
South China Sea
Syllabus: Places in News
Context
- Recently, the United States deployed two warships near the disputed Scarborough Shoal in the South China Sea following a collision between Chinese naval vessels attempting to block a Philippine coast guard ship.
About the South China Sea
- It is a vital maritime corridor in the Indo-Pacific, bordering China and Taiwan to the north, Vietnam, Malaysia, Thailand, and Singapore to the west, Indonesia and Brunei to the south, and Philippines to the east.
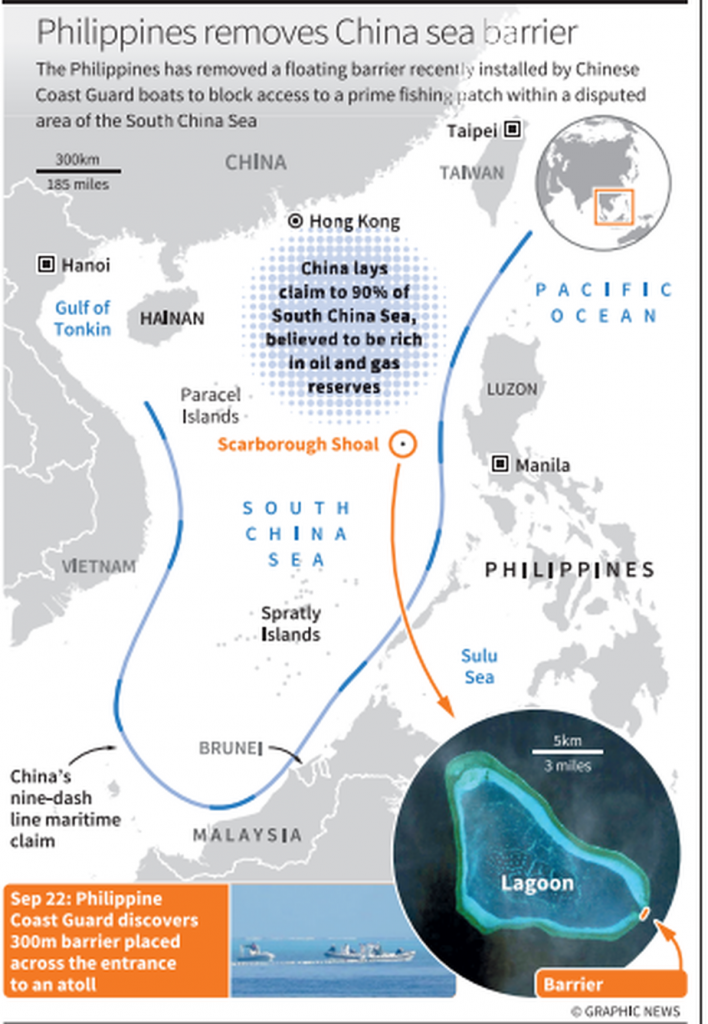
- It has become a flashpoint of geopolitical tension, territorial disputes, and strategic maneuvering, including Spratly Islands, Paracel Islands, and Scarborough Shoal.
- China asserts control over nearly the entire region via its ‘nine-dash line’.
- China has built artificial islands and military outposts, defying a 2016 international tribunal ruling that invalidated its expansive claims.
- Philippines, Vietnam, Malaysia, Brunei, and Taiwan have overlapping claims.
- Scarborough Shoal is claimed by China, Philippines, Vietnam, Malaysia, Brunei, and Taiwan.
India’s Position and Engagement
- India views the South China Sea as part of the global commons and supports freedom of navigation under international law.
- India’s evolving approach includes:
- Backing the 2016 tribunal ruling in favor of the Philippines.
- Participating in oil exploration projects in Vietnam’s EEZ through ONGC Videsh.
- Transitioning from Look East to Act East, emphasizing strategic engagement with ASEAN and Indo-Pacific partners.
India’s First Commercial Earth Observation Satellite Constellation
Syllabus: GS3/Science & Technology
Context
- Recently, India launched its first fully indigenouscommercial Earth Observation (EO) satellite constellation.
