Syllabus: GS1/Geography
Context
- The Brahmaputra, Teesta, and Dharla rivers have become unpredictable, eroding land faster than ever before.
About Riverbank Erosion
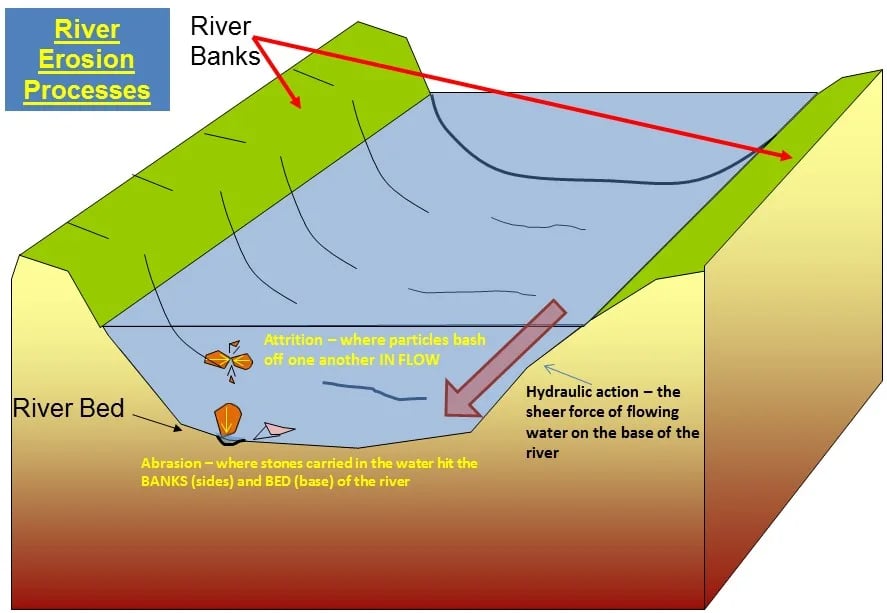
- Riverbank erosion is the wearing away of the banks of a river due to the continuous action of flowing water.
- It is a natural geomorphological process but can be accelerated by human activities or environmental changes.
- When water flows along a river channel, it exerts shear stress on the riverbanks.
- Over time, this force removes soil, sand, and rock particles from the bank, leading to undercutting, collapse, and retreat of the riverbank.
Causes of Riverbank Erosion
- Natural Causes
- Strong river currents: Fast-flowing water erodes the outer banks of bends (meanders).
- Floods: High water volume and velocity during floods intensify erosion.
- Soil composition: Loose or sandy soils erode more easily.
- Lack of vegetation: Roots help bind the soil; their absence makes banks fragile.
- River meandering: Continuous shifting of river channels causes lateral erosion.
- Human-Induced Causes:
- Deforestation near riverbanks.
- Sand mining and gravel extraction.
- Construction of dams and embankments altering natural flow.
- Overgrazing or cultivation close to the river edge.
Impacts
- Loss of agricultural land and livelihoods.
- Displacement of people, which is also a major problem in states like Assam and West Bengal.
- Damage to infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and embankments.
- Sedimentation downstream, affecting navigation and aquatic life.
Control and Mitigation Measures
- Bioengineering methods: planting grasses, shrubs, and trees to stabilize banks.
- Construction of revetments, spurs, and gabion walls.
- River training and dredging to manage flow.
- Community-based riverbank management and land-use planning.
Source: TH
Previous article
News in Short – 10 November, 2025
Next article
India and Vietnam: Strengthening Defence Ties