India Secures Copper Exploration Block in Zambia
Syllabus: GS1/Geography/Critical Minerals
Context
- India has secured a 9,000-sq-km exploration block to explore copper and cobalt in Zambia.
- Zambia is the 7th largest copper producer globally.
Recent Trends in Global Copper Market
- As per a Bloomberg report, global copper ore supply is shrinking, intensifying the race for resources.
- China controls 50% of global copper smelting and refining capacity.
- Copper demand is rising, driven by EV batteries, renewable energy, and clean technologies.
- Chile, Peru, China, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), and the United States lead in global copper production.
- India, China, and the U.S. are securing copper supply chains, leading to increased geopolitical competition over the next decade.
India’s Copper Situation
- Domestic ore production in 2023-24 was 3.78 million tonnes (8% lower than 2018-19).
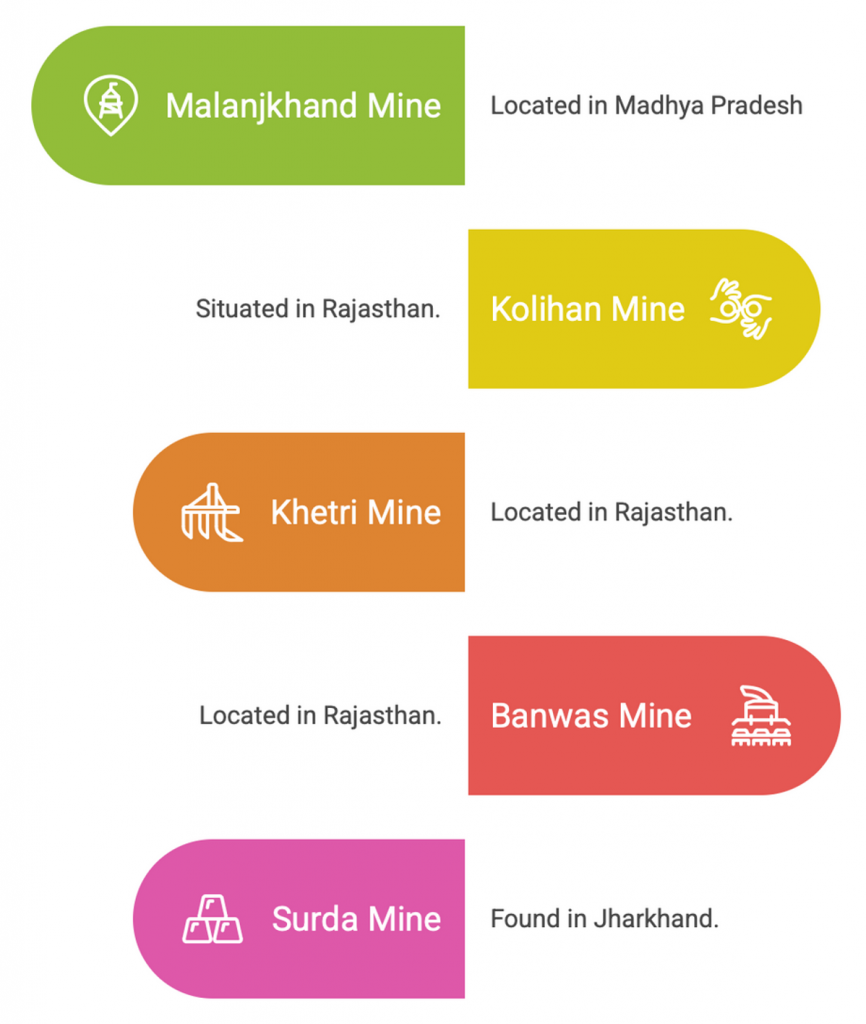
- Madhya Pradesh is the leading producer of copper in India followed by Rajasthan.
- Copper Mines in India:
- Copper Imports: India’s copper concentrate imports have doubled in value to Rs 26,000 crore in 2023-24 from 2018-19.
- Challenges with Domestic Deposits: India has large copper deposits, but they require extensive exploration before mining.
- The global average time to operationalize a copper mine is 17 years.
- Overseas Investment Strategy: India is securing copper assets in Zambia, Chile, and the DRC for short-term demand.
- However, overseas investments carry significant geopolitical risks.
