Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
In News
- Denmark has launched the world’s first commercial-scale e-methanol plant in Kasso.
- Developed by European Energy (Denmark) and Mitsui (Japan), the plant will produce 42,000 metric tonnes of e-methanol annually.
What is Methanol?
- About: Methanol (CH₃OH) is a light, volatile, and flammable liquid alcohol. Conventionally produced from natural gas and coal, it is used in chemicals, fuels, and plastics.
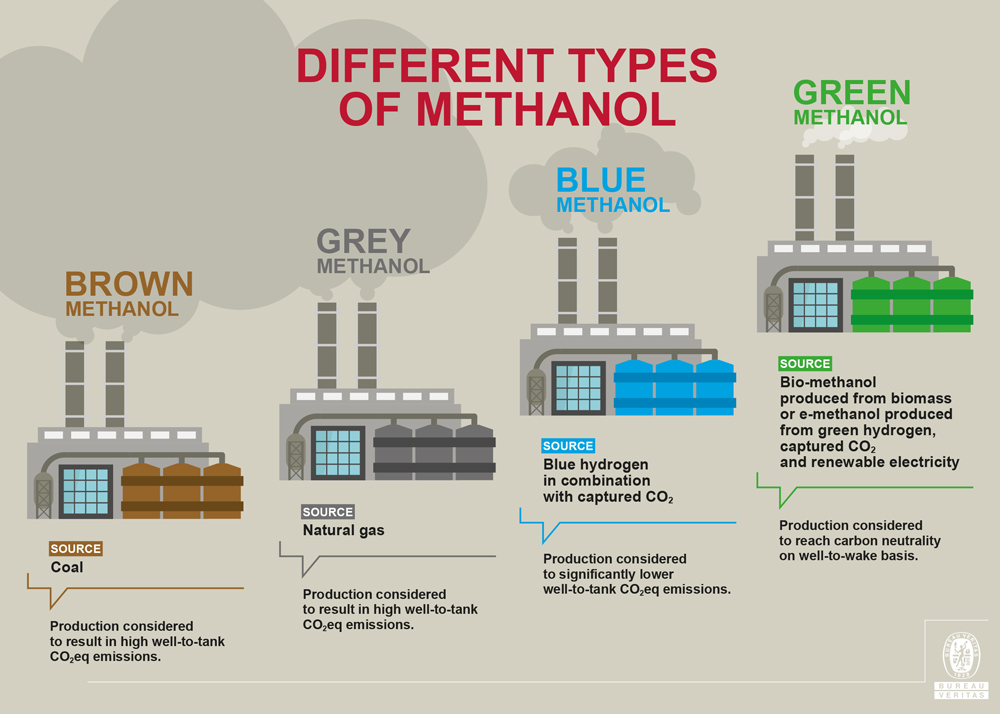
- Applications: Used in shipping fuel, plastic production, manufacturing fuel cells etc.
Challenges in e-Methanol Adoption
- High Cost: Not yet price-competitive with fossil fuels; price parity expected around 2035.
- Scale of Production: Infrastructure for large-scale green methanol is nascent.
- CO₂ Sourcing: Sustainable and reliable CO₂ capture remains a technological challenge.
- Storage and Distribution: Needs new or adapted logistics infrastructure.
India’s Methanol Economy Programme
- About: Launched by NITI Aayog, the Methanol Economy Programme aims to reduce oil import bills, curb pollution and promote cleaner alternatives of fuel.
- Key Pillars: Production of methanol from coal, biomass, and municipal waste can be used in LPG blend, power generation, and transportation which eventually helps in reducing India’s oil import bill & greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- The program targets a 10% reduction in crude oil imports by 2030 by substituting it with methanol.
- Government Initiatives and Progress: The Department of Science and Technology (DST) has initiated the Methanol Economy Research Programme (MERP) to support research and development in methanol production and utilization.
- Blending of 15% methanol in gasoline (M15) has been notified, and test standards are being developed.
- National Policy on Biofuels 2018 recognizes methanol and DME (dimethyl ether) as alternative fuels.
Source: TH
Previous article
Natural Farming Certification System
Next article
How is the Shipping Industry Tackling Emissions?