- It is the first time a private Indian consortium, led by PixxelSpace, will design, build, launch, and operate under a PPP model.
Satellite Capabilities and Applications
- This commercial Earth Observation (EO) satellite constellation aims to feature cutting-edge sensors like Panchromatic, Multispectral, Hyperspectral and Microwave Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR).
- It aims to deliver Analysis Ready Data (ARD) and Value-Added Services (VAS).
- Key Applications: Climate change monitoring, Disaster management, Agriculture and infrastructure planning, Marine surveillance, Urban development, and National security.
- Strategic Significance: Reduce India’s reliance on foreign satellite data, ensure national data sovereignty, and position India as a global leader in geospatial intelligence.
| Working of Earth Observation (EO) Satellites – EO satellites work by capturing electromagnetic radiation reflected or emitted from Earth’s surface. 1. They use specialized sensors to detect and record data across various spectral bands—visible, infrared, microwave, and more. – These satellites orbit the Earth in Low Earth Orbit (LEO) or Sun-Synchronous Polar Orbit (SSPO), allowing them to revisit the same location at regular intervals and capture high-resolution imagery. – Key Components and Payloads: 1. Electro Optical Infrared (EOIR): To capture images in mid-wave and long-wave infrared bands, useful for day/night surveillance, fire detection, and environmental monitoring. 2. Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR): To penetrate cloud cover and darkness to provide all-weather imaging. 3. Hyperspectral Sensors: To detect hundreds of spectral bands for detailed analysis of vegetation, minerals, and pollution. 4. GNSS-Reflectometry (GNSS-R): It uses reflected GPS signals to measure ocean surface winds, soil moisture, and flood zones. 5. SiC UV Dosimeter: It monitors UV radiation, especially for crewed missions like Gaganyaan. – EO satellites transmit raw data to ground stations where it is processed into Analysis Ready Data (ARD) and Value-Added Services (VAS), and processed data disseminated. – Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) – It is an autonomous, single-window agency under the Department of Space, Government of India. – It is designed to promote, enable, authorize, and supervise space activities by non-governmental entities (NGEs). – It acts as a bridge between ISRO and private players, facilitating the growth of a vibrant commercial space ecosystem. |
BNS Section 152
Syllabus :GS2/Governance
In News
The Supreme Court Friday issued a notice on a plea challenging the constitutional validity of Section 152 of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS).
- The petition contends that the provision “reintroduces the colonial sedition law”.
Section 152 of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita
- It penalizes anyone who, knowingly or purposely, through speech, writing, signs, electronic means, or financial support, promotes or attempts to promote secession, armed rebellion, subversive or separatist activities, or endangers India’s sovereignty, unity, and integrity.
- Punishment includes life imprisonment or up to seven years in prison, along with a fine.
Supreme Court’s Observations
- The Supreme Court questioned whether the potential misuse of Section 152 of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita could make the law unconstitutional.
- This arose during a hearing on a petition filed by the Foundation of Independent Journalism and editor of The Wire, who faces an FIR under Section 152 in Assam over a news article.
- The Court reaffirmed the importance of protecting press freedom while maintaining public order.
Source :TH
Dhirio
Syllabus :GS1/Culture
In News
Goa MLAs across party lines recently called for the legalisation of bull fighting, known locally as dhirio or dhiri, arguing it is a vital part of the state’s cultural heritage.
Dhirio
- It is also spelled Dhiri and refers to traditional bullfighting events in Goa, where two bulls are pitted against each other.
- The bulls fight head-to-head until one retreats or is injured.
- It is historically tied to post-harvest festivities and church feasts.
- Bulls were named (e.g., Tyson, Rambo) and had fan followings.
Legal Status
- It was banned in 1996 by the Bombay High Court at Goa under the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals Act, 1960 due to concerns over animal welfare.
- In 2014, the Supreme Court passed an order prohibiting all animal races and fights
- Despite the ban, clandestine fights continue, especially in South Goa’s coastal villages.