Africa’s Rising Share in Critical Minerals
- The continent produces 70% of global cobalt and 16% of global copper.
- The DRC is set to become the world’s second-largest copper supplier by 2030.
- India’s Efforts in Africa: India’s Ministry of Mines is working in the DRC, Tanzania, Mozambique, and Rwanda to acquire critical mineral assets.
Source: IE
Swavalambini
Syllabus: GS2/ Governance
Context
- The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), in collaboration with NITI Aayog, launched Swavalambini, a Women Entrepreneurship Programme.
About
- Swavalambini aims to establish a structured and stage-wise entrepreneurial journey for young women.
- This programme aims to nurture the entrepreneurial spirit among young women in Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) by providing them with the necessary mindset, resources, and mentorship to successfully build and scale their ventures.
Key Features of the Swavalambini Programme
- Faculty Development Programme (FDP): Swavalambini focuses on training faculty members from participating Higher Education Institutions (HEIs) with five-day training sessions.
- Mentorship: Once participants have developed their business plans, they receive mentorship from industry experts and successful entrepreneurs. Additionally, the programme facilitates:
- Access to funding opportunities through government schemes and private investors.
- Networking opportunities with established business leaders and professionals.
- Women Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP): Building on the foundation laid in the EAP, the Entrepreneurship Development Programme (EDP) provides a deeper understanding of:
- Business planning, Leadership and decision-making skills,
- Financial literacy and investment strategies.
- Market research and competitive analysis.
Source: PIB
Doctrine of Equality
Syllabus :GS 2/Polity
In News
- The Supreme Court of India ruled that visually challenged candidates cannot be deemed unsuitable for judicial service.
Supreme Court’s Recent Rulings
- The court emphasized the principle of inclusivity and equality, noting that ‘disability’ should be added as a ground for non-discrimination in Article 15 of the Constitution.
- The court stressed that any indirect discrimination, such as rigid cut-offs or procedural barriers, that excludes persons with disabilities (PwD) from judicial service should be removed to ensure equality.
Right to Equality in India
- Articles 14 to 18 deal with different aspects of the right to equality.
- Article 14 – It ensures that all persons are equal before the law and have equal protection of the laws within India, without discrimination on grounds such as religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth.
- Article 15 – It prohibits discrimination by the state on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex, or place of birth.
- Allows for special provisions to be made for the welfare of women, children, socially and educationally backward classes, and SCs/STs.
- Also prohibits discrimination in public spaces like shops, restaurants, and public entertainment venues.
- Article 16 -It guarantees equality of opportunity for all citizens in public employment, prohibiting discrimination in employment based on religion, race, caste, sex, descent, place of birth, or residence.
- Article 17 – It abolishes untouchability and prohibits its practice in any form.
- Article 18 – It prohibits the state from granting titles other than military or academic distinctions.
Source:TH
US Announces Creation of Crypto Strategic Reserve
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
In News
- The U.S. government has announced the creation of a Crypto Strategic Reserve.
What is the Crypto Strategic Reserve?
- The Crypto Strategic Reserve will serve as a national stockpile of digital assets, managed under a federal regulatory framework. The reserve will consist of five major cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin, Ethereum, Ripple, Solana & Cardano.
- This initiative aims to integrate cryptocurrencies into the U.S. financial infrastructure.
Significance of the Initiative
- The establishment of a Crypto Strategic Reserve draws parallels to the Strategic Petroleum Reserve.
- By holding digital assets, the U.S. can mitigate financial risks and expand its economic portfolio.
- Cryptocurrencies can serve as a safeguard against inflation and traditional market fluctuations.
Source: TH
Ferrihydrite
Syllabus: GS3/Space
Context
- A study by NASA and ESA suggests that Mars’ red color originates from ferrihydrite.
About
- Formation of Ferrihydrite: Ferrihydrite requires cool water to form, indicating that Mars may have had liquid water in its past.
- Mars was thought to have turned red due to slow oxidation in dry conditions over billions of years.
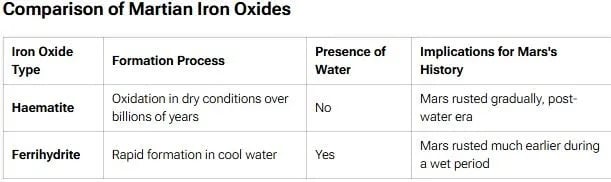
- Implication for Habitability: The presence of ferrihydrite implies that Mars could have been habitable in the past, with conditions that allowed liquid water.
