Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed
Syllabus: GS1/ History/Personalities in News
Context
- The President of India paid tributes to Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed, former President of India on his birth anniversary.
About Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed
- Early Life and Career: Born in 1905, Ahmed pursued his education in Delhi and later at the University of Cambridge. Upon returning to India, he practiced law and joined the Indian National Congress.
- Role in Freedom Struggle: He actively participated in the individual Satyagraha and Quit India Movement for which he was arrested in 1942.
- He was a close associate of Mahatma Gandhi.
- Career in Independent India: He was elected to the Rajya Sabha in 1952 and subsequently to the Lok Sabha in 1967. He held portfolios such as Food and Agriculture, Cooperation, Education, Industrial Development, and Company Laws.
- Presidency: He served as the fifth President of India from August 24, 1974, until his untimely demise on February 11, 1977.
- He was the second President of India to die in office, after Dr. Zakir Husain.
- During his presidency, he signed the proclamation of Emergency in 1975 following a meeting with Prime Minister Indira Gandhi, one of the most significant and controversial moments in India’s constitutional history.
Source: PIB
India rejects US Claim of Mediation
Syllabus: GS2/IR
Context
- India pushed back against US President Donald Trump’s offer to mediate on Kashmir and his claim that he used trade to prevent a “nuclear war” between India and Pakistan.
About
- On Nuclear War: India underlined that all military actions launched by its armed forces in response to the escalatory offensives by Pakistan were in the domain of ‘conventional’ warfare.
- On Ceasefire: India dismissed Trump’s claim that the US had made the two nations agree on a ‘ceasefire’ by using the threat of stopping trade with both India and Pakistan.
- Trade did not figure in any conversation between Indian and American leaders from the time of Operation Sindoor.
- To halt firing and military actions was worked out between the Directors General of Military Operations (DGMOs) of India and Pakistan.
- On Kashmir Issue: India’s long-standing position has been that any issues related to Jammu and Kashmir have to be addressed by India and Pakistan bilaterally. That stated policy has not changed.
Source: TOI
India to move UNSC 1267 to Declare TRF a Terror Group
Syllabus: GS2/IR
Context
- India has decided to send a team to the United Nations Security Council’s 1267 Sanctions Committee meeting to seek the designation of The Resistance Front (TRF) as a terrorist organisation.
About
- The team will present new evidence pointing to Pakistan’s involvement in supporting terrorism.
- The evidence will highlight TRF’s role in the attack.
- Pakistan, a non-permanent member of the UNSC, has been protecting TRF at the council with support from China.
1267 Sanctions Committee
- It is also called the ISIS and Al-Qaeda Sanctions Committee, was established under a UNSC resolution in 1999, to focus on combating terrorism linked to ISIS, Al-Qaeda, and related groups.
- Member States may at any time submit to the Committee listing requests for inclusion of individuals, groups, undertakings and entities.
- The Committee comprises all 15 members of the Security Council and makes its decision by consensus.
- Sanctions Measures Include:
- Asset Freeze: All assets of designated individuals/entities are frozen.
- Travel Ban: Listed individuals are banned from entering or transiting through any member state.
- Arms Embargo: Prohibition on supplying arms or related material.
US-Saudi Arabia Deals
Syllabus: GS2/ International Relations
Context
- The United States and Saudi Arabia signed a defence agreement worth nearly $142 billion, as part of a broader Saudi commitment to invest $600 billion in the US.
Key Components of the Agreement
- Defence Package:
- Arms, military systems, and services form the core of the deal.
- Discussions also included Saudi Arabia’s interest in Lockheed Martin’s F-35 fighter jets, though no final purchase has been confirmed.
- Commercial Deals:
- General Electric (GE): Gas turbines and energy solutions exports worth $14.2 billion.
- Boeing: Sale of 737-8 passenger aircraft worth $4.8 billion.
Source: IE
India’s Retail Inflation Hits Six-Year Low
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
In News
- Retail inflation in India, as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI), fell to 3.16% in April 2025, marking the lowest level in 69 months (since July 2019).
Key Takeaways from the Report
- Food Inflation Decline: Improved supply-side management, buffer stocks, and government interventions in pulses.
- Base Effect: A statistical phenomenon where current year prices are compared with abnormally high prices of the previous year, resulting in seemingly low inflation figures.
- Cooling demand: A slowdown in demand for housing, possibly due to factors like high prices, interest rates, or economic uncertainty, could lead to a moderation in price increases.
