Helgoland
Syllabus :GS1/Places
In News
- Helgoland is remembered as the birthplace of quantum mechanics.
Helgoland
- It is a tiny red-sandstone island in the North Sea, about 50 km off Germany’s coast.
- It is Less than a square kilometre in size and it was once a naval fortress and later became a holiday destination for those seeking fresh air.
Relevance
- It became a pivotal site in the history of physics in June 1925 when 23-year-old Werner Heisenberg developed the foundation of quantum mechanics.
- Abandoning classical ideas of electrons orbiting nuclei, he focused solely on measurable data — the frequencies and intensities of light absorbed or emitted by atoms — and organized these into matrices.
- Noticing that the order of multiplication mattered, he derived equations that accurately described hydrogen’s spectrum, marking the birth of matrix mechanics.
- This breakthrough, followed by contributions from Max Born, Pascual Jordan, and Erwin Schrödinger, led to the uncertainty principle and key developments in quantum theory, which underpin modern technologies like lasers and semiconductors.
Source :TH
Taiwan Strait
Syllabus: GS1/ Geography, GS2/ IR
Context
- Taiwan condemned China’s move to open a sensitive aviation route that runs through the Taiwan Strait, warning the change could increase tensions between the two sides and “regional unease”.
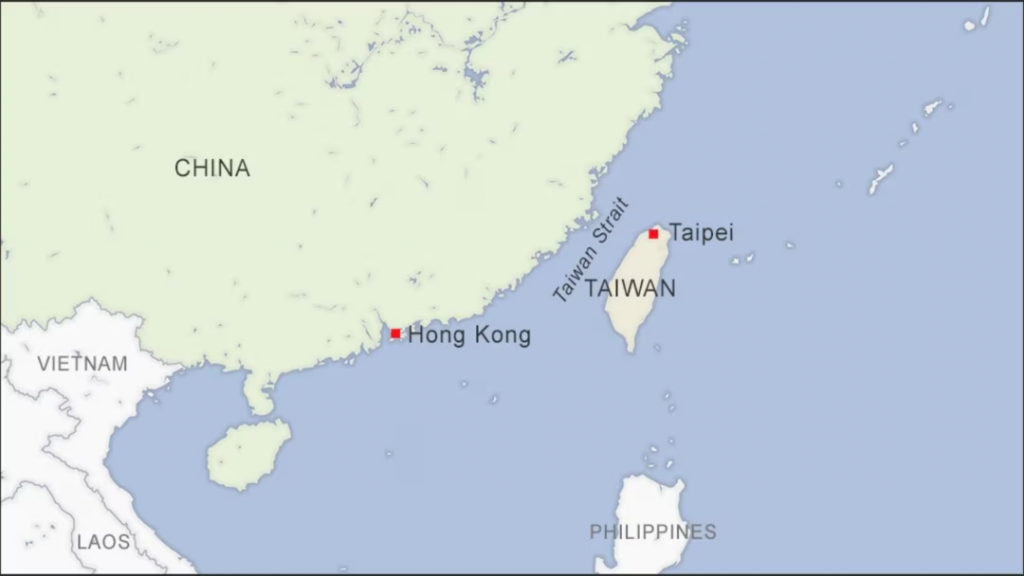
About Taiwan Strait
- Location: The Taiwan Strait also known as the Formosa Strait or the Tai-hai (the Tai Sea) separates mainland China (Fujian Province) from the island of Taiwan.
- It connects the South China Sea to the East China Sea and is a vital shipping lane.
- It is approximately 180 kilometers wide at its narrowest point.
- Geopolitical Tensions: China views Taiwan as a renegade province and asserts its claim over the island and the strait.
Source: TH
Blue Nile
Syllabus: GS1/Geography
Context
- Ethiopia has announced the completion of a Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam (GERD), Africa’s largest hydro-electric power plant on the Blue Nile, a project that has long been a source of tension with Egypt and Sudan.
