
Syllabus :GS3/Environment
In News
- The Solar Energy Corporation of India Limited (SECI) has conducted its first-ever auction for Green Ammonia procurement via SIGHT Scheme (Mode-2A) under National Green Hydrogen Mission.
Hydrogen
- It is the lightest and most abundant element in the universe and rarely found in nature in its elemental form and must always be extracted from other hydrogen-containing compounds.
- It is categorised into three categories, namely, Grey, Blue and Green.
- Grey Hydrogen: It is produced via coal or lignite gasification (black or brown), or via a process called steam methane reformation (SMR) of natural gas or methane (grey). These tend to be mostly carbon-intensive processes.
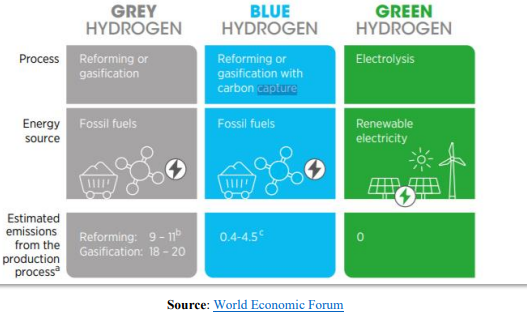
- Blue Hydrogen: It is produced via natural gas or coal gasification combined with carbon capture storage (CCS) or carbon capture use (CCU) technologies to reduce carbon emissions.
- Green Hydrogen: It is produced using electrolysis of water with electricity generated by renewable energy. The carbon intensity ultimately depends on the carbon neutrality of the source of electricity (i.e., the more renewable energy there is in the electricity fuel mix, the “greener” the hydrogen produced)
National Green Hydrogen Mission

- It was launched on 4th January 2023, with an outlay of Rs. 19,744 crores up to FY 2029-30.
- It will contribute to India’s goal to become Aatma Nirbhar (self-reliant) through clean energy and serve as an inspiration for the global Clean Energy Transition.
- It will lead to significant decarbonisation of the economy, reduced dependence on fossil fuel imports, and enable India to assume technology and market leadership in Green Hydrogen.
Mission Subcomponents
- SIGHT Programme: Under the Strategic Interventions for Green Hydrogen Transition Programme (SIGHT), two distinct financial incentive mechanisms – targeting domestic manufacturing of electrolysers and production of Green Hydrogen – will be provided under the Mission.
- Pilot projects: The Mission will also support pilot projects in emerging end-use sectors and production pathways. Regions capable of supporting large scale production and/or utilization of Hydrogen will be identified and developed as Green Hydrogen Hubs.
- R&D Projects: Public-Private Partnership framework for R&D (Strategic Hydrogen Innovation Partnership – SHIP) will be facilitated under the Mission. R&D projects will be goal-oriented, time bound, and suitably scaled up to develop globally competitive technologies.
- Skill Development: A coordinated skill development programme will also be undertaken under the Mission.
Benefits
- Decarbonization: Significant reductions in CO2 emissions from industrial, mobility, and energy sectors.
- Making India a leading producer and supplier of Green Hydrogen in the world.
- Reduced Dependence on Imports: Diminished reliance on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy security.
- Creation of export opportunities for Green Hydrogen and its derivatives.
- Indigenous Manufacturing: Development of domestic capabilities in green hydrogen technology and infrastructure.
- Employment Opportunities: Creation of over 6 lakh jobs throughout the value chain, from production to utilization.
- Technological Innovation: Advancement of cutting-edge technologies and innovation ecosystems within the country.
Source:PIB
Previous article
Biochar
Next article
News In Short 07-08-2025