Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- The Supreme Court expressed concern over the unregulated nature of Bitcoin trading in India, likening it to a “refined way of Hawala business.”
What is Bitcoin?
- Bitcoin is a type of digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography for security, making it difficult to counterfeit or double-spend.
- It operates on decentralized networks based on blockchain technology—a distributed ledger enforced by a network of computers.
- Cryptocurrencies are typically not controlled by any central authority, which makes them theoretically immune to government interference or manipulation.
| Blockchain technology – Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger system that records transactions across many computers in a way that ensures security and transparency. – Blockchain networks rely on consensus algorithms to validate transactions and maintain network integrity. 1. These mechanisms ensure that only legitimate transactions are added to the chain. |
Concerns of Bitcoin
- Lack of Regulation: Despite repeated judicial nudges, the government has not issued a clear legal framework for virtual currency.
- Potential for Misuse: Due to the absence of KYC/AML enforcement and its cross-border nature, cryptocurrency can be misused for illicit activities, including a digital form of Hawala.
- Threat to Financial Integrity: The unregulated market could jeopardize India’s efforts to curb black money and maintain capital controls.
India’s Cryptocurrency Landscape
- At present, India does not have any Law or provision which specifically deals with Cryptocurrency. India has not officially banned or allowed cryptocurrency trading.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: In 2018, the Central Board of Direct Taxes proposed a ban on cryptocurrencies, and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) restricted banks from facilitating cryptocurrency transactions labeling it as a “macro-economic risk.”
- This decision was overturned by the Supreme Court in 2020.
- Taxation Policies: The Indian government imposed a 30% tax on income from transfers of virtual digital assets in 2022, along with a 1% tax deducted at source (TDS) on each transaction.
- These stringent measures have dampened domestic enthusiasm for cryptocurrency trading.
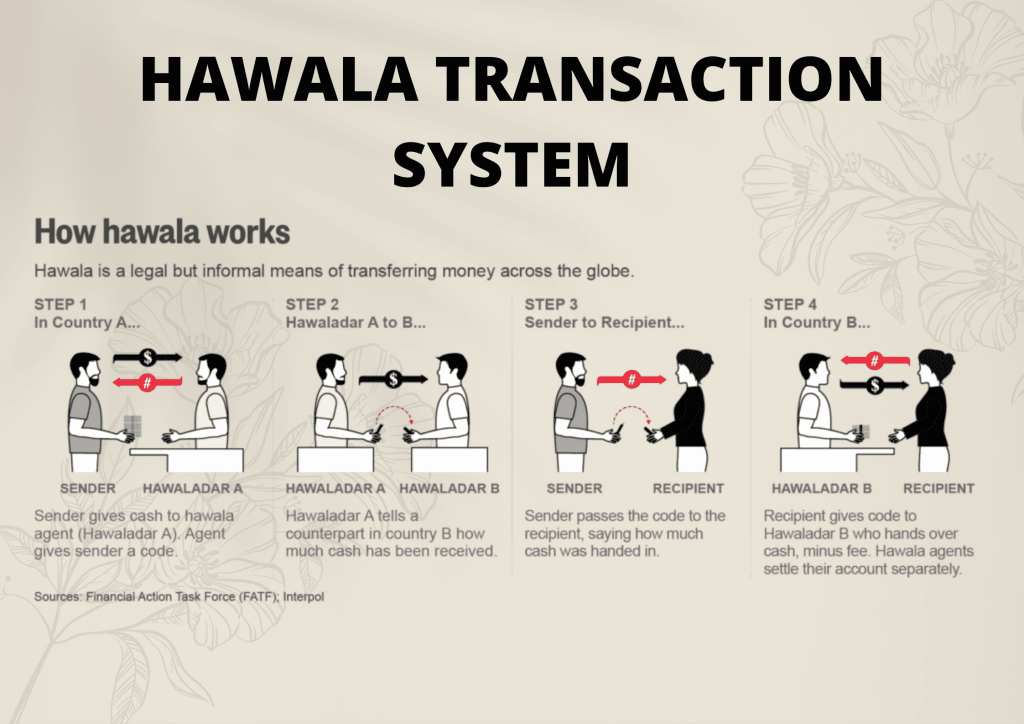
What is Hawala?
- Hawala is an informal method of transferring money without any physical movement of cash.
- It works outside traditional banking channels and is often used for money laundering, terror financing, and tax evasion.
How Bitcoin can be in Hawala?
- Anonymity: Traditional Hawala relies on trust and secrecy.
- Bitcoin allows pseudonymous transactions that are hard to trace, mimicking Hawala’s secrecy.
- Cross-Border Transfers: In traditional Hawala, money doesn’t physically cross borders; balances are settled informally.
- With Bitcoin, a person in one country can send Bitcoin to a counterpart in another country, who can convert it into local currency and deliver it to the intended recipient—mirroring the Hawala model.
- Quick Transfers: Unlike traditional remittances that take days and charge fees, Bitcoin transactions can be near-instantaneous and low-cost, making it attractive for illicit transfers.
Way Ahead
- Comprehensive Legislation: India must enact a clear legal framework defining and regulating cryptocurrencies, exchanges, and wallets.
- Strengthen Enforcement: Enhance capabilities of financial intelligence units to monitor crypto transactions.
- International Cooperation: Work with FATF and G20 to establish global norms on crypto governance.
Source: TH
Previous article
CCI Notifies New Definitions to Curb Predatory Pricing
Next article
News In Short-9-05-2025