Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context
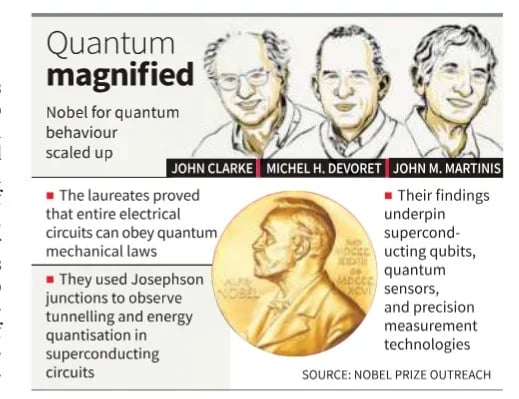
- John Clarke, Michel Devoret and John Martinis will share the 2025 Nobel Prize in physics for their discovery of a phenomenon called quantum mechanical tunneling in an electrical circuit.
About
- They showed that the process of tunneling can occur not only in subatomic particles but also in an electrical circuit made of superconductors.
- Tunneling literally is the ability of particles to pass through physical walls.
- Such strange behaviour cannot be observed at the macroscopic level but these scientists showed that it was possible to organise a multitude of single particles and coerce them to exhibit “tunnelling” properties.
| Do you Know? – Quantum mechanics was first formally described by German physicist Werner Heisenberg in 1925. – One-hundred years later the United Nations declared 2025 the international year of quantum science and technology to celebrate the centenary of the breakthrough. – Quantum technology is a rapidly advancing field that leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to develop new technologies with unprecedented capabilities. 1. Quantum mechanics is the branch of physics that studies the behavior of particles at the quantum level, where classical physics no longer applies. |
How was it done?
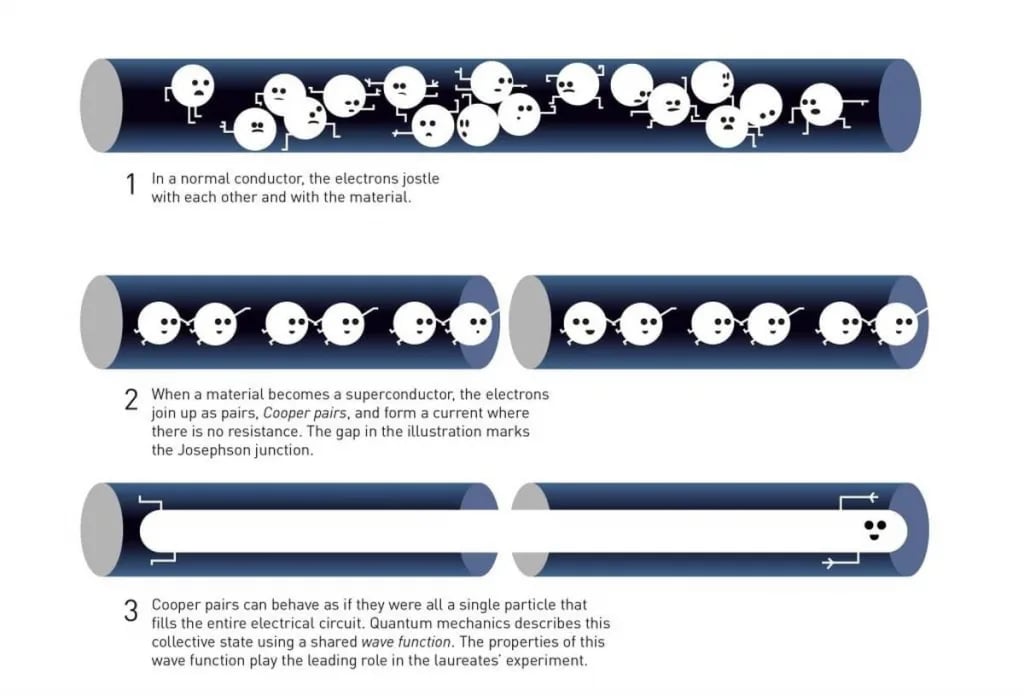
- A Josephson junction is a device made of two superconductors separated by a very thin insulating barrier.
- It allows Cooper pairs (pairs of electrons in a superconductor) to tunnel through the insulator without resistance, even though it is classically forbidden — this is known as the Josephson effect.
- Quantum Tunnelling: When the current was below a critical value, electrons were trapped (no voltage).
- Classically, this state should persist indefinitely, but quantum mechanics allows tunnelling — electron pairs “escape” through the barrier, producing a small voltage.
Applications of Josephson Junctions and Related Work
- Quantum Computing: Josephson junctions form the basis of superconducting qubits, which use quantised energy levels for computation.
- The field of circuit quantum electrodynamics (cQED) — coupling superconducting circuits with microwave resonators arises from this work.
- Precision Measurements: Used in Josephson voltage standards for precise definition of the volt.
- SQUIDs (Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices) use Josephson junctions to detect extremely weak magnetic fields.
- Quantum Technologies:
- Quantum amplifiers: Boost weak signals with minimal noise.
- Microwave-to-optical converters: Interface between quantum processors and optical networks.
- Quantum simulators: Model complex materials and reactions.
Source: TH
Previous article
News in Short – 7 October, 2025
Next article
Abhidhamma Divas