Source :IE
Whale strandings increased tenfold in a decade: CMFRI study
Syllabus :GS3/Environment
In News
Whale strandings along India’s southwest coast (Kerala, Karnataka, Goa) rose tenfold in the past decade.
Whale
- Whales are marine mammals classified under Cetacea, comprising baleen (Mysticeti) and toothed (Odontoceti) species.
- They breathe air and they are warm-blooded mammals
- Blue whales are the largest animals ever known to have lived on Earth.
Ecological Role
- Whales are crucial to ocean health: each great whale sequesters tons of CO₂, acting as a carbon sink.
- Their nutrient-rich fecal plumes stimulate plankton growth, which captures CO₂ and produces atmospheric oxygen.
- Six of the 13 great whale species are classified as endangered or vulnerable
Threats
- Whale Strandings rose from 0.3% per year (2003–2013) to 3% per year (2014–2023), with nine cases reported in 2023 alone, mostly between August and November.
- Causes include climate change, high vessel traffic, fishing, noise pollution, ship strikes, habitat degradation, and shallow coastal areas.
- Bryde’s whales are the most commonly stranded species, with blue whales occasionally found. Two genetically distinct forms of Bryde’s whale exist in Indian waters.
- Rising sea temperatures and strong coastal currents contribute to strandings.
Suggestions
- There are calls for the development of region-specific conservation strategies, including real-time alert systems, marine conservation networks, fisher training, and enhanced citizen science efforts to better protect these endangered marine mammals.
Source :IE
Export Promotion Mission Plans
Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- The government is revising its earlier Export Promotion Mission plans to focus more on specific sectors, in response to the higher tariffs the U.S. has imposed on Indian imports.
About
- In the Union Budget for 2025-26, the Finance Minister announced an Export Promotion Mission with a ₹2,250 crore allocation for the current financial year.
- It would facilitate easy access to export credit, cross-border factoring support, and support to MSMEs to tackle non-tariff measures in overseas markets.
- Ministeries: Driven jointly by the Ministries of Commerce and Industry, the Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises, and the Ministry of Finance.
- Revised Mission Plans: This would entail reducing the cost of credit for medium, small, and micro enterprise (MSME) borrowers in the worst-hit sectors, expediting clearances, and providing them with some sort of export incentives.
- The sectors that will be most impacted by the U.S. tariffs are apparel and textiles, shrimp exporters, organic chemicals, and machinery and mechanical appliances.
- The revised plan will be a joint effort across several Ministries and involves detailed consultations with industry stakeholders.
Source: TH
Kancha Gachibowli Forest
Syllabus: GS3/Environment
Context
- The Chief Justice of India said that the Telangana government must submit a proposal to restore the “devastated” Kancha Gachibowli forest.
- The government had cleared over 100 acres in the Kancha Gachibowli forest area abutting the University of Hyderabad for an IT infrastructure project.
About Kancha Gachibowli Forest (KGF)
- Kancha Gachibowli Forest (KGF) is a vital urban forest spanning around 400 acres adjacent to the University of Hyderabad, located in Telangana.
- It belongs to the Deccan scrub forest ecosystem—one of India’s most ecologically significant and under-protected landscapes.
- Biodiversity: About 233 bird species, including migratory ones, approximately 72 tree species, and over 40,000 trees.
- Scheduled and protected fauna, including spotted deer, wild boars, monitor lizards, star tortoises, Indian rock pythons, peacocks, and the rare tree-trunk spider (Murricia hyderabadensis)—the only known habitat of this species.
The Deccan Thorn Scrub Forests
- The Deccan Thorn Scrub Forests are a tropical dry shrubland ecoregion found mainly in the Deccan Plateau and adjoining areas of India and parts of northern Sri Lanka.
- They represent the driest and most degraded form of tropical dry deciduous forests, occurring in regions with very low and erratic rainfall.
- These areas are often subject to overgrazing, fuelwood collection, and agricultural expansion, leading to sparse vegetation.
