Syllabus: GS3/ Agriculture
In Context
- The Union Cabinet approved the Revision of Livestock Health and Disease Control Programme (LHDCP).
- The Pashu Aushadhi is a new component added to the LHDCP scheme.
Overview of LHDCP
- Total Outlay: ₹3,880 crore for the years 2024-25 and 2025-26
- Objective:
- To improve livestock health through prophylactic vaccination programs.
- To enhance capacity building, disease surveillance, and veterinary infrastructure.
- To prevent economic losses due to livestock diseases.
- Key Components of the Revised Scheme:
- The revised LHDCP consists of three major components:
- National Animal Disease Control Programme (NADCP)
- Livestock Health & Disease Control (LH&DC)
- Pashu Aushadhi (Newly Introduced Component)
- Sub-Components of LH&DC:
- Critical Animal Disease Control Programme (CADCP): Focuses on controlling Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR) and Classical Swine Fever (CSF).
- Establishment & Strengthening of Veterinary Hospitals & Dispensaries – Mobile Veterinary Units (ESVHD-MVU): Aims to provide doorstep veterinary healthcare to farmers.
- Assistance to States for Control of Animal Diseases (ASCAD): Covers state-prioritized exotic, emergent, and zoonotic animal diseases, including Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD).
- The revised LHDCP consists of three major components:
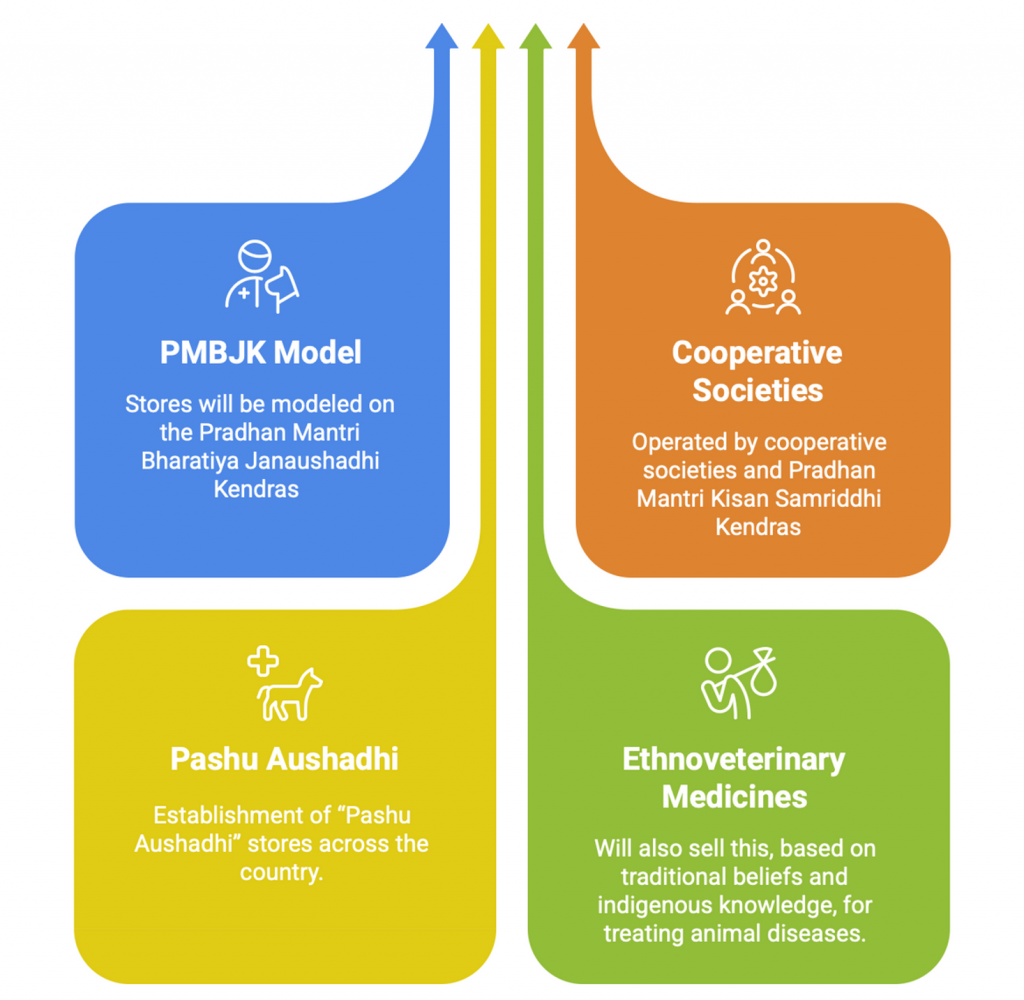
Pashu Aushadhi Initiative
- Objective: To ensure the availability of affordable generic veterinary medicines for livestock farmers.
