Syllabus: GS3/Space
Context
- India’s space sector is projected to surge from USD 8.4 billion in 2022 to USD 44 billion by 2033, aiming to capture 8% of the global market.
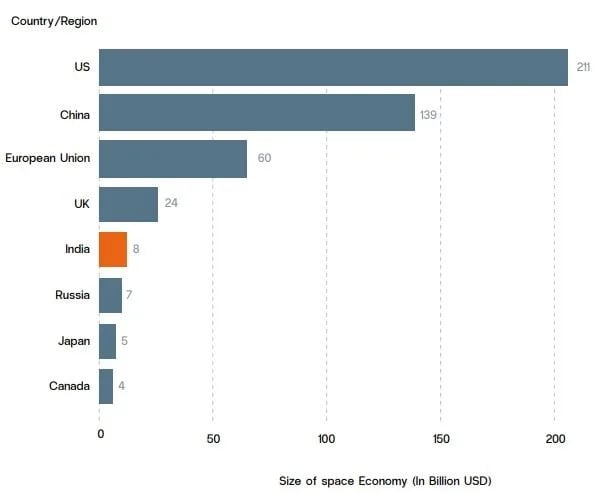
India’s share in the Space Industry
- India’s space economy contributes 2-3% of the global space economy, and this is expected to rise to 8% by 2030 and further to 15% by the year 2047.
- With over 400 private space companies, India ranks fifth globally in the number of space companies.
- Private players in the Space Industry: The number of space startups in India increased to nearly 200 in 2024 from just one in 2022.
- The funding received by these start-ups reached a total of $124.7 Mn in 2023 from $67.2 Mn in 2021.
- Skyroot have launched India’s first privately built rocket, Vikram-S, into space, with plans to revolutionise satellite launches.
| Roles and responsibilities of Various Organizations Under the Indian Space Policy 2023: – IN-SPACe (Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Center): It is an autonomous single-window agency responsible for: 1. Authorizing all government and private space activities. 2. Promoting industry clusters, incubation centers, and accelerators. 3. Facilitating technology transfer from ISRO to private players. 4. Approving remote sensing data dissemination and launch manifests. – Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) refocused on: 1. R&D in new space technologies, human spaceflight, and scientific exploration. 2. Transitioning operational space systems to industry. 3. Providing open access to remote sensing data. 4. Supporting academia and industry collaboration. 5. Enabling long-term human presence in space. – NewSpace India Limited (NSIL): Acts as the commercial arm of the Department of Space: 1. Commercializes space technologies developed by ISRO. 2. Manufactures and procures space assets. 3. Serves both government and private sector clients on commercial terms. – Department of Space (DoS): Acts as the policy coordinator: 1. Ensures smooth role distribution among stakeholders. 2. Oversees implementation of the policy. 3. Coordinates international cooperation and compliance. 4. Ensures safe operations and resolves disputes. 5. Maintains global standards and interoperability in navigation systems. |
Steps Taken by the Government
- Space Sector Reforms (2020): The Government allowed private sector participation, defining the roles of IN-SPACe, ISRO, and NSIL.
- Venture Capital (VC) Fund: The Union Cabinet has approved the establishment of a Rs.1,000 crore Venture Capital (VC) Fund dedicated to supporting India’s space sector.
- ISRO’s Structural Strength & Cost-Effectiveness: ISRO’s track record of high-impact, cost-efficient missions—such as Chandrayaan-3 and the Mars Orbiter Mission—has positioned India favorably on the global stage.
- Space Vision 2047: Aims for Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) by 2035 and an Indian Moon landing by 2040.
- Gaganyaan programme has entered its final phase, with the first human spaceflight now scheduled for the first quarter of 2027.
- Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS) first module by 2028.
- Next Generation Satellite Launch Vehicle (NGLV) by 2032.
- Chandrayaan-4 by 2027, to collect moon samples and demonstrate return technology.
- Venus Orbiter Mission (VOM) by 2028, to study Venus.
- Indian Space Policy, 2023: Ensures a level playing field for Non-Government Entities (NGEs) in space activities.
- SpaceTech Innovation Network (SpIN): SpIN is a one-of-its-kind public-private collaboration for start-ups and SMEs in the space industry.
- Under the amended FDI policy,100% FDI is allowed in the space sector.
