Syllabus :GS3/Science and Technology
In News
- Recently, a UK-based biotech company developed genetically-engineered bananas that have a longer shelf-life and do not brown as much.
Ripening of Bananas
- Bananas undergo a ripening process triggered by ethylene, a hormone they produce in large quantities.
- Ethylene activates genes that produce polyphenol oxidase (PPO), an enzyme that causes browning by breaking down the yellow pigment in bananas.
- Bruising increases ethylene production, speeding up ripening and browning.
Latest Developments
- Scientists genetically modified bananas by silencing the gene that produces PPO, preventing browning.
- This genetic modification does not stop ripening but keeps the fruit looking fresh longer.
- A similar technique was used in Arctic apples, which have been commercially sold since 2017.
What is Gene Editing?
- It is a method that allows scientists to modify the DNA of various organisms (plants, bacteria, animals).
- It leads to changes in physical traits (e.g., eye color) and disease risk.
- Early genome editing technologies were developed in the late 1900s.
- The CRISPR tool, invented in 2009, revolutionized genome editing by making it simpler, faster, cheaper, and more accurate.
- CRISPR is now widely used by scientists for genome editing due to its efficiency and precision.
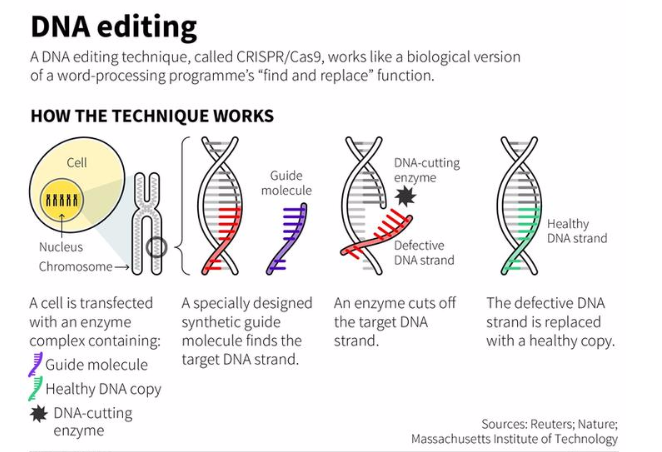
Recent Trends in Gene Editing
- CRISPR Technology Advancements: While CRISPR-Cas9 remains a cornerstone, research is expanding to explore other Cas enzymes (like Cas12 and Cas13) and alternative CRISPR systems.
- Improved Delivery Methods: Researchers are developing more efficient and targeted delivery systems, including viral vectors, lipid nanoparticles, and other innovative approaches.
- Gene Therapy for Genetic Diseases: Gene editing is showing promise for treating inherited disorders like sickle cell disease, cystic fibrosis, and Huntington’s disease.
- Crop Improvement: Gene editing is being used to develop crops with enhanced traits, such as increased yield, improved nutritional value, and resistance to pests and diseases.
Regulations in India
- Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) under MoEFCC oversees gene-editing approvals.
- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) regulates genetically modified (GM) food products.
Current Status In India
- India has approved GM Mustard hybrid DMH-11 for its seed production and testing but has not yet approved CRISPR-based crops.
- The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) is exploring gene-editing research aimed at enhancing climate resilience and pest resistance in crops.
Source :IE
Previous article
Farm Lending: Rise of Kisan Credit Card Bad Loans
Next article
Space-Tech for Good Governance