper. – India’s aluminium industry is strategically strong and among the world’s largest, supported by a rich bauxite resource base and led by major producers such as NALCO, Hindalco, BALCO and Vedanta Aluminium. – Aluminium is widely used across power, transport, construction, packaging, machinery, aerospace and consumer goods, and demand is rising, especially in automobiles, housing, solar energy and power transmission. |
Green Aluminium
- It refers to aluminium produced using methods that minimize greenhouse gas emissions and environmental impact.
- Traditional aluminium production is energy-intensive and relies heavily on fossil fuels, contributing to carbon emissions.
- Green aluminium is manufactured using renewable energy sources, recycled materials, and innovative technologies to reduce its environmental footprint.
Importance
- Green aluminium significantly cuts carbon emissions, saves energy through recycling, and supports a circular economy by reducing waste.
- It enhances corporate sustainability credentials while retaining aluminium’s key qualities—lightweight, durable, corrosion-resistant, and versatile—without compromising performance.
Source :IE
Indiaphonte Bijoyi: Microscopic Crustacean From Kavaratti
Syllabus: GS3/Species
In News
- Scientists have discovered a tiny crustacean from the Kavaratti lagoon in the Lakshadweep islands and identified it as both a new genus and a new species.
About Microscopic crustacean
- It is a microscopic crustacean (copepod) belonging to the family Laophontidae under the order Harpacticoida.
- The name Indiaphonte honours India, while bijoyi recognises marine scientist S. Bijoy Nandan.
- The genus Indiaphonte is considered new due to its unique set of physical features that do not match any known genus within the Laophontidae family.
- Description The organism has a semi-cylindrical body, wider in the middle and tapering at the rear, with antenna-like appendages at the front.
- Females are slightly larger than males, measuring between 518 and 772 micrometres.
- It is classified as meiofauna and these microscopic animals live in aquatic sediments and play an important role in ecosystem health.
Source :TH
Previous article
Power Distribution Utilities Post Profit After Years of Losses
Next article
IMEC’s Relevance to India and its Chokepoints