President Murmu visits Dholavira
Syllabus: GS1/Indian Ancient History; Art & Culture
In News
- The President of India visited the UNESCO World Heritage Site Dholavira in Gujarat.
About Dholavira
- Discovery: Discovered in 1968 by archaeologist Jagat Pati Joshi.
- Location: Dholavira, the southern centre of the Harappan Civilization, is sited on the arid island of Khadir in the Kachchh district, Gujarat.
- Lies on the Tropic of Cancer.
- Historical Significance: It is the 6th largest Harappan site and flourished between 3000-1500 BCE.
- UNESCO Recognition: It was inscribed in 2021 as India’s 40th World Heritage Site.

Dholavira’s Architectural Brilliance
- The walled city consists of a fortified Castle with attached fortified Bailey and Ceremonial Ground, and a fortified Middle Town and a Lower Town.
- A series of reservoirs are found to the east and south of the Citadel.
- Use of Stone: Unlike other IVC sites, Dholavira extensively used stone instead of bricks.
Economic Significance
- Trading Hub for copper, shells, semi-precious stones, timber.
- Trade Routes linked to Mesopotamia (Iraq), Magan (Oman), and other IVC cities.
- Exported finished products, especially beads, metals, and pottery.
Decline of Dholavira
- Climate Change & Aridity: Drying up of Saraswati River.
- Trade Disruptions: Collapse of Mesopotamian Civilization impacted commerce.
- Desertification: Rann of Kutch, once navigable, became a mudflat.
Source: PIB
Article 136 of the Constitution
Syllabus :GS 2/Governance
In News
- Vice President Jagdeep Dhankhar, speaking at a conference on arbitration, highlighted concerns regarding the misuse of Article 136 of the Constitution.
Article 136 of the Constitution
- Also called a special leave petition (SLP).
- Article 136 of the Constitution allows the Supreme Court to grant special leave to appeal from any judgment, decree, or order made by any court or tribunal in India.
- It allows the Supreme Court to entertain appeals even in cases where no other legal provision provides an automatic right of appeal.
- It can be filed in both civil and criminal cases.
- It is essentially a discretionary power of the Supreme Court, and the court is not bound to accept the appeal.
Source: TH
Sources and Health Effects of PM2.5
Syllabus: GS2/ Health
Context
- A study published in the journal Nature Communications has investigated the sources and health impacts of PM2.5 in Northern India, particularly in the Indo-Gangetic Plain.
What is PM2.5?
- PM2.5 refers to fine particulate matter with a diameter of less than 2.5 micrometers.
- Due to its small size, it can penetrate deep into the respiratory system and cause severe health issues.
- It is primarily emitted from combustion activities, industrial emissions, and vehicular pollution.
Sources of PM2.5 in Northern India
- In Delhi, PM2.5 is dominated by ammonium chloride and organic aerosols from vehicular emissions, residential heating, and fossil fuel oxidation.
- Outside Delhi, ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate, and biomass- burning derived organic aerosols are more prominent.
- The oxidative potential of PM2.5 in Indian cities is among the highest globally, exceeding levels in Chinese and European cities by up to five times.
- It is primarily influenced by organic aerosols from incomplete combustion of biomass and fossil fuels.
- Cow dung combustion during winter for heating and cooking contributes to cold-season primary organic aerosols.
| WHO air quality guideline – They serve as a reference for governments and organizations to set national air quality standards and are not legally binding. – Recommended Limits of Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10); 1. PM2.5: WHO recommends an annual average limit of 5 µg/m³ and a 24-hour limit of 15 µg/m³. 2. PM10: The guideline suggests an annual average limit of 15 µg/m³ and a 24-hour limit of 45 µg/m³. |
Health Impacts of PM2.5
- The study highlights that PM2.5 in Indian cities has one of the highest oxidative potentials globally, surpassing levels in Chinese and European cities by up to five times.
- High PM2.5 exposure is linked to:
- Respiratory diseases: Asthma, bronchitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Cardiovascular issues: Increased risk of heart attacks and hypertension.
- Neurological disorders: Cognitive decline and neurodevelopmental issues in children.
