
Syllabus :GS2/Governance; GS3/Internal Security
In News
- On India’s 79th Independence Day, Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced a high-powered demography mission to protect the country from the dangers posed by illegal immigrants.
Illegal immigration in India
- It is a multifaceted issue involving unauthorized entry, overstaying of visas, and undocumented migration across porous borders.
- India faces challenges from cross-border migration, especially in northeastern states like Assam and West Bengal, leading to concerns over jobs, social stability, and culture.
Causes of Illegal Migration
- Porous Borders: India shares unfenced borders with Bangladesh, Myanmar, Nepal, and Bhutan, making clandestine entry easier.
- Political Instability ,Ethnic and Religious Persecution: Rohingya Muslims from Myanmar and minorities from Bangladesh and Pakistan often flee persecution, seeking refuge in India.
- Economic Disparities: Migrants from neighboring countries seek better employment opportunities and living conditions.
- Lack of Legal Framework: India is not a signatory to the 1951 UN Refugee Convention, and lacks a national refugee law, making it difficult to distinguish refugees from illegal immigrants.
Impacts of Illegal Migration
- Demographic & Social Impact: Alters population composition in border states like Assam, Tripura, West Bengal.
- Can fuel ethnic tensions (e.g., Assam Movement of the 1980s).
- Strain on education, housing, healthcare, sanitation in urban centres (Delhi, Mumbai).
- Economic Impact: Migrants often work for lower wages, affecting local workers.
- Increase in unregulated jobs, reducing tax revenues.
- Burden on Welfare Schemes as Free/subsidised rations, healthcare, and education diverted to non-citizens.
- Security Concerns: Possibility of cross-border infiltration by extremist groups (ULFA, HuJI, ISI-backed outfits).
- Fake documents (Aadhaar, ration cards, voter ID) used for unlawful activities.
- Smuggling, human trafficking, and narco-terrorism networks exploit porous borders.
- Political Impact: Illegal immigrants become a vote-bank through forged documents.
- Leads to polarised politics (CAA–NRC debates).
- Inter-state disputes over settlement of migrants (e.g., North-east vs Centre).
- Diplomatic & Neighbourhood Relations: Strains ties with neighbours like Bangladesh & Myanmar, who deny responsibility for outflow.
- India’s pushbacks (e.g., Rohingya deportation) criticised by international agencies on humanitarian grounds.
- Environmental Impact: Pressure on land, water, and forests due to rising population density.
- Encroachment into ecologically fragile areas (e.g., wetlands of Assam, forests of Northeast).
- Contributes to urban slums and unsustainable resource use.
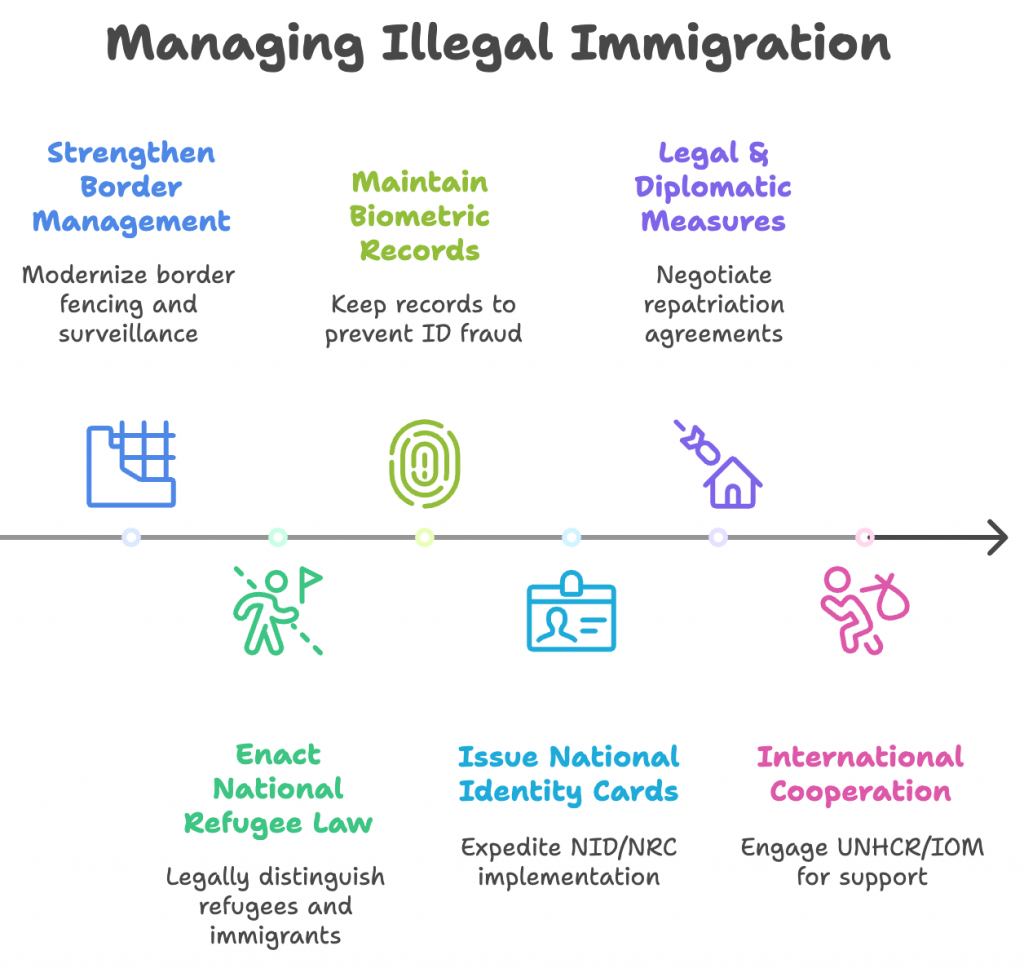
Steps Taken
- India reiterated its commitment to ensuring a crime-free border by effectively addressing the challenges of cross-border criminal activities, smuggling, movement of criminals and trafficking.
- Barbed wire fencing, border lighting, installation of technical devices and cattle fences are measures for securing the border.
- India plans to fence entire Myanmar border with anti-cut, anti-climb technology to deter illegal infiltration
- Legal Instruments: Citizenship (Amendment) Act, 2019 excludes certain religious minorities from the definition of illegal migrants.
- National Register of Citizens (NRC) used in Assam to identify undocumented migrants.
Source :TH
Previous article
How ‘Honour’ Killings in India are Reinforced and Legitimised?
Next article
PM Announced Next-gen GST Reforms