- Major states: Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu.
Ecological Importance
- Provides habitat for arid-adapted species and endemic birds.
- Acts as a buffer against desertification.
- Grazing lands for pastoral communities.
Source: TH
Expanding SC/ST Scholarships
Syllabus: GS2/Vulnerable Sections of Society
Context
- The Union government is considering major reforms to its scholarship programs for Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) for the next financial cycle (FY 2026–27 to FY 2030–31).
Post and pre-matric scholarships for SCs, Scheduled Tribes (STs), and OBCs
- The government runs post and pre-matric scholarships for SCs, STs, and OBCs as centrally sponsored schemes, funded jointly by the Union and State governments in a 60:40 ratio (90:10 for northeastern states).
- Post-matric scholarships are for Indian students studying beyond 10th grade, while pre-matric scholarships are mainly for grades IX and X
- However, SC students from classes 1 to X are also eligible if their parents work in hazardous or unclean occupations.
- In both cases, the annual parental income must be below ₹2.5 lakh for eligibility.
Current Trends
- SC pre-matric scholarships fell by 30.63% between 2020–21 and 2024–25.
- SC post-matric scholarships dropped by 4.22% in the same period.
- ST scholarships also saw declines: pre-matric by 4.63 lakh, post-matric by 3.52 lakh.
- For OBCs, EBCs, and DNTs, pre-matric beneficiaries dropped from 58.62 lakh in 2021–22 to 20.25 lakh in 2023–24.
Proposed Expansions
- Raising income limits to ₹4.5 lakh for ST scholarships (currently below ₹2.5 lakh);
- Similar revisions for SC, OBC, and DNT scholarships under discussion by the Social Justice Ministry;
- Extending pre-matric scholarships to younger OBC students (from Class V onwards).
- Currently, only if parents are in hazardous occupations.
- Increasing scholarship amounts (e.g., up to ₹60,000 annually under new schemes)
| Constitutional Provisions Related to SCs and STs in India Definitions and Identification – Article 341 (SCs): The President may, by public notification, specify castes, races, or tribes deemed to be SCs in relation to a State or Union Territory, after consulting the Governor. 1. Parliament can amend this list by law. – Article 342 (STs): It allows the President to notify tribal communities and Parliament to modify the list. – Article 366(24) & (25): It provides definitions for SCs and STs as per Articles 341 and 342. Fundamental Rights and Social Safeguards – Article 15(4): It allows the State to make special provisions for the advancement of SCs and STs. – Article 16(4): It permits reservation in public employment for backward classes, including SCs and STs, not adequately represented. – Article 17: It abolishes untouchability and makes its practice punishable by law. – Article 25(2)(b): It enables the State to open Hindu religious institutions of public character to all classes and sections of Hindus. Educational and Economic Safeguards – Article 46: It directs the State to promote the educational and economic interests of SCs and STs and protect them from social injustice and exploitation. – Article 330 & 332: It provides for reservation of seats for SCs and STs in the Lok Sabha and State Legislative Assemblies. – Article 335: It states that claims of SCs and STs shall be considered in appointments to services and posts, consistent with administrative efficiency. Schemes Related To SCs & STs – Education-Based Schemes: 1. National Overseas Scholarship: For SC/ST students pursuing higher education abroad; Income ceiling: ₹6–8 lakh/year. 2. Dr. B.R. Ambedkar International Scholarship: Offers guidance and financial support for SC/ST students seeking global academic opportunities. – Employment and Skill Development: 1. Welfare of SC/ST Jobseekers Scheme: Implemented via 25 National Career Service Centres; Offers vocational guidance, computer training, and pre-recruitment coaching. 2. Free Coaching for SC/OBC Students: Central Sector Scheme offering coaching for competitive exams like UPSC, NEET, JEE. 3. Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY): Skill training for SC/ST youth across sectors; Includes reskilling and entrepreneurship modules. – Infrastructure and Residential Support: 1. SCSP-TSP (Scheduled Castes Sub-Plan & Tribal Sub-Plan): Residential schools in underserved areas; Hostels for UPSC aspirants in Delhi; Laptops and stipends for students. |
Norms governing Overseas Citizens of India (OCI)
Syllabus: GS2/Polity and Governance
Context
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has tightened the norms governing Overseas Citizens of India (OCI).