Significance of the Study
- Evidence of Water: The presence of ferrihydrite indicates prolonged water activity.
- Past Habitability: Suggests an environment more suitable for sustaining life.
- Climate Insights: Helps reconstruct Mars’ transition from a wet to a dry planet.

| About Mars – Mars is the fourth planet from the sun and has a distinct rusty red appearance and two unusual moons. 1. Phobos: ~6000 km above Mars; Deimos: ~20 000 km above Mars. – It has a very thin atmosphere, but dusty. – Gravity: 3.711 m/s2 (about one third of Earth’s gravity) – Mars also has the largest volcanoes in the solar system, Olympus Mons being one of them. – Atmosphere: 95.32% carbon dioxide, 2.7% nitrogen, 1.6% argon, 0.13% oxygen |
Source: ET
National Board for Wildlife
Syllabus: GS3/Environment
Context
- The Prime Minister chaired the 7th meeting of the National Board for Wildlife at Gir National Park in Gujarat.
Key Outcomes of the Meeting
- A report on the country’s first riverine dolphin estimation was released.
- 6,327 river dolphins recorded across 28 rivers in 8 states.
- Uttar Pradesh has the highest population followed by Bihar, West Bengal, and Assam.
- Foundation stone of National Referral Centre for Wildlife laid in Junagadh for wildlife health and disease management hub.
- To deal with Human-Wildlife Conflict, a Centre of Excellence will be established at the Wildlife Institute of India’s campus in SACON (Salim Ali Centre for Ornithology and Natural History), Coimbatore.
- Rapid Response Teams to be equipped with technology for conflict mitigation.
- Plans to introduce cheetahs in Gandhisagar Sanctuary (Madhya Pradesh) and Banni Grasslands (Gujarat) to strengthen reintroduction efforts.
National Board for Wildlife
- Established: Reconstituted in 2022 (Replacing the earlier Indian Board for Wildlife, which was formed in 1952).
- Leadership:
- Chairperson: Prime Minister of India (Ex-officio).
- Vice-Chairperson: Minister of Environment, Forest & Climate Change (MoEFCC).
- Structure:
- The 47-member committee includes government officials, conservationists, ecologists, environmentalists, and military personnel.
- Approval from NBWL is Required for:
- Construction of tourist lodges.
- Alteration of Protected Area (PA) boundaries.
- Destruction/diversion of wildlife habitat.
- De-notification of Tiger Reserves.
| Gir National Park – Location: Situated in the Saurashtra region of Gujarat. – Established: In 1965, as a sanctuary, and later upgraded to a national park in 1975. – It is the only place in the world outside Africa where a lion can be seen in its natural habitat. 1. Since the late 1960s, Asiastic lion numbers have increased from less than 200 to 674 (Census 2020). – Gir is a home to 40 species of mammals and 425 species of birds. |
Source: TOI
First Comprehensive Estimate of River Dolphins in India
Syllabus: GS3/ Conservation, Species in News
In News
- India’s first comprehensive survey of river dolphins, conducted under Project Dolphin (launched in 2020), estimates a population of 6,327 dolphins, primarily in the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Indus river basins.
Key Findings
- India is home to two species of freshwater dolphins: Ganges (Platanista gangetica) and Indus (Platanista minor).
- There are 6,324 Ganges river dolphins, and three Indus river dolphins.
- Highest populations recorded in Uttar Pradesh, followed by Bihar, West Bengal, and Assam.
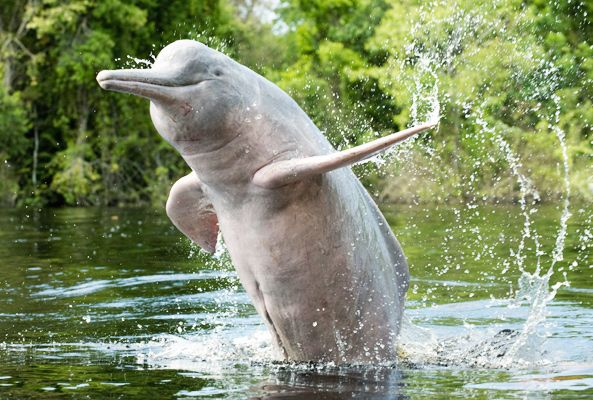
Ganges River Dolphin (Platanista Gangetica)
- Characteristics:
- Functionally blind; relies on echolocation for hunting.
