Syllabus: GS2/Government Policy & Intervention; GS3/Urban Infrastructure
Context
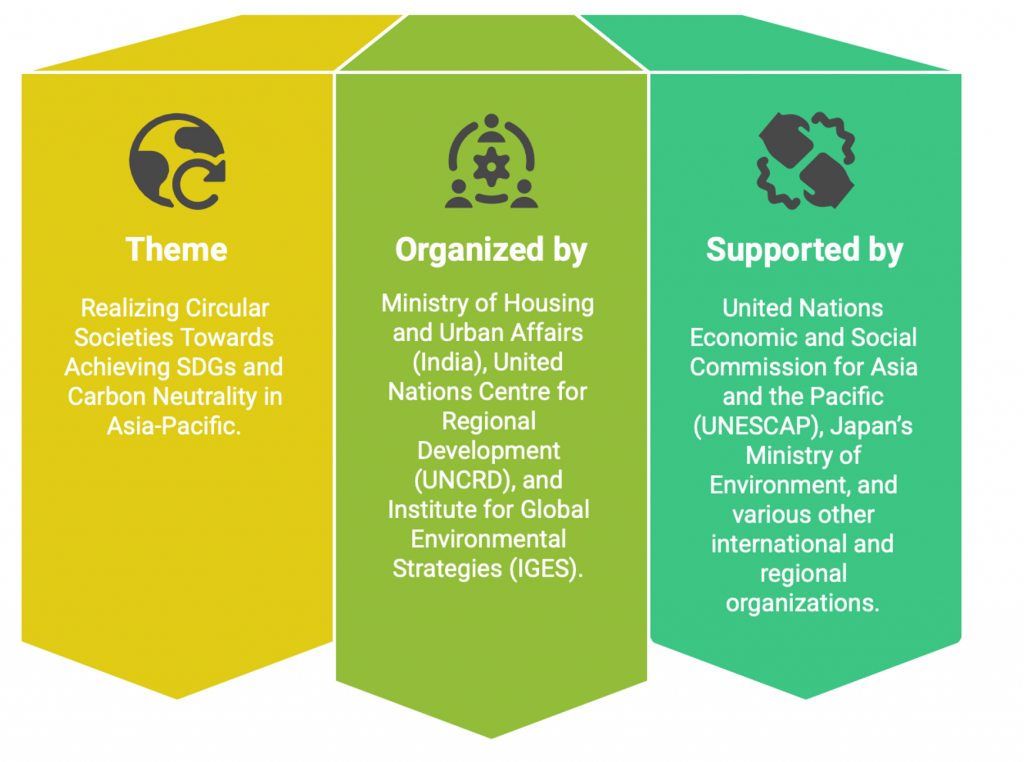
- Recently, India has launched the Cities Coalition for Circularity (C-3), a multi-nation alliance aimed at fostering city-to-city collaboration, knowledge-sharing, and private sector partnerships during the 12th Regional 3R and Circular Economy Forum in Asia and the Pacific, held in Jaipur.
| Key Highlights of the Event – The Prime Minister of India emphasized India’s commitment to the Pro-Planet People (P3) approach and the importance of the 3R (Reduce, Reuse, Recycle) for sustainable urban development. – A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for CITIIS 2.0 (City Investments to Innovate, Integrate, and Sustain) was signed. 1. It involves agreements worth ₹1,800 crore, benefiting 18 cities across 14 states and serving as lighthouse projects for other urban areas. |
Background
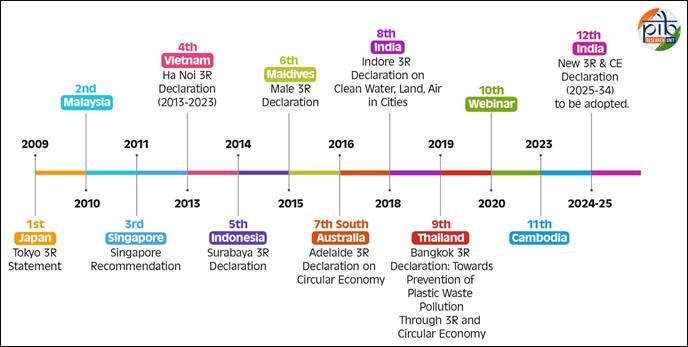
- The Regional 3R and Circular Economy Forum in Asia and the Pacific forum was launched in 2009 with the objective of regional cooperation for sustainable waste management and circular economy initiatives in the rapidly urbanizing and industrializing Asia-Pacific.
- Hanoi 3R Declaration (2013-2023) outlined 33 voluntary goals for shifting towards a more resource efficient and circular economy.
- It has been actively negotiating for a ‘Global Plastic Treaty’.

Cities Coalition for Circularity (C3)
- About: It is a multi-nation alliance designed to help urban centers adopt circular economy principles by integrating sustainable practices into urban planning, waste management, and resource utilization.
- Objectives: Focuses on reducing waste generation through segregation, composting, and upcycling, enhancing resource efficiency by promoting reuse and shared materials, and encouraging sustainable infrastructure.
Importance of C3 for Urban Sustainability
- Mitigating Climate Change: By reducing waste and optimizing resource use, C3 helps cut greenhouse gas emissions.
- Economic Benefits: Transitioning to a circular economy can create new business opportunities in recycling, remanufacturing, and waste management sectors.
- Resilient Cities: A circular economy model ensures that cities become less dependent on finite resources, making them more resilient to supply chain disruptions and economic downturns.
- Job Creation: It generates employment in sectors like renewable energy, sustainable construction, and eco-friendly product manufacturing.
- Improved Quality of Life: Cleaner environments, better waste management, and greener urban spaces lead to improved public health and enhanced overall well-being for citizens.
Global and Indian Context
- Several cities across the globe, such as Amsterdam, Copenhagen, and Tokyo, have already implemented circular economy policies under the C3 framework.
- In India, circularity is gaining traction through initiatives like:
- Swachh Bharat Mission: Encouraging waste segregation and recycling.
- Smart Cities Mission: Promoting sustainable urban development.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): Holding companies accountable for the lifecycle of their products.
- GOBAR-Dhan Scheme: Currently covers 67.8% of the total number of districts in India.
Challenges in Implementing Circularity in Cities
- Lack of Awareness and Technical Expertise.
- High Initial Investment Costs.
- Resistance to Change from Businesses and Consumers.
- Insufficient Policy Support and Enforcement Mechanisms.
Way Forward
- Develop and enforce policies that mandate circular economy practices.
- Invest in research and innovation for sustainable materials and processes.
- Promote awareness campaigns to educate communities on circular living.
- Strengthen public-private partnerships to scale up circular economy projects.
Previous article
News In Short-03-03-2025
Next article
Capital Account Convertibility