Syllabus: GS3/Energy
Context
- India’s power distribution utilities have recorded a collective Profit After Tax (PAT) of ₹2,701 crore in FY 2024–25.
About
- The distribution utilities have been reporting PAT losses for the past several years since unbundling and corporatization of State Electricity Boards.
- This marks a new chapter for the distribution sector and is a result of several steps that have been taken to redress the concerns of the distribution sector.
Initiatives in the Distribution Sector
- Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS): Enhancing financial viability through infrastructure modernization and accelerated smart metering.
- Additional Prudential Norms: Linking access to finance for Power sector Utilities to achievement against performance benchmarks to promote fiscal and operational discipline.
- Amendments to Electricity Rules: Enforcing timely cost adjustments, prudent tariff structures, and transparent subsidy accounting to ensure full cost recovery.
- Electricity Distribution (Accounts and Additional Disclosure) Rules, 2025: Introducing uniform accounting and enhanced transparency across Distribution utilities for improved financial governance.
- Late Payment Surcharge Rules: Enforcing legal contracts through timely payments in the power sector thereby supporting investment in new RE projects.
India’s Power Sector
- India is the third-largest producer and consumer of electricity in the world, with an installed capacity of 476 GW as of June 2025.
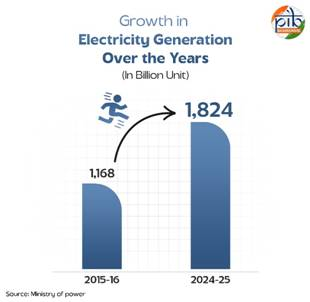
- India ranks fourth globally in renewable energy installed capacity, fourth in wind power, and third in solar power as of 2025.
- Electricity consumption remains led by industry at 41.8%, followed by households at 24.3%, agriculture at 17%, and commercial use at 8.3%.
- India met a record peak demand of 250 GW in June 2025, highlighting the scale of demand growth.
- India achieved 100% village electrification by 2018 and has since connected more than 2.8 crore households to the grid.
Concerns of Power Sector
- High transmission and distribution losses: Power theft, inadequate metering, and outdated infrastructure lead to Transmission & Distribution (T&D) losses well above global standards.
- Fuel supply and energy security challenges: Coal shortages, logistical constraints, and rising dependence on imported coal and gas expose the power sector to global price volatility.
- Renewable energy integration constraints: The growing share of solar and wind power poses challenges related to intermittency, lack of energy storage and grid balancing issues.
- Inadequate transmission and grid infrastructure: Transmission networks have not expanded in pace with generation capacity, particularly in renewable-rich regions, causing congestion and inefficient power evacuation.
- Rising demand and peak power shortage: Rapid growth in electricity demand driven by urbanisation, industrialisation, climate-induced cooling needs, and EV adoption has increased pressure on peak capacity and grid stability.
Government Initiatives
- National Solar Mission (NSM): It was launched in 2010, it has set ambitious targets for solar capacity installation, including grid-connected and off-grid solar power projects.
- National Clean Energy Fund (NCEF): It was established to support research and innovation in clean energy technologies and projects that help in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- National Wind Energy Mission: Focuses on the development and expansion of wind energy in India. The target for wind energy capacity is set at 140 GW by 2030.
- Financial Support & Incentives: Viability Gap Funding (VGF) for large-scale solar and hybrid projects.
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme for solar PV manufacturing.
- Subsidies for rooftop solar and off-grid systems.
- Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) to promote green power trading.
- Infrastructure Development: Green Energy Corridor to improve RE grid integration.
- PM-KUSUM Scheme for solarizing agricultural pumps.
- Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS) to strengthen DISCOMs.
- Emerging Technologies & Projects: Support for Battery Storage, hybrid systems, and RTC power.
- Promotion of offshore wind and floating solar projects.
- Focus on Hydrogen Mission for green hydrogen development.
- International Partnerships: ISA (International Solar Alliance) launched by India to promote global solar cooperation.
- Collaboration with countries & global funds for clean energy investment and technology.
Source: PIB
Previous article
India & Global Stock Market Surge
Next article
News In Short 19-01-2026