- Premature mortality: Prolonged exposure increases the risk of early deaths due to lung and heart diseases.
Source: TH
Link of High levels of Selenium in Wheat to Hair Loss
Syllabus: GS 2/Health
In News
- An investigation by ICMR and AIIMS found high selenium levels in the blood and hair of affected individuals, linking it to wheat supplied by Public Distribution System (PDS) outlets.
Selenium
- It is an essential mineral found in many foods and available as a dietary supplement.
- Found as a byproduct of metal sulphide ore refining, not in pure elemental form. It is present in soil and groundwater in inorganic forms, which plants convert to organic forms like selenomethionine and selenocysteine.
- It is a key component of 25 selenoproteins, including thioredoxin reductases and glutathione peroxidases, which are involved in thyroid hormone metabolism, DNA synthesis, reproduction, and protection against oxidative damage and infections.
Applications
- Glassmaking: Used to decolorize glass and produce red-colored glass/enamels.
- Electronics: Used in photocells, light meters, and solar cells (replaced by silicon-based devices).
- Pigments: Adds a red color to ceramics, paints, and plastics.
- Rubber Industry: Enhances rubber durability & resistance via vulcanization.
Selenium Toxicity (Selenosis)
- Causes: Overconsumption via diet, supplements, or environmental exposure.
- Symptoms: Including hair loss, and excessive selenium intake from food or water is the likely cause of the hair loss in Shegaon taluka.
Source: TH
Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs) in DNA
Syllabus :GS 2/Health
In News
- Researchers have discovered ultra-conserved elements (UCEs) in the genome.
Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs)
- UCEs are DNA segments that have remained unchanged for over 80 million years across species like humans, rats, mice, chickens, dogs, and fish.
- These elements are thought to have remained intact due to some biological constraint.
Function of UCEs
- They play a crucial role in regulating protein production.
- They do not code for proteins, but they influence gene expression by acting as “poison exons” within mRNA (it is a type of single-stranded RNA involved in protein synthesis)
- In the Tra2b gene, the UCE helps prevent excessive production of the Tra2β protein by causing premature termination of protein synthesis.
- The UCE in the Tra2b gene is crucial for fertility, maintaining a delicate balance in protein production.
- Even a single change in the UCE could disrupt its function, explaining why it has been conserved over millions of years.
Research Breakthrough
- A study identified a UCE in the mouse Tra2b gene that plays a role in limiting protein production.
- Deleting this gene in mouse testes led to overproduction of the Tra2β protein, causing death of sperm-producing cells and infertility.
- Researchers used Cre protein to delete the UCE in the Tra2b gene in sperm-producing cells of mice.
Importance
- The research provides insight into the biological importance of UCEs and how their preservation across species helps regulate essential functions like fertility.
- The study marks a significant step in understanding the role of UCEs in genome stability and evolution.
| DNA to Protein Conversion – DNA Structure: Double-helix with four nitrogenous bases (Adenine (A) – Thymine (T) and Cytosine (C) – Guanine (G)). – Gene: A small section of DNA that carries instructions for making a protein. – Transcription (DNA → mRNA): DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA). 1. mRNA leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome. – Translation (mRNA → Protein): Ribosome reads mRNA in codons (3-base sequences). 1. Transfer RNA (tRNA) brings amino acids to build a protein. 2. Stop codon signals the end of protein synthesis. |
Source: TH
Kurd Issue
Syllabus: GS2/IR
Context
- The Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK) militant group declared an immediate ceasefire, a major step towards ending a 40-year insurgency.
About
- Kurds: Ethnic group of about 40 million, mainly in Iran, Iraq, Syria, and Turkey.
- Speak various Kurdish dialects, not related to Turkish or Arabic; mostly Sunni Muslims.
- In Syria, Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) control the northeast.
- Concerns: They were promised a nation post-WWI, but never granted.
- Faced rebellions, state suppression of language and culture.
- Insurgency: The group launched an armed insurgency against the Turkish state in the early 1980s, originally seeking independence for the Kurds.
- They make up about 15% or more of Turkey’s population.
- Peace Efforts: Multiple efforts to end the Turkey-PKK conflict have been made, but all of them collapsed.
