Syllabus: GS3/Security; Science & Technology
Context
- Recently, India thwarted Pakistani aerial attacks along the western border through its air defence systems, and successfully neutralized an air defence system in Lahore, Pakistan.
About the Air Defence Systems
- These are critical components of a nation’s security infrastructure, designed to detect, track, and neutralize aerial threats such as enemy aircraft, missiles, and drones.
- These systems operate through layered defense mechanisms, combining radars, missile interceptors, electronic warfare tools, and command centers to safeguard airspace.
Key Components of Air Defence Systems
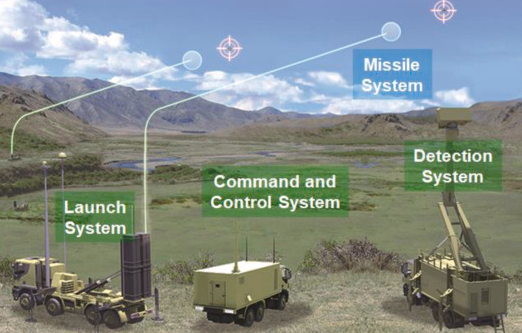
- Detection and Surveillance:
- Radar Systems: Air defence begins with high-frequency radar waves that detect incoming threats by bouncing signals off objects in the sky.
- Satellite and Infrared Sensors: Advanced systems use satellite imaging and infrared tracking to identify stealth aircraft and hypersonic missiles.
- Tracking and Target Identification: Once a threat is detected, tracking systems analyze its speed, altitude, and trajectory to determine its nature—whether it’s a fighter jet, ballistic missile, or drone.
- Command centers assess the threat level and decide on the appropriate response.
- Engagement and Neutralization:
- Surface-to-Air Missiles (SAMs): These missiles intercept enemy aircraft or incoming projectiles before they reach their target.
- Electronic Warfare (EW) Systems: Jammers disrupt enemy communications and radar signals, reducing their ability to coordinate attacks.
- Anti-Aircraft Artillery: In close-range combat, high-caliber guns provide an additional layer of defense.
Types of Air Defence Systems
- Short-Range Air Defence (SHORAD): Designed to counter low-altitude threats, including drones and cruise missiles.
- Example: Barak-8 Missile System.
- Medium-Range Air Defence (MRAD): Covers larger areas, intercepting fighter jets and long-range missiles.
- Examples: Patriot Missile System, S-400 Triumf.
- Long-Range Air Defence (LRAD): Protects entire regions, capable of neutralizing intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs).
- Examples: THAAD, Aegis Ballistic Missile Defense.
| Key Air Defence Systems in India – Akash Missile System: It is a Surface-to-Air Missile (SAM) system designed to neutralize multiple airborne threats simultaneously, using command guidance and phased array radar. – S-400 Triumf Missile System: It is procured from Russia, which enhances India’s air defence capabilities. 1. It can detect and intercept ballistic missiles, fighter jets, and drones at distances up to 400 km. 2. It is also used by China, and Turkey for ballistic missile and aircraft defense. – Integrated Counter-UAS Grid: India has deployed counter-drone technology to neutralize hostile UAVs along sensitive borders. 1. It integrates radar detection, electronic jamming, and kinetic interception to prevent aerial intrusions. – Barak-8 Missile System: It is jointly developed by India and Israel, and provides high-speed interception against airborne threats. 1. It enhances naval and land-based air defence capabilities. Other Air Defence Systems in the World – Patriot Missile System (United States): It is widely deployed for missile interception and aerial threat neutralization. 1. It is used by the U.S., Germany, Japan, and Saudi Arabia for high-altitude defense. – Iron Dome (Israel): It is designed for short-range missile interception, particularly effective against rocket attacks. 1. It is used extensively by Israel to protect urban areas and military installations. – Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) – United States: It is a high-altitude missile defense system capable of intercepting ballistic missiles in their terminal phase. 1. It is deployed by the U.S., South Korea, and Japan for regional security. |
Previous article
India’s latest MMR Shows a Declining Trend