Syllabus: GS2/E-Governance
Context
- The Minister of Science and Technology has said that India’s Space technology is playing a major role in revolutionising governance at the “Good Governance” Conclave.
What is Space Technology?
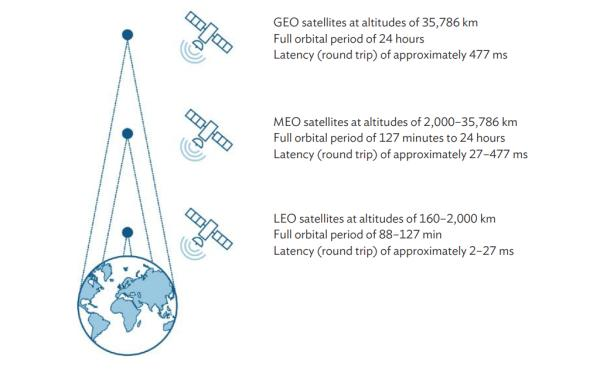
- Space technologies designate technologies used to enable activities conducted in outer space:
- such as Earth observation, satellite communication, satellite navigation or even robotic and human space exploration beyond Earth’s orbits.
- Governments use space technology, geospatial data, and field information for planning, monitoring, and evaluating developmental activities.
| Future Prospects and Economic Growth – Growth: India’s space economy is growing rapidly, with a tripled space budget and over 300 space startups. 1. The space sector’s value is expected to rise from $8 billion to $44 billion, marking India as a key global space player. – Vital Missions: Trials for India’s first human spaceflight, Gaganyaan Mission, will begin by the end of 2025. 1. India aims to send an astronaut to the Moon by 2040 and establish the Bharat Antariksh Station by 2035. |
Use of Space Technology in Governance
- Disaster Management and Response: National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) provides satellite data that helps in identifying flood-affected areas, mapping damage, and planning rehabilitation.
- The Indian National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) uses it for disaster relief operations.
- Agriculture and Rural Development: FASAL (Forecasting Agricultural output using Space, Agrometeorology, and Land-based observations) uses satellite data to predict crop yields, helping farmers make informed decisions.
- Soil Health Management and irrigation management are optimized using remote sensing technologies.
- Efficient Land Management: Initiatives like “Swamitva Yojana” use satellite mapping for land record management.
- This initiative simplifies land verification and promotes transparency in land ownership.
- Environmental Monitoring: Bhuvan an Indian web-based application developed by ISRO provides satellite data for various environmental and land-use applications.
- Satellites like the Oceansat series provide data on sea surface temperatures, sea level rise, and coastal erosion.
- Security and Defense: Satellites help in remote sensing for border surveillance.
- Administrative Efficiency: Satellite data helps in the implementation of the Digital India initiative by enabling access to e-governance services.
Challenges
- High Costs: The development, maintenance, and launch of satellites are expensive.
- Technical and Infrastructure Gaps: Lack of adequate ground infrastructure, technical expertise, and trained personnel in remote areas.
- Data Interpretation and Accuracy: Space-based data requires accurate interpretation and analysis, and errors in data processing can lead to wrong decisions in governance.
- Privacy Concerns: Increased surveillance and monitoring through space technology raise privacy and security concerns among citizens.
- Environmental Impact: Increased space missions and satellite launches can contribute to space debris and environmental pollution.
Way Ahead
- Develop and upgrade ground infrastructure, data centers, and communication systems to support space-based services effectively.
- Encourage collaboration between the government and private sector to reduce costs, foster innovation, and improve the application of space technology.
- Increase the number and diversity of satellites for better coverage, particularly in remote and underserved regions of the country.
- Encourage research in space technology and its applications to address emerging governance challenges, including climate change and urban planning.
- Adopt sustainable practices for satellite launches and space missions to minimize environmental impacts and manage space debris effectively.
Source: PIB
Previous article
Gene-Edited Bananas
Next article
news-in-short-11-march-2025