Syllabus :GS3/Economy
In News
- India’s foreign trade dynamics have shifted significantly over the past two decades, with “invisibles”—exports of services and remittances from Indians abroad—now playing a more crucial role than physical goods.
India’s Service Sector
- India’s services sector covers a wide variety of activities such as trade, hotel and restaurants, transport, storage and communication, financing, insurance, real estate, business services, community, social and personal services, and services associated with construction.
- The Economic Survey 2024-25, presented by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, highlights the service sector as the ‘Old War Horse’ of India’s economy, driving growth both domestically and globally.
Present Status
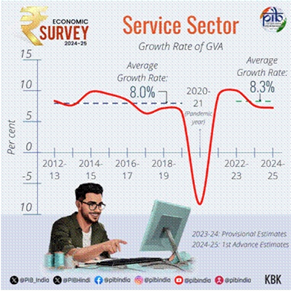
- Services have consistently supported GDP growth, contributing around 55% to India’s Gross Value Added (GVA) in FY25, up from 50.6% in FY14.
- The sector has maintained an average growth rate above 6% annually over the past decade, except during the pandemic, with post-pandemic growth accelerating to 8.3%.
- It employs about 30% of the workforce and it also boosts manufacturing through ‘servicification’—the increasing integration of services in industrial processes.
- India’s global share in services exports has risen steadily, now ranking seventh worldwide with 4.3% of the market.
- India remained amongst the top five major countries in terms of growth in services exports in FY25 (April-September).
- India’s services export growth accelerated to 12.8% in April-November FY25 from 5.7% in FY24. Computer services and business services exports account for around 70% of India’s total services exports.
Potential
- India is a unique emerging market in the globe due to its unique skills and competitive advantage created by knowledge-based services.
- The Indian services industry, which is supported by numerous government initiatives like smart Cities, clean India, and digital India is fostering an environment that is strengthening the services sector.
- The sector has the potential to open up a multi-trillion-dollar opportunity that might stimulate symbiotic growth for all nations.
Challenges and Issues
- India’s service sector faces key challenges including infrastructure gaps—especially in digital connectivity and logistics—that limit growth outside urban areas.
- There is also a significant skill shortage, with many workers lacking specialized training for high-value services, impacting productivity and innovation.
- Regulatory complexities and limited access to global markets further restrict export growth.
- It also remains vulnerable to global economic fluctuations.
| Governments efforts – The Government of India actively promotes growth in the services sector through various incentives and focused initiatives across key areas like healthcare, tourism, education, IT, banking, and finance. – It has launched an ‘Action Plan for Champion Sectors in Services’ targeting 12 priority sectors, with tourism expected to generate $50.9 billion by 2028. – The country hosts over 1,000 universities, supporting education and skill development through programs like the Mahatma Gandhi National Fellowship. – Financial inclusion is strengthened by schemes such as Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana, which has opened over 47 crore bank accounts. – The government also supports manufacturing with production-linked incentives and healthcare infrastructure through missions like Ayushman Bharat and a planned credit incentive program. – Foreign direct investment limits in insurance have been raised to encourage investment. |
Conclusion and Way Forward
- India’s service sector remains strong and vital for growth and jobs.
- India’s services-led surplus and remittances have kept its overall current account deficit manageable.
- This shift underscores India’s emergence as the “office of the world,” driven less by trade in tangible products and more by global flows of intangibles.
- Improving infrastructure, enhancing skills, easing regulations, and boosting global market access can help India realize its full potential and reinforce its role as a global services leader.
Source :IE
Previous article
Concern over Falling Household Savings in India
Next article
News In Short-07-07-2025