Syllabus: GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
- The Maharashtra government has introduced Facial Recognition System technology for entry into Mantralaya, to improve security and efficiency in government operations.
What is Facial Recognition System?
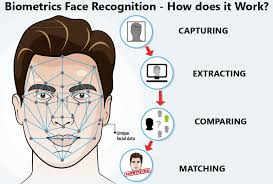
- A facial recognition system is a technology potentially capable of matching a human face from a digital image or a video frame against a database of faces.
- Core Technologies of FRS are as;
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Machine learning and deep learning enable systems to improve accuracy over time.
- Computer Vision: It extracts, analyzes, and interprets visual data from images and videos.
- Biometric Analysis: It identifies unique facial features for authentication.
- Neural Networks (CNNs): It is essential for image recognition and feature extraction.
Examples of facial recognition systems
- Amazon Rekognition: A cloud-based service that uses facial recognition to analyze images and videos.
- Microsoft Azure Face API: A facial recognition API that’s part of Microsoft’s cloud computing services.
- DeepFace: A facial recognition program developed by Facebook.
Applications of Facial Recognition System
- Security & Surveillance: It is used in law enforcement, border control, and public space monitoring to enhance security.
- Access Control & Authentication: It unlocks devices, secures workplaces, and replaces passwords for digital logins.
- Financial Services: It enables secure banking, fraud detection, and contactless payments.
- Healthcare: It is used to identify patients, assist in diagnosis, and monitor mental health.
- Retail & Marketing: It enhances customer experience, enables targeted ads, and prevents shoplifting.
Concerns of FRS
- Privacy Violations: Unauthorized surveillance and data collection infringe on individuals’ privacy without consent.
- Data Security Risks: Facial recognition databases are vulnerable to hacking, leading to identity theft and data misuse.
- Bias and Inaccuracy: Studies have shown that facial recognition systems have higher error rates for people of color, women, and non-binary individuals, leading to wrongful arrests and misidentifications.
- Misuse for Profiling: Governments and corporations exploit the technology for racial profiling and intrusive advertising.
- Deepfake: AI-generated deepfakes can manipulate identities, undermining biometric security.
Way Ahead
- Governments should establish clear laws to prevent mass surveillance and misuse of facial recognition technology.
- Strict cybersecurity measures must be enforced to protect facial recognition databases from breaches and identity theft.
Source: IE