Syllabus: GS3/Economy; Employment; Growth & Development
Context
- A recent study commissioned by the Office of the Principal Scientific Advisor and executed by the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and others has revealed significant gaps in the support provided to deep tech start-ups by public-funded R&D organisations in India.
About Deep Tech Start-ups
- Deep Technology refers to innovations founded on advanced scientific and technological breakthroughs such as AI, quantum computing, biotechnology, and space tech and of its disruptive nature.
- Deep tech start-ups differ from traditional start-ups primarily in their technology-driven approach, longer development cycles, and higher risk factors.
- Traditional start-ups often rely on business model innovation, such as e-commerce, SaaS, or consumer services.
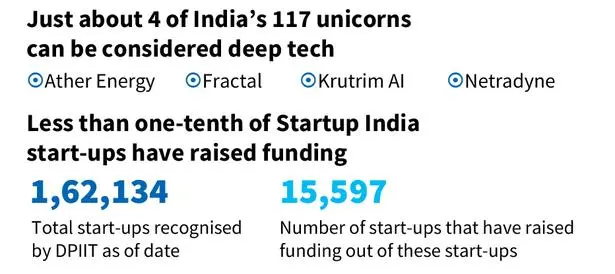
Key Findings of the Study
- Limited Incubation Support:Only one in four public-funded R&D organisations provide incubation support to start-ups.
- Support for deep tech start-ups is even lower, with only one in six institutions engaging in such initiatives.
- Weak Industry Collaboration: A mere 15% of organisations collaborate with overseas industries, highlighting an urgent need for global partnerships.
- Restricted Access to Facilities: Half of the organisations fail to open their infrastructure to external researchers and students, reducing opportunities for knowledge-sharing and innovation.
Budget Allocation and Workforce Trends
- R&D Expenditure: The Central government’s R&D expenditure was approximately ₹55,685 crore in 2020-21, with ₹24,587 crore allocated to key scientific agencies.
- Around 25% of participating institutions reported spending 75%-100% of their budgets on R&D, while others fell below the median share.
- Declining Permanent Staff: Observed from 2021-22 to 2022-23, accompanied by increased reliance on contractual staff.
- The share of young researchers increased to 58%, up from 54% in the previous year, however, the number was around 63% to 65% for the period from 2017-18 to 2019-20.
Efforts Related To Deep Tech Start-Ups
- National Deep Tech Startup Policy (NDTSP): It aims to strengthen India’s deep tech ecosystem by fostering research-driven innovation.
- It focuses on economic security, knowledge-driven growth, and ethical innovation.
- Quantum Computing and Deep Tech Innovation: India is making strides in quantum computing, with start-ups like QpiAI launching advanced quantum systems.
- The National Quantum Mission supports deep tech ventures in life sciences, drug discovery, and sustainability.
Recommendations for Strengthening Deep Tech Innovation
- Enhanced Industry Collaboration: Establish stronger ties with domestic and international industries to foster innovation and leverage global expertise.
- Focus on Deep Tech and Start-ups: Increase support for deep tech ventures and incubation programs to catalyse breakthroughs in emerging technologies.
- Open Access to Facilities: Public R&D institutions should provide greater access to their facilities for external researchers and students to encourage knowledge-sharing and interdisciplinary research.
- Aligning Mandates to Viksit Bharat Goals: To accelerate India’s journey toward Viksit Bharat@2047, public-funded R&D institutions must reassess their mandates and align with national strategic priorities.