Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
In News
- Delhi is set to launch its first-ever cloud seeding trial to combat its persistent air pollution through artificial rain. The initiative is coordinated by IIT Kanpur and IMD Pune.
What is Artificial Rain?
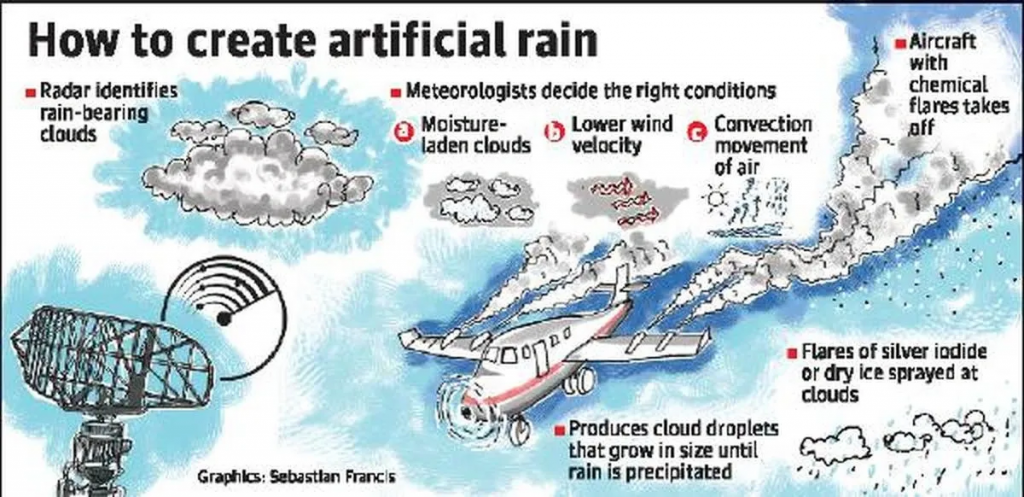
- Artificial rain refers to inducing precipitation by injecting certain chemicals into clouds to accelerate the process of raindrop formation.
- Cloud seeding involves dispersing substances like:
- Silver iodide (AgI)
- Potassium iodide
- Sodium chloride
- Dry ice (CO₂)
- These act as condensation nuclei, attracting water droplets, which then combine to form rain.
- Conditions Required: Potential rain-bearing clouds, sufficient humidity and atmospheric instability & Favorable wind and temperature conditions.
Advantages of Cloud Seeding
- Air Pollution Mitigation: In cities like Delhi, artificial rain can wash down particulate matter and other pollutants, providing temporary relief from severe air pollution.
- Drought Mitigation and Water Resource Augmentation: States like Maharashtra and Karnataka have used cloud seeding to combat water shortages (e.g., “Project Meghdoot” and “Varshadhari”).
- Forest Fire Control: By increasing moisture levels, cloud seeding can potentially reduce the risk and intensity of wildfires.
- Science-backed Intervention: Several countries like China, Thailand, UAE, and USA (Texas, Nevada) use cloud seeding for weather control, drought mitigation, and even clearing skies during major events (e.g., 2008 Beijing Olympics).
Concerns & Criticism
- Environmental Damage: Runoff from cloud-seeded rains can contaminate lakes, rivers, and groundwater.
- Temporary Solution to a Structural Problem: Core issues like stubble burning, vehicular emissions, and urban planning remain unaddressed.
- Ethical and Legal Issues: The ability to manipulate weather raises complex ethical questions about human intervention in natural processes & its implications.
- Health and Ecosystem Risks: Long-term chemical accumulation in soil may affect plant growth, reduce soil fertility, and enter the food chain.
Way Ahead
- Use Artificial Rain as a Last Resort: Should be opted only when AQI breaches dangerous levels.
- Robust Scientific Backing: Need for real-time satellite data, Doppler radars, and meteorological modelling.
- Invest in Permanent Air Quality Solutions: Electric vehicle (EV) push, Green infrastructure (urban forests, vertical gardens) & crop residue management (e.g., PUSA bio-decomposer).
Source: TOI
Previous article
India’s External Debt Rises to $736 Billion
Next article
News In Short-30-06-2025