- Core Inflation Remains Higher: Excluding food inflation, the overall inflation would have been considerably higher at 4.1%, suggesting that the cooling is largely concentrated in the food sector.
What is CPI?
- About:
- Retail inflation reflects the rise in prices of goods and services at the consumer level and is calculated through the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- The CPI tracks price changes by comparing the current cost of a fixed basket of goods and services (such as food, clothing, housing, transportation, healthcare, and fuel) to its cost in a base year.
- In India, the current base year for CPI is 2012, and the index is compiled by the National Statistical Office (NSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- Significance of CPI: CPI as a macroeconomic tool used for:
- Inflation targeting by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- Policy formulation in areas like taxation, subsidies, and pensions.
- Measuring real economic growth as a deflator in national income accounts.
- Social welfare planning, particularly for vulnerable sections
- Types of CPI in India:
- CPI (Combined): Represents all-India retail inflation for both urban and rural consumers. It is the headline CPI used by the RBI for inflation targeting.
- CPI (IW): For Industrial Workers, used for wage indexation and labour policies.
- CPI (AL): For Agricultural Labourers, useful for rural poverty assessments and welfare schemes.
- CPI (RL): For Rural Labourers, often overlaps with CPI-AL, but used for specific rural wage analysis.
Source: TH
Weather Balloons
Syllabus: GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
- In the wake of budget cuts by the USA, a Silicon Valley startup will soon start to replace the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA’s) weather balloons with AI-powered alternatives.
Advent of weather balloons
- French meteorologist Leon Teisserenc de Bort pioneered the use of weather balloons in the late 19th century.
- Initially, these balloons carried meteorographs, which recorded pressure, temperature, and humidity.
- After bursting at high altitudes, the instruments gently descended to Earth, where data would be recovered.
- The 1930s saw a revolution with the invention of radiosondes — small instruments that could transmit data in real time to ground stations.
- Over time, these devices became lighter and more efficient, equipped with longer battery life and integrated with GPS for accurate location and wind tracking.
Global Weather Balloon Programme
- Currently, around 900 weather stations worldwide, including India’s 56 radiosonde stations, launch balloons twice a day in a coordinated international effort.
- These provide:
- Critical upper-air data for weather forecasts,
- Inputs for numerical weather prediction (NWP) models,
- Insights for climate monitoring and disaster preparedness.
Source: IE
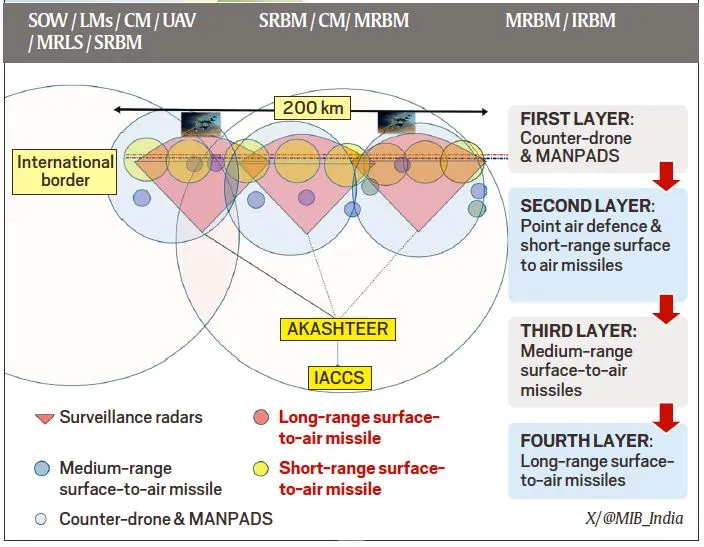
India’s Air Defence Shield
Syllabus: GS3/Defence
Context
- At the media briefing on Operation Sindoor, military officers displayed a picture of the Integrated Air Command and Control System (IACCS) node of the Indian Air Force (IAF).
About IACCS
- IACCS is an automated command and control system that integrates data from all air defence assets.
- It is developed by the public sector aerospace and defence electronics company Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL).
- The availability of the consolidated dataset, along with real-time updates, provides military commanders at multiple levels with a comprehensive picture and overall situational awareness during air operations.
The Army’s Akashteer
- The Indian Army has a similar air defence control and reporting system called Akashteer, which connects the units of its air defence.
- Akashteer too has been developed by BEL.
- Akashteer would enable the monitoring of low-level airspace over battle areas, and effectively control ground based air defence weapon systems.
- Akashteer operates at a comparatively small scale at present. It is in the process of being integrated with IACCS for effective coordination between the Army and Air Force air defence operations.
Source: IE