
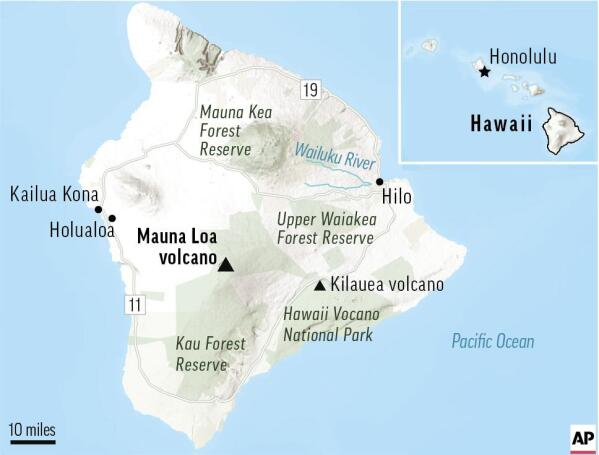
Kilauea Volcano
Syllabus: GS1/Geography
Context
- Hawaii’s Kilauea Volcano, one of the world’s most active, has started erupting again.
About Kilauea
- It is one of six active volcanoes in the Hawaiian Islands. It is a shield volcano and is known for effusive lava flows rather than explosive eruptions.
- It is located within the Hawaii Volcanoes National Park, alongside Mauna Loa (the largest volcano in the world).
- Although smaller than Mauna Loa, Kilauea is more active, erupting frequently since 1983.
What is a Volcano?
- An opening/crack in Earth’s crust through which magma, gases, and ash escape from the interior to the surface.
- Can be classified as:
- Active Volcano: Erupts regularly (e.g., Kilauea, Barren Island).
- Dormant Volcano: Inactive for long but can erupt again (e.g., Vesuvius in Italy).
- Extinct Volcano: No eruption for thousands of years, unlikely