Syllabus: GS2/International Relation
Context
- India has intensified efforts to diversify its global economic partnerships, and is focusing on large-scale connectivity projects such as the India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC).
IMEC: Historical Background
- IMEC was unveiled during the G20 Summit (2023) in India, representing a vision for transcontinental connectivity, backed by leaders from the EU, France, Germany, Italy, and Saudi Arabia.
- Abraham Accords: It fostered optimism for peace and cooperation in West Asia, creating opportunities for new cross-border infrastructure projects.
- India’s growing ties with the UAE, Saudi Arabia, UK, EU along with its improving relationship with the US, led to the establishment of the I2U2 framework (India, Israel, UAE, US).
Strategic Vision of IMEC
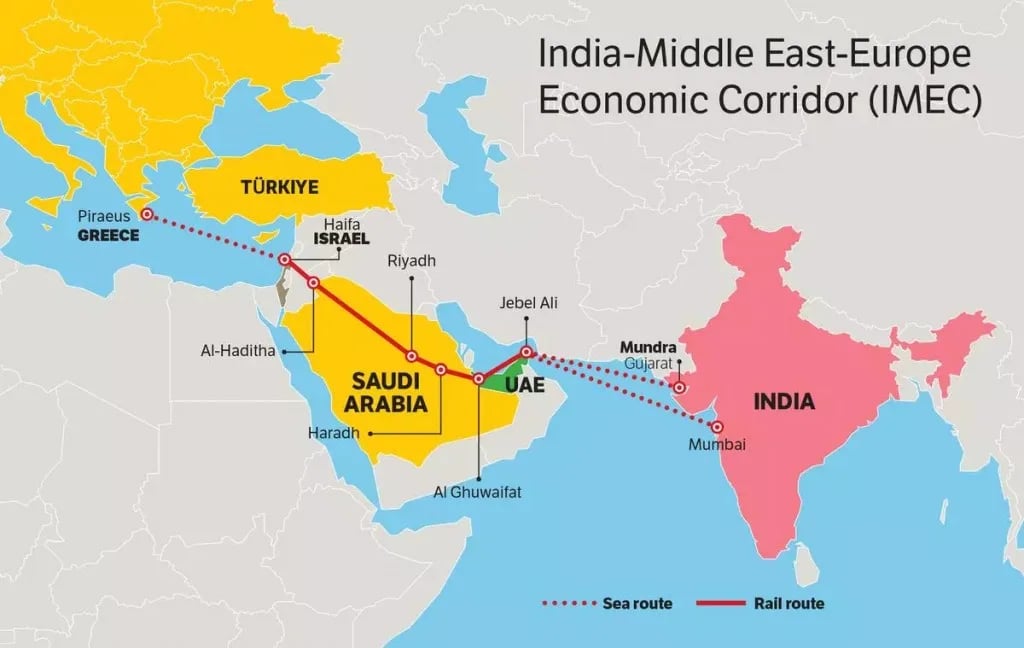
- Connectivity: IMEC is envisioned as a comprehensive network linking India to Europe through the Arabian Peninsula. The corridor includes:
- Maritime routes from Indian ports to the UAE;
- Rail networks across Saudi Arabia, Jordan, and Israel to European ports like Haifa;
- Infrastructure: IMEC is part of the Partnership for Global Infrastructure and Investment (PGII), co-chaired by India and the US during the G20 Summit. It reflects:
- A collaborative model of development, involving the EU, UAE, Saudi Arabia, and others;
- A counterweight to China’s Belt and Road Initiative, offering transparency and sustainability;
- Supporting infrastructure such as a clean hydrogen pipeline, electricity cable, and undersea digital network.
- Economic Efficiency: IMEC could cut logistics costs by up to 30% and reduce transport time by 40%, boosting trade competitiveness.
- It supports India’s ambition to become a global manufacturing and export hub, especially for sectors like electronics, textiles, and pharmaceuticals.
Importance of IMEC
- Europe’s Continuing Relevance to India: Developing resilient supply chains and efficient logistics networks between India and Europe is central to maintaining competitiveness.
- The EU is India’s largest trading partner, with bilateral trade exceeding $136 billion.
- High per capita income, technological leadership, and educational excellence ensure Europe’s ongoing importance for India’s export-driven growth.
- For Mediterranean Economies: IMEC is crucial to maintaining relevance in global shipping as trade potentially shifts northward for countries such as Italy and France.
- Italy, with only a Mediterranean coastline, views IMEC as vital to protecting its maritime influence.
Geopolitical and Economic Challenges in IMEC
- Regional Instability in West Asia: Ongoing conflicts and deteriorating security situation in West Asia threaten the corridor’s northern leg, slowing implementation.
- Security and Infrastructure Risks: India has acknowledged concerns about the safety and security of infrastructure created under IMEC, especially in conflict-prone zones.
- The corridor’s success depends on stable maritime and land routes, which are vulnerable to sabotage, piracy, and regional tensions.
- Economic Uncertainty and Investment Risks: India has invested significantly in IMEC, but returns are uncertain due to geopolitical disruptions.
- The corridor’s viability hinges on multilateral funding, and any withdrawal or delay by partner nations could stall progress.
- Diplomatic Balancing Act: India needs to navigate complex alliances—balancing ties with the US, EU, Gulf nations, and Israel—while maintaining strategic autonomy.
- Trade friction with the US and evolving EU dynamics require India to diversify its economic engagements and avoid overdependence on any single bloc.
- Coordination Across Jurisdictions: IMEC involves multiple sovereign countries, each with distinct regulatory frameworks, customs protocols, and political priorities.
- Harmonizing these systems is a logistical and diplomatic challenge, requiring sustained dialogue and trust-building.
- Opening of New Routes: The opening of new Arctic trade routes are reshaping global maritime patterns, offering faster and cheaper alternatives for northern economies like the US, Russia, and China.
Way Forward: Strengthening the IMEC
- The India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) represents more than an infrastructure project—it is a strategic vision for transcontinental integration, energy security, and digital cooperation.
- India needs to focus more on infrastructure expansion and port modernization like development of multimodal logistics hubs; upgrades to key ports like Mumbai and Mundra; and integration with digital platforms such as MAITRI to streamline trade.
- India also needs diplomatic engagements and bilateral cooperation in the region highlighting IMEC’s role in boosting prosperity across regions, as it has the potential to transform India’s trade ecosystem.
| Daily Mains Practice Question [Q] Discuss the potential of the India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) in reshaping global trade dynamics. What challenges could hinder its realization, and how might India navigate them to ensure long-term strategic success? |
Previous article
Addressing Caste-Based Atrocities in India