Syllabus: GS1/ Physical Geography
In News
- A long-dormant volcano in Ethiopia erupted after 12,000 years, causing ash plumes across the red sea towards Yemen, Oman, and even parts of India.
Ethiopia’s Afar Depression and the East African Rift
- The Hayli Gubbi volcano is located approximately 800 kilometers northeast of Addis Ababa in Ethiopia’s Afar region.
- The Afar Depression, also known as the Danakil Depression, is a geological marvel where three tectonic plates meet: the African (Nubian) Plate, the Somalian Plate, and the Arabian Plate.
- This region is part of the broader East African Rift System (EARS), one of the most geologically active zones on Earth.
- Under the East African Rift System (EARS), the African Plate is divided into the Nubian Plate (western) and Somalian Plate (eastern).
What is Volcanism?
- Overview: Volcanism (or volcanic activity) is the phenomenon where molten rock (magma), gases, and volcanic ash escape to the Earth’s surface through vents or fissures in the crust.
- Eruption: In the upper mantle, a weaker layer called the asthenosphere allows partially molten material to accumulate; buoyant magma then rises through cracks in the lithosphere. As pressure drops near the surface, dissolved gases (water vapour, carbon dioxide, sulphur gases, etc.) expand violently, driving magma upwards and producing an eruption.
- Once magma emerges at the surface it is termed lava, which may be fluid (basaltic) or viscous (andesitic–rhyolitic) depending on composition.
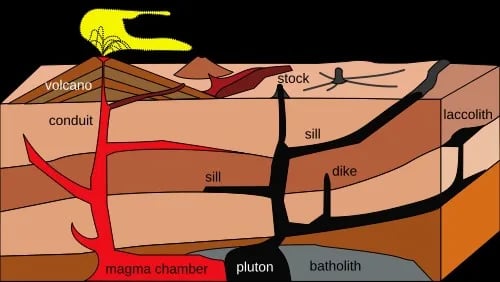
- Positive Consequences: Helps scientists infer the structure and composition of Earth’s interior from erupted rocks and gases.
- Weathered volcanic ash produces highly fertile soils rich in nutrients.
- Eruptions can also contribute to short-term global cooling when sulphur aerosols in the stratosphere reflect solar radiation, temporarily lowering surface temperatures.
- Negative Consequences: Volcanic eruptions degrade air quality through ash and toxic gases, leading to respiratory illness and acid rain that damages crops, water bodies, and infrastructure.
- They can trigger associated hazards like earthquakes, landslides, lahars, pyroclastic flows, and lava flows, causing large-scale loss of life and property.
- The volcanic plume has the potential to block visibility, and interfere with flight operations like fine particles could enter the engines and melt inside.
Source: TH
Previous article
News in Short – 24 November, 2025
Next article
Justice Surya Kant Becomes 53rd CJI