Syllabus: GS3/ Agriculture
Context
- According to data presented in the Lok Sabha by the Union Minister of State for Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying, India’s total milk production stands at 239.30 million tonnes.
Milk Production in India
- Global Leadership: India has been the world’s largest milk producer since 1998, currently accounting for 25% of global output.
- Decadal Growth: From 2014–15 to 2023–24, production jumped by 63.56%, from 146.3 to 239.2 million tonnes, averaging an annual growth of around 5.7%, well above the global 2%.
- Per Capita Availability: Rose to 471 g/day in 2023–24, substantially above the world average of 322 g/day.
- Top Producing states: Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh.
Significance
- Economic Contribution: India’s dairy is the single largest agricultural commodity, contributing 5 percent to the national economy and directly employing more than 8 crore farmers.
- Nutritional Security: Milk is a major source of protein, calcium, and vitamins, improving dietary diversity.
- Export Potential: India is emerging as a supplier of dairy products like skimmed milk powder, butter, and ghee to Asia and Africa.
- Women’s Participation: 35% of members in dairy cooperatives are women, highlighting the sector’s role in gender-inclusive growth.
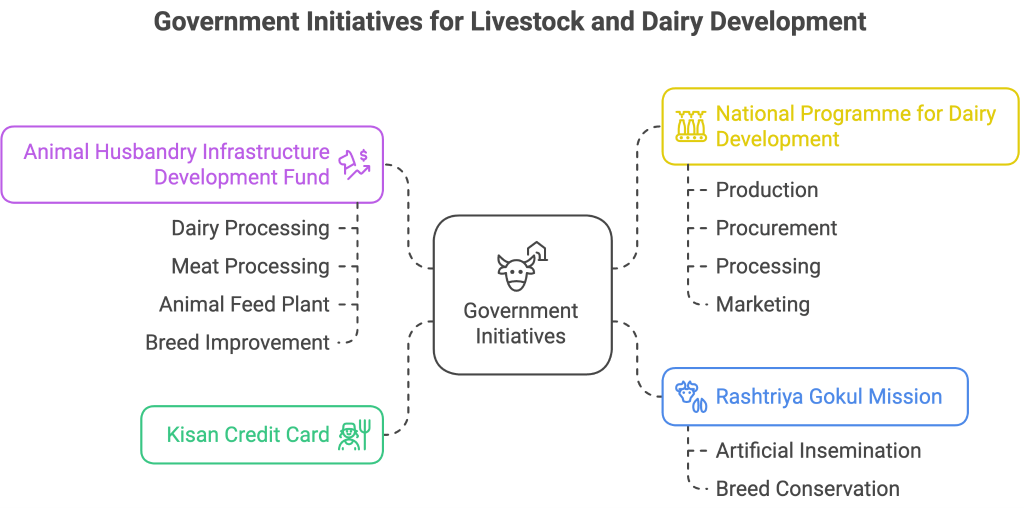
Challenges
- Breed Productivity Gaps: Yields still lag behind advanced dairy nations, especially among indigenous breeds.
- Pricing Volatility: Inconsistent procurement prices reduce incentive for farmers to invest in feed and breed improvement
- Climate Impact & Market Volatility: Extreme heat reduces yields and drives up prices.
- Slowing Growth: Production growth has slowed, from ~6% in earlier years to 3.78% in 2023–24, with buffalo milk output declining 16%.
- Post-Harvest Losses: Inadequate cold-chain and processing infrastructure cause wastage.
Way Ahead
- Boost Productivity: Intensify breed improvement (AI, IVF, indigenous genetics), nutrition reforms.
- Strengthen Infrastructure: Develop cold chains, chilling centres, and organized collection systems.
- Expand Cooperative Reach: Bring more farmers into organized frameworks; local-level cooperatives can cut inefficiencies.
- Risk Mitigation: Promote climate-resilient breeds, improve animal health (vaccination drives), and stable pricing frameworks.
- Enhance Inclusivity: Empower women through targeted interventions and enhanced participation.
Source: TH
Next article
NASA Plans to put a Nuclear Reactor on the Moon