- Up to 74% (Automatic route) for satellite-related activities; beyond that, government route.
- Up to 49% (Automatic route) for launch vehicles and spaceports; beyond that, government route.
- 100% (Automatic route) for manufacturing components and sub-systems for satellites and ground/user segments.
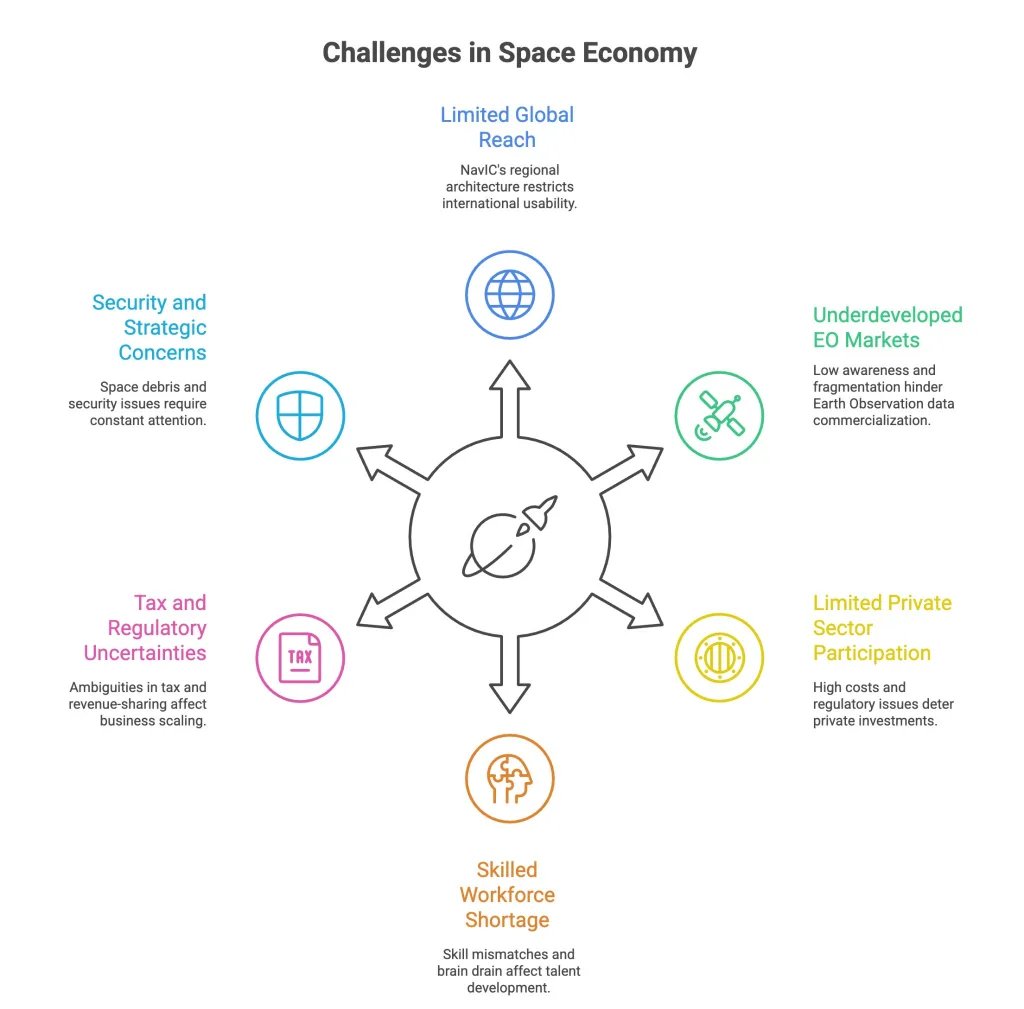
Way Ahead
- Private entities are now actively involved in crucial aspects of research, manufacturing, and fabrication of rockets and satellites, fostering a vibrant ecosystem of innovation. It is expected to integrate Indian companies into global value chains.
- With this, companies will be able to set up their manufacturing facilities within the country, duly encouraging ‘Make In India (MII)‘ and ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat‘ initiatives of the Government.
Source: ET
Previous article
Political Crisis in Nepal and Its Implications for India
Next article
EnteroMix – mRNA Cancer Vaccine