About OCI
- Introduced: 2005
- Purpose: Offers multiple-entry, multi-purpose lifelong visas to persons of Indian origin (PIOs) and their spouses.
- Benefits:
- No need to register with Foreign Regional Registration Officer or Foreign Registration Officer for any length of stay in India. However, permission is required to visit protected areas in India.
- Can open special bank accounts, buy non-farm property, apply for driver’s licence and PAN card.
- Eligibility Criteria
- It provides for registration as an OCI of all Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs) who were citizens of India on 26th January, 1950, or thereafter, or were eligible to become citizens of India on the said date.
- A foreign national who;
- Belonged to a territory that became part of India after 15th August, 1947; or
- A child or a grandchild or a great grandchild of such a citizen; or
- A minor child of such persons mentioned above; or
- A minor child whose both parents are citizens of India or one of the parents is a citizen of India is eligible for registration as OCI cardholder.
- Restrictions:
- No person whose parents, grandparents, or great-grandparents are or were citizens of Pakistan or Bangladesh is eligible for registration as an OCI cardholder.
- Foreign military personnel either in service or retired are also not entitled for grant of OCI.
- OCI is not to be misconstrued as ‘dual citizenship’.
Key Updates
- OCI registration will be cancelled if an individual:
- Is sentenced to imprisonment for 2 years or more, or
- Is charge-sheeted for an offence punishable with imprisonment of 7 years or more.
- This applies whether the offence occurs in India or abroad, as long as it is recognised under Indian law.
- These rules are notified under the Citizenship Act, 1955, and Citizenship Rules, 2009, which allow the central government to cancel OCI registration under specified conditions.
Source: AIR
International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics
Context
The 18th International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics (IOAA) is being hosted in India.
International Olympiad on Astronomy and Astrophysics (IOAA)
- It was established in 2006 to provide a global platform for high school students interested in astronomy.
- The first IOAA was held in 2007 in Thailand, with 21 countries participating and the event marking the formal adoption of its statutes and governance structure.
- Annual editions of the Olympiad have been hosted by counties across Asia, Europe, and South America, including Brazil, China, Colombia, Georgia, Greece, Hungary, India, Indonesia, Iran, Poland, and Romania.
- The Olympiad aims to promote scientific education and international collaboration among young astronomers.
- This year’s highlights : over 300 high school students from 64 countries participating in the 10-day event.
- This is the second time that India is hosting the IOAA, after the 2016 edition in Bhubaneswar.
- This year’s theme is ‘Vasudaiva Kutumbakam’, the “ancient Indian idea of the world is family under one sky”.
Source :TH
SabhaSaar
Syllabus: GS2/Government Initiative
Context
- The Union Government will launch ‘SabhaSaar’ in Tripura on Independence Day (15 August), with plans to extend it to other states.
About SabhaSaar
- Purpose: AI-powered tool to automatically generate minutes of gram sabha meetings.
- Functioning:
- Generates transcriptions from audio or video recordings.
- Panchayat officials can upload recordings using e-GramSwaraj login credentials.
- Technology Base: Built on Bhashini, the government’s AI-powered language translation platform.
- Language Support: All major Indian languages — Hindi, Bengali, Tamil, Telugu, Marathi, Gujarati — and English.
| Do you know? – Gram Sabha: Primary body of the Panchayati Raj system, comprising all registered voters in a gram panchayat. – Meetings: At least four times a year — 26 Jan, 1 May, 15 Aug, and 2 Oct. – There are 2,55,397 village panchayats, 6,742 intermediate panchayats, 665 district panchayats, and 16,189 traditional local bodies across the country. |
Source: IE