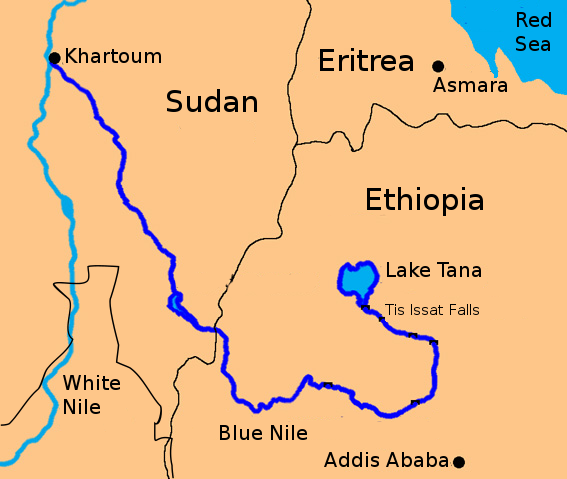
About the Blue Nile
- The Blue Nile originates in Lake Tana, located in the Ethiopian Highlands of eastern Africa.
- It joins the White Nile at Al-Muqrin in Khartoum (the capital of Sudan). From this confluence, the river flows north through Sudan and Egypt, eventually emptying into the Mediterranean Sea as the Nile.
- The Nile River is the longest river in the world, flowing through 11 countries: Democratic Republic of the Congo, Burundi, Uganda, Kenya, South Sudan, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Rwanda, Tanzania, Sudan and Egypt.
Source: BBC
National Commission for Minorities (NCM)
Syllabus :GS2/Governance
In News
- The National Commission for Minorities (NCM) has been non-functional since April 2025 due to the retirement of its Chairperson.
National Commission for Minorities (NCM)
- It is a statutory body established by the Government of India under the National Commission for Minorities Act, 1992.
- Its primary mandate is to safeguard and protect the interests of India’s notified religious minority communities, which currently include Muslims, Christians, Sikhs, Buddhists, Parsis (Zoroastrians), and Jains.
- The Commission consists of a Chairperson, Vice-Chairperson, and five Members, all nominated by the Central Government. At least five, including the Chairperson, must be from minority communities.
- Each member, including the Chairperson, holds office for three years and is eligible for reappointment.
- While investigating, the NCM has powers equivalent to a civil court, such as:
- Summoning and enforcing the attendance of individuals.
- Requiring the production of documents.
- Receiving evidence on affidavits.
- Requisitioning public records from courts or offices.
| Constitutional Safeguards – Article 29: It protects both religious and linguistic minorities and ensures their right to preserve their culture, language, and script. It also prohibits discrimination in admission to educational institutions on specific grounds. – Article 30: It gives minorities the right to establish and manage educational institutions and protects them from discrimination in receiving government aid. It applies to both religious and linguistic minorities. |
Source: TH
NMC Relaxes Regulations on Medical Education Infrastructure
Syllabus :GS 2/Governance
In News
- The National Medical Commission (NMC) has introduced the Medical Institutions (Qualifications of Faculty) Regulations, 2025.
The National Medical Commission (NMC)
- It was established under the National Medical Commission Act, 2019, which came into effect on September 25, 2020, replacing the Medical Council of India.
- Its mission is to improve access to quality and affordable medical education, ensure the availability of skilled medical professionals across the country
- It aims to promote equitable and community-focused healthcare, encourage adoption and contribution to medical research, and conduct transparent assessments of medical institutions.
- It also maintains a national medical register, upholds high ethical standards in medical services, and provides an effective grievance redressal mechanism.
Medical Institutions (Qualifications of Faculty) Regulations, 2025.
- It aims to support the Union Government’s plan to add 75,000 new medical seats over five years by broadening faculty eligibility and enabling the expansion of MBBS and MD/MS seats.
- Key provisions include designating non-teaching government hospitals with over 220 beds as teaching institutions, appointing experienced specialists as faculty without mandatory senior residency, and expanding the use of M.Sc. and Ph.D. holders in additional departments.
- The regulations also raise the senior resident age limit to 50 for preclinical and paraclinical subjects and allow more flexible criteria for professor and assistant professor posts based on experience in NBEMS-recognised institutions.
Impacts
- The NMC says the regulations shift the focus from rigid norms to competency, experience, and academic merit.
- While the National M.Sc. Medical Teachers’ Association welcomed the move, some doctors criticized it as a dilution of teaching standards, warning it may impact quality of medical education and patient care.
Source: TH
Previous article
‘Invisible Hand’ in India’s Foreign Trade
Next article
Practice of Witchcraft in India