- To reduce treatment costs for farmers by promoting non-branded, cost-effective veterinary drugs.
- Implementing Ministry: Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying.
- Key Features:
Major Livestock Diseases Targeted
- LHDCP focuses on controlling various critical livestock diseases that impact productivity and cause economic losses:
- Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD): Leads to reduced milk production and weight loss in cattle, buffaloes, and pigs.
- Brucellosis: Causes infertility, abortions, and low milk yield in cattle and buffaloes.
- Peste des Petits Ruminants (PPR): A highly fatal disease affecting sheep and goats.
- Classical Swine Fever (CSF): A viral disease in pigs, leading to high mortality rates.
- Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD): Affects cattle, causing skin lesions and severe economic losses.
Status of Livestock Sector in India
- About:
- India has the world’s largest population of livestock and plays a crucial role in the global meat and dairy industry.
- India is the largest producer of buffalo meat and the second-largest producer of goat meat.
- India ranks first in milk production, contributing 23% of global milk production.
- Significance of the Livestock Sector in India:
- Key Economic Contributions: In 2021-22, the total Livestock Gross Value Added (GVA) at constant prices was 30.19% of Agricultural and Allied Sector GVA and 5.73% of Total GVA.
- Employment Generation: Livestock rearing is a major source of livelihood for over 70% of rural households in India.
- Food and Nutritional Security: Livestock products such as milk, meat, and eggs are rich in essential nutrients, playing a crucial role in combating malnutrition.
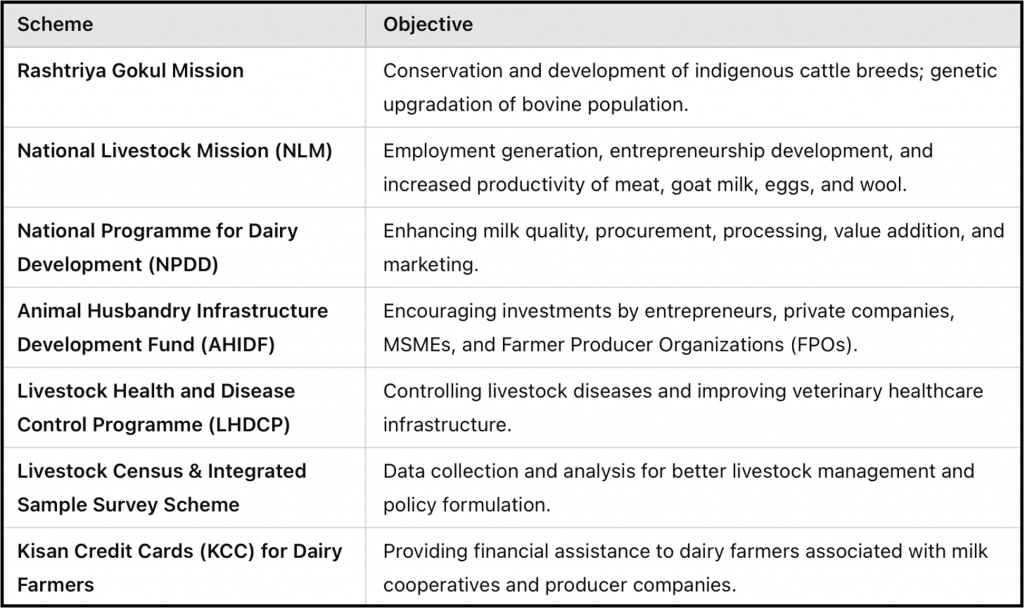
Other Government Initiatives Supporting Livestock Sector
Source: IE
Previous article
MeitY Launches AIKosha and Other Initiatives
Next article
India’s AI Revolution