Source: IE
Firefly’s Blue Ghost: A Historic Private Lunar Landing
Syllabus: GS3/Space
Context
- Firefly Aerospace successfully landed its Blue Ghost lander on the Moon, becoming the first private mission to land upright.
- It landed near Mons Latreille, a volcanic formation in Mare Crisium on the Moon’s northeastern near side.
About
- Nicknamed “Ghost Riders in the Sky,” the Blue Ghost mission is part of NASA’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) program, which encourages private-sector involvement in lunar exploration.
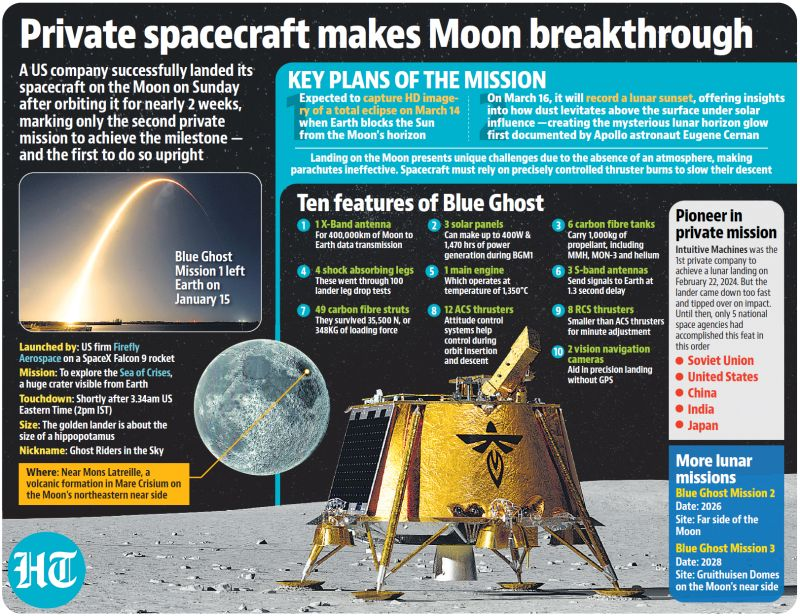
Image Courtesy: HT
- The mission aims to support Artemis mission goals, that aims to establish a long-term human presence on the Moon.
- The Blue Ghost lander is equipped with ten high-tech instruments like lunar soil analyser, radiation-tolerant computer, drill & vacuum system etc designed for scientific and technological research.
- Duration: Expected to operate for a full lunar day (14 Earth days).
Challenges of Lunar Landings
- Thin Atmosphere: Unlike Mars or Earth, the Moon has an extremely thin atmosphere, requiring precise thruster control to slow down from kilometers per second to a perfect halt.
- Rugged Lunar Terrain: Craters, boulders, and slopes increase the risk of failure.
- No Atmospheric Drag: Spacecraft cannot use parachutes to slow down.
Future Plans: More Private Landings
- Intuitive Machines’ Athena lander: Expected to land near the Moon’s south pole in the coming days
- ispace (Japan) Resilience lander: Another attempt following a failed mission in 2023.
| Do you Know? – The Artemis Accords, established in 2020 by the U.S. State Department and NASA, with seven founding members (Australia, Canada, Italy, Japan, Luxembourg, UAE, and the UK), set common principles for peaceful space exploration. – They build on the 1967 Outer Space Treaty to govern civil use of the Moon, Mars, comets, and asteroids. – India is a signatory to the Artemis Accords. |
Source: TH
Einstein Ring
Syllabus: GS3/Space
Context
- Recently, the Euclid space mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) spotted an Einstein ring in the galaxy NGC 6505, about 590 million lightyears from the earth.
What is an Einstein Ring?
