Syllabus :GS3/Science and Technology
In News
- The Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) reactor in China maintained plasma in a steady state for over 1,000 seconds (17 minutes), setting a new record in fusion research.
About Nuclear Fusion
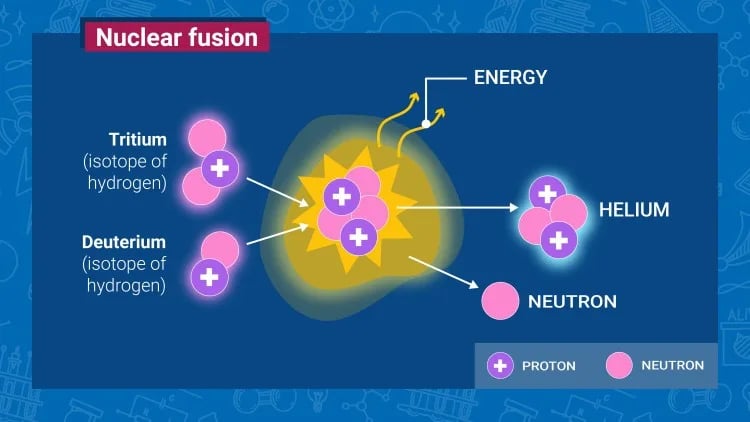
- Fusion is the process where two light atomic nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing massive energy.
- It takes place in plasma (hot, charged gas of ions and electrons) with unique properties different from solids, liquids, or gases.
- It occurs in the Sun at temperatures of around 10 million degrees Celsius.
- On the Sun, extremely high temperatures and gravity create conditions for fusion.
Potential and Importance
- Fuel sources like deuterium (from seawater) and tritium (from lithium) are abundant and long-lasting.
- Fusion could provide limitless, clean, safe, and affordable energy.
- It generates 4 times more energy per kilogram of fuel than fission and nearly 4 million times more energy than burning oil/coal.
- Fusion is intrinsically safe, with no risk of a runaway reaction or meltdown.
- Environmental Benefits: Fusion does not emit carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases, offering a potential low-carbon electricity source.
Challenges
- Conditions related: Earth requires temperatures exceeding 100 million°C and intense pressure to achieve fusion.
- Achieving and maintaining these extreme conditions for stable fusion is a challenge.
- Confining the plasma and maintaining the fusion reaction long enough for a net power gain is a major challenge.
- Current experiments have achieved conditions close to those required but need improved plasma confinement and stability.
- Technological and Financial Barriers: Fusion reactors require complex and expensive technology.
- Securing funding and overcoming regulatory hurdles are ongoing challenges.
Latest Developments in China
- China is building a large laser-ignited fusion research center, which may also have military applications for thermonuclear weapons.
- China’s nuclear arsenal has grown significantly, from 410 warheads in January 2023 to an estimated 500 in January 2024. Projections suggest China may match the U.S. and Russia in intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) by the end of the decade.
| Comparison with India – India’s nuclear arsenal is estimated at 172 warheads. – India operates 23 nuclear power reactors, generating about 6% of its electricity. – China has 55 operational reactors and is rapidly expanding its nuclear energy capacity, including the commercialisation of third-generation reactors and plans to build 6-8 new reactors annually. – China is also leading in nuclear power generation, with advanced reactors like the Shidaowan-1, a fourth-generation gas-cooled reactor, as part of its strategy to shift to cleaner energy sources. |
Implications
- Nuclear Weapons: The technology could enhance China’s nuclear weapons design capabilities without the need for traditional nuclear tests, improving confidence in existing weapons designs while adhering to international testing bans.
- Energy Production: It could also contribute to clean fusion energy research, offering the potential for nearly limitless, environmentally friendly power.
- Concerns for India: The new fusion facility will significantly enhance China’s capabilities in both nuclear weapons development and clean energy production, widening the gap between China and India’s nuclear capabilities.
Conclusion and Way Forward
- Nuclear Fusion has the potential to meet humanity’s energy needs for millions of years, making it a long-term, sustainable energy source.
- And China’s recent breakthrough in nuclear fusion marks a major milestone in the global pursuit of sustainable energy.
- For India, it poses both a challenge and an opportunity, motivating the country to accelerate its fusion research and seek new partnerships to secure its position at the forefront of future energy advancements.
Source :IE
Previous article
PM Surya Ghar Scheme
Next article
ISRO’s 100th Launch from Sriharikota