
Syllabus: GS3/Environment
Context
- Delhi Chief Minister has said cloud seeding is essential for the national capital as it could play a key role in controlling rising pollution levels during the winter season.
Why is Delhi’s Air Quality Severe in Winter?
- Temperature Inversion: During winter, the air near the ground becomes cooler than the air above it.
- This inversion layer traps pollutants (such as particulate matter and gases) close to the surface, preventing their vertical dispersion into the upper atmosphere.
- Low Wind Speeds: Winds are generally weaker in winter, which reduces horizontal dispersion of pollutants, allowing them to accumulate in the lower atmosphere.
- Crop Residue Burning: Each year, post-harvest stubble burning in neighbouring states like Punjab, Haryana, and western Uttar Pradesh releases large amounts of smoke and particulate matter.
- Prevailing wind patterns carry this pollution towards Delhi, worsening air quality.
- Dust and Urban Pollution Entrapment: Urban dust and vehicular emissions linger longer in the atmosphere due to low boundary layer height in winter, compounding the pollution problem.
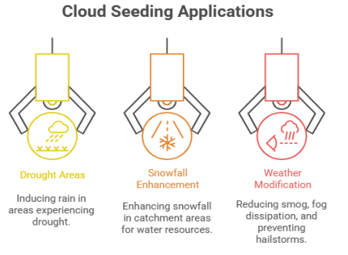
What is Cloud Seeding?
- Cloud seeding is a weather modification method to enhance a cloud’s ability to produce rain or snow.
- History: First demonstrated in 1946 by Vincent J. Schaefer, an American chemist and meteorologist.
- Seeding Agents: Clouds are usually injected with salts like silver iodide, potassium iodide, or sodium chloride to trigger condensation.
- Silver iodide and dry ice (solid CO2) – effective in supercooled clouds (below freezing).
- Calcium chloride – used for warmer clouds (above freezing).
- Working Principle: The salts, or the seeding agents, serve as nuclei around which water droplets can form or ice can crystallise.
- As water droplets grow, they collide with others in the cloud. As they become heavy, the cloud gets saturated and it rains.
- Meteorologists identify clouds for seeding which have sufficient moisture but are unable to produce enough precipitation on their own.
- Methods of Delivery: These particles are dispersed into clouds using special aircraft, rockets, or dispersion devices kept on the ground.
Can Cloud Seeding Help in Combating Air Pollution?
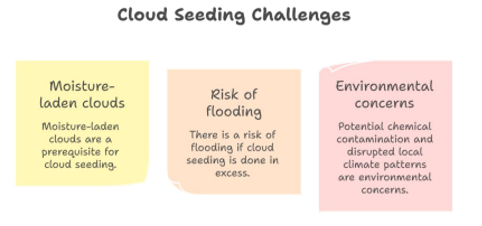
- Dependence on Natural Cloud: Cloud seeding depends on natural clouds; it can’t create them.
- And even when clouds exist, the evidence that seeding reliably increases rainfall remains weak and contested.
- Impact on Pollution: When it rains and reduces pollution, the respite is temporary, the pollution levels go back up within a day or two.
- Efficiency: Fine particulate matter (PM 2.5) and PM10 get washed away with prolonged precipitation.
- However, there is no impact on other pollutants such as ozone and sulphur dioxide.
What can be Other Measures?
- Root Causes Identified by Science: Long-standing scientific consensus attributes hazardous air quality to emissions from vehicles, industries, power plants, construction, waste burning, and agricultural stubble fires.
- Known Long term Solutions: Cleaner transport systems (electric mobility, public transport, emission norms).
- Sustainable energy transition (phasing out coal, promoting renewables).
- Effective waste management and dust control in construction.
- Urban planning that minimizes congestion and reduces pollution sources.
- Focus on Quick Fixes: There is an increasing reliance on temporary measures like smog towers, artificial rain, or short-term bans though they are effective in short terms.
- The Need for Evidence-Based, Ethical Action: Real change demands systemic reforms and long-term enforcement of emission controls.
Source: TH
Previous article
Makhananomics
Next article
News in Short – 25 October, 2025