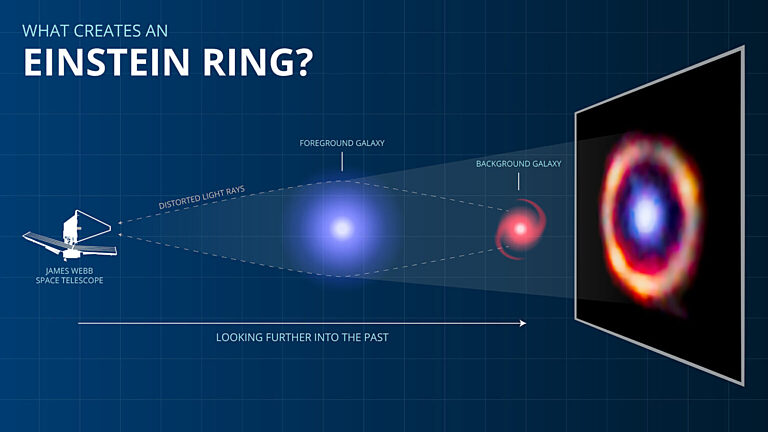
- Einstein’s Prediction: Light bends near massive objects due to spacetime distortion, forming the basis of his general theory of relativity.
- An Einstein Ring is a phenomenon that occurs when a massive object, acting as a gravitational lens, distorts and magnifies light from a distant background object.
- The light forms a circular pattern around the lens due to perfect alignment between the distant object, the lens, and the observer. This effect is a special case of strong gravitational lensing.
Significance of Einstein Rings
- Probing Dark Matter: Dark matter, which makes up 85% of the universe’s total matter, does not emit or absorb light, making it difficult to observe directly.
- Einstein rings provide indirect evidence of dark matter’s gravitational influence.
- Understanding Distant Galaxies: These rings help scientists study galaxies that would otherwise be too faint or distant to observe.
- Insights into Cosmic Expansion: The bending of light provides crucial data about the expansion of the universe, as the space between celestial bodies is continuously stretching.
| Euclid Mission (2023) – Mission: To explore the composition and evolution of the dark Universe. – Objective: Create a map of the Universe’s large-scale structure across space and time. 1. Observing billions of galaxies up to 10 billion light-years away, covering over a third of the sky. – Focus Areas: Investigating the expansion of the Universe, structure formation, and the roles of gravity, dark energy, and dark matter. |
Source: TH
Gene Therapy for Maple Syrup Urine Disease
Syllabus: GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
- Scientists have created a new gene therapy for a debilitating genetic disorder called maple syrup urine disease (MSUD).
Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)
- MSUD is a rare genetic disorder characterized by deficiency of an enzyme complex, Branched-Chain Alpha-Keto Acid Dehydrogenase (BCKDH).
- This complex is crucial for breaking down branched-chain amino acids—leucine, isoleucine, and valine.
- The absence or malfunction of this complex leads to the accumulation of toxic metabolites, resulting in severe neurological damage and, in extreme cases, death.
- Characteristic Odor: The disease gets its name from the distinct sweet smell in the urine of affected individuals.
- Treatment Options: Dietary Management and Liver Transplantation.
New Gene Therapy
- Scientists have introduced a gene replacement therapy for two types of classic MSUD using an adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector to deliver functional copies of the BCKDHA and BCKDHB genes.
- The therapy successfully restored metabolic function in knockout cells.
Source: TH
Planetary Parade
Syllabus: GS3/ Space
In News
- February 28, 2025, witnessed a rare planetary parade.
What is a Planetary Parade?
- A celestial event where multiple planets appear in a straight line in the night sky.
- Planets in Alignment: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.
Source: TH
Exercise Desert Hunt 2025
Syllabus: GS3/ Defence
Context
- The Indian Air Force conducted Exercise Desert Hunt 2025, an integrated Tri-Service Special Forces exercise, at Air Force Station Jodhpur, Rajasthan.
About
- The exercise involved Para (Special Forces) of the Indian Army, Marine Commandos (MARCOS) of the Indian Navy, and Garud (Special Forces) of the Indian Air Force.
- It aimed to enhance interoperability, coordination, and synergy among the three Special Forces units for swift and effective responses to security challenges.
- Key operations included: airborne insertion, precision strikes, hostage rescue, counter-terrorism operations, combat free falls and urban warfare scenarios wherein the combat readiness of the forces was tested under realistic conditions.
Source: PIB
Next article
Cities Coalition for Circularity (C-3) Launched