Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
Context
- In a bid to boost consumer trust and farmer incomes, the central government is likely to introduce a nationwide Natural Farming Certification System (NFCS).
What is Natural Farming?
- Natural Farming is a chemical-free farming system rooted in Indian tradition enriched with modern understanding of ecology, resource recycling and on-farm resource optimization.
Key Features of Natural Farming
- Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF): A popular model promoted by Subhash Palekar, aimed at drastically reducing input costs.
- Core practices:
- Beejamrit: Natural seed treatment.
- Jeevamrit: Soil inoculation using fermented cow dung and urine.
- Mulching and Waaphasa: Moisture retention and aeration of soil.
- Low input, high sustainability: Reduces dependence on market-bought inputs.
Benefits of Natural Farming
- Lower Input Costs: Natural farming requires fewer external inputs like chemical fertilizers and pesticides, which can reduce overall production costs for farmers.
- Ensures Better Health: As Natural Farming does not use any synthetic chemicals, health risks and hazards are eliminated.
- The food has higher nutrition density and therefore offers better health benefits.
- Environment Conservation: Natural Farming ensures better soil biology, improved agro-biodiversity and a more judicious usage of water with much smaller carbon and nitrogen footprints.
- Sustainable Farming Practices: By avoiding the overuse of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, natural farming promotes a more sustainable and regenerative approach to agriculture.
Why is Certification Needed?
- Trust Building: It helps consumers distinguish genuine natural farm produce.
- Market Access: It enables farmers to fetch premium prices and enter niche markets (domestic and international).
- Standardisation: It brings uniformity to natural farming practices.
- Monitoring and Accountability: It ensures traceability and quality control.
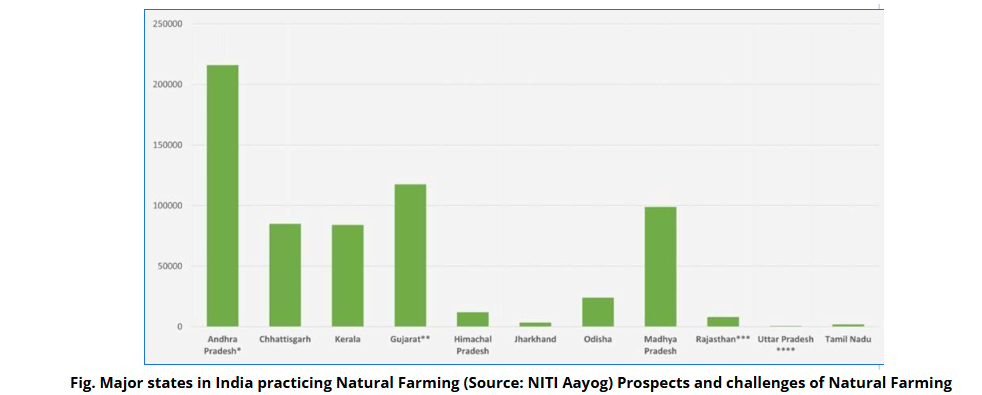
Challenges in Scaling Natural Farming
- Initial Yield Reduction: During the transition from conventional to natural farming, many farmers reported a temporary decline in crop yields.
- Limited Scientific Backing: Although natural farming is promoted as environmentally sustainable, there is limited large-scale, long-term scientific research validating its productivity, resilience, and scalability across diverse agro-climatic zones.
- Inadequate Institutional Support: Coordination between agriculture departments, research bodies, and rural institutions is limited.
| National Mission on Natural Farming – Aim: To promote natural farming among one-crore farmers across the country. – Cluster-Based Approach: Targeting 15,000 clusters in Gram Panchayats allows for focused implementation and better resource allocation. – Bio-Input Resource Centers (BRCs): Establishing 10,000 BRCs will ensure easy access to essential bio-inputs, making it convenient for farmers to adopt natural farming practices. – Model Demonstration Farms: 2000 NF Model Demonstration Farms shall be established at Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs), Agricultural Universities (AUs) and farmers’ fields. 1. They shall be supported by experienced and trained Farmer Master Trainers. – Certification and Market Access: A simplified certification system and dedicated branding will facilitate market access for natural farming products. |
Source: MINT
Previous article
Strengthening Inland Water Transport in India