- Known as Susu due to the sound it makes while breathing.
- Exclusively freshwater species, inhabiting Ganga and Brahmaputra river basins in India, Nepal, and Bangladesh.
- Threats: Habitat destruction, pollution and hunting.
- Conservation Status:
- Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species): Appendix I
- CMS (Convention on Migratory Species): Appendix I
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- National & State Recognition:
- Declared India’s National Aquatic Animal in 2009.
- Recognized as the State Aquatic Animal of Assam.

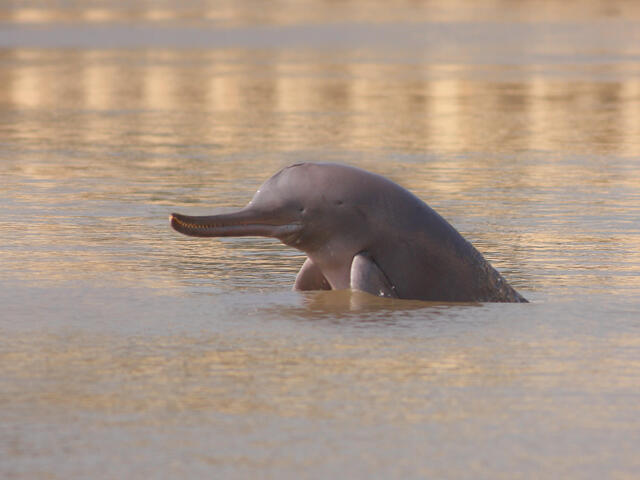
Indus River Dolphin (Platanista minor)
- Characteristics:
- Functionally blind, navigates using echolocation.
- Locally called Bhulan in the region.
- Found mainly in the Indus River System (Pakistan) with a small population in India’s Beas River.
- Threats: Habitat fragmentation, Restricted range, leading to population isolation.
- Conservation Status:
- Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Schedule I
- CITES: Appendix I
- IUCN Red List: Endangered
- State Recognition:
- Declared the State Aquatic Animal of Punjab.

| Do You Know? – One more species of Dolphin i.e. Irrawaddy dolphin found in India in Chilika Lake (Asia’s largest brackish water lagoon) in Odisha. – Unlike the other two species, Irrawaddy dolphins are not blind and have a bulbous head with no beak. – IUCN Red List Conservation status: Critically Endangered. |
Importance of River Dolphins
- River dolphins reflect the overall health of freshwater ecosystems. Help in carbon sequestration, flood regulation, and water purification.
- They play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance by controlling fish populations.
- The Ganges River Dolphin (Susu) and Indus River Dolphin (Bhulan) hold cultural and religious significance in many communities.
- They promote sustainable tourism and local economic development.
Source: TH
Oscars
Syllabus :Miscellaneous
In News
- The 97th Academy Awards was held recently.
Oscars
- The Oscars, officially known as the Academy Awards, is an annual event which has recognized excellence in cinematic achievements.
- It was first established in 1929 by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences
- Categories: The Oscars feature a variety of categories, with Best Picture being the most coveted.
- Other major awards include Best Director, Best Actor, Best Actress, and Best Original Screenplay.
Major Highlights of Recent awards
- “Anora,” an indie film from Brighton Beach, New York, won five Oscars, including Best Picture.
- It is a drama about a sex worker who marries the son of a Russian oligarch.
- Director Sean Baker won Best Director, Best Original Screenplay, and Best Editing with a $6 million budget.
- Mikey Madison won Best Actress for her role in Anora, despite lacking precursor wins (no BAFTA, Golden Globe, or SAG).
- Adrien Brody won Best Actor for The Brutalist, making him the only actor to win twice without a loss in the category.
- Technical Wins: The Brutalist won Best Cinematography and Best Original Score for its use of VistaVision.
- Flow became the first non-dialogue animated film to win Best Animated Feature.
- Paul Tazewell became the first Black person to win Best Costume Design for Wicked.
Source :TH
Previous article
Bose Metal
Next article
Women’s Role in India’s Inclusive Growth