Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- Union Minister Dr. Jitendra Singh said that India’s Bioeconomy grew more than 10 times in the last 10 years.
What is BioEconomy?
- The BioEconomy is the knowledge-based production and use of biological resources to provide products, processes and services in all economic sectors within the frame of a sustainable economic system.
- It encompasses sectors like agriculture, forestry, fisheries, food production, biotechnology, and bioenergy.
- Subsectors of the BioEconomy in India are;
- BioPharma or BioMedical: It includes the development and production of medical products and services, such as pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and lab-grown organoids.
- BioAgri: It includes the development and production of genetically modified crops and animals, precision agriculture technologies, and bio-based products. EX: Bt Cotton.
- BioIndustrial: It includes the development and production of biobased chemicals and products using enzymes, biosynthetic routes, and recombinant DNA technology.
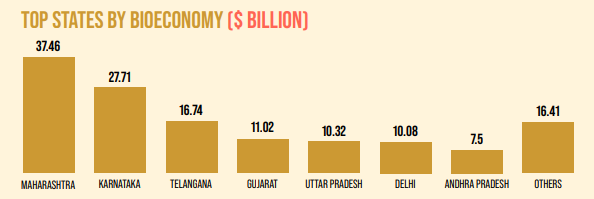
BioEconomy of India
- India’s BioEconomy has grown 13-fold over the last decade, from $10 billion in 2014 to over $130 billion in 2024, with a projection to reach $300 billion by 2030.
- In the Global Innovation Index, India has climbed from 81st place in 2015 to 40th out of 132 economies.
- India ranks 3rd in the Asia-Pacific region and 12th globally in terms of biomanufacturing.
- Biotechnology, a sunrise sector, has achieved a valuation of Rs 75,000 crore over the past 10 years.
- In 2022, BioEconomy accounted for 4% of India’s gross domestic product (GDP) of $3.47 trillion and employs over 2 million people.
Government Initiatives
- Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC) established by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) is aimed at strengthening and empowering emerging biotechnology enterprises to undertake strategic research and innovation.
- Policy initiatives of the Government of India (GoI) such as Startup India and Make in India programs are aimed to develop India as a world-class Biotechnology and Bio-manufacturing hub.
- Favorable Government Policies like Draft R&D Policy 2021, PLI Schemes and Clinical trial rules have propelled India to be the ‘pharmacy of the world’.
Challenges for BioEconomy of India
- Global Competition: India’s BioEconomy faces stiff competition from more established bio Economies in countries like the USA, EU, and China, which have more advanced infrastructure, funding, and R&D capabilities.
- Intellectual Property (IP) Protection: Protecting intellectual property in the biotech sector is challenging, leading to concerns over innovation theft and lack of incentives for research.
- Lack of Infrastructure: Insufficient infrastructure for research, development, and commercialization of biotechnology innovations.
- Brain Drain: Talented scientists and researchers leave India for better opportunities abroad, reducing the country’s capacity for innovation.
Way Ahead
- Encourage increased public and private investment in biotech R&D through grants, tax incentives, and venture capital support.
- Engage in global research collaborations to leverage expertise, share resources, and accelerate the development of new technologies.
- Develop innovation clusters/ecosystems where academia, industry, and government entities can collaborate closely on BioEconomy initiatives.
Source: PIB
Previous article
Paris Agreement Target is at Risk
Next article
News In Short-07-03-2025