Syllabus: GS3/Infrastructure
Context
- The Digital India program was launched by the Government on July 1, 2015, envisions transforming India into a knowledge-based economy and digitally empowered society.
Digital Economy
- The digital economy is growing fast, contributing 11.74% to the national income in 2022–23 and expected to reach 13.42% by 2024–25.
- According to the State of India’s Digital Economy Report 2024, released by ICRIER, India now ranks third in the world for digitalisation of the economy.
- By 2030, India’s digital economy is projected to contribute nearly one-fifth of the country’s overall economy, outpacing the growth of traditional sectors.
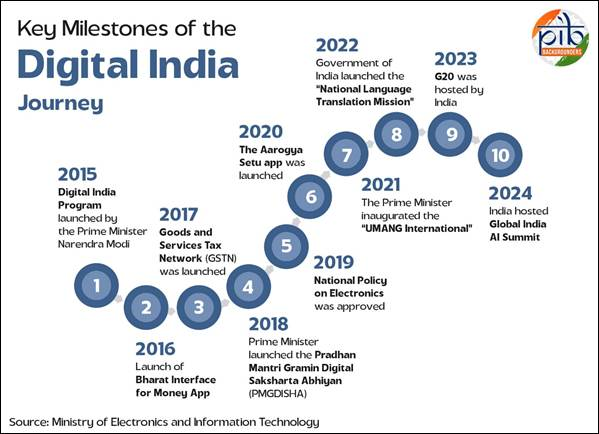
Key Focus Areas and Services Under Digital India
- Connectivity and Infrastructure: Over the years, Digital India has built strong digital infrastructure across the country. Mobile connectivity has expanded to almost every village.
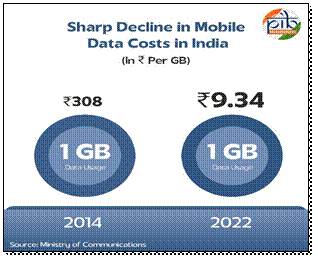
- Telecom and Internet Penetration: Total telephone connections in India rose from 93.3 crore in 2014 to over 120 crores in 2025, with tele-density increasing from 75.23% to 84.49% by 2024.
- UPI: According to the ACI Worldwide Report 2024, India handled 49% of global real-time transactions in 2023. UPI now lives in over seven countries, boosting global digital payments and financial inclusion.
- Aadhaar: The Aadhaar-based e-KYC system has helped simplify processes in both banking and public services. It made verification faster, reduced paperwork, and brought transparency across sectors.
- Direct Benefits Transfer (DBT): DBT uses Aadhaar to deliver welfare payments directly and remove fake beneficiaries.
- Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC): Launched in 2022, ONDC helps small businesses enter digital markets. By 2025, it covers 616+ cities and has registered more than 7.64 lakh sellers and service providers.
- IndiaAI Mission: It focuses on enabling access to computing, supporting innovation, improving datasets, funding startups, and ensuring ethical AI use.
- By May 2025, India’s national computer power crossed 34,000 GPUs, marking a major milestone in AI infrastructure growth.
- India Semiconductor Mission: With a ₹76,000 crore outlay, the mission supports local chip and display manufacturing. It offers up to 50% support for fabs and incentives for chip design and production.
- E-Governance: E-Governance in India has revolutionized the way citizens interact with the government by making services more accessible, transparent, and efficient.
- It involves initiatives like Mission Karmayogi, DigiLocker, and UMANG App.
Source: TH
Previous article
Sovereign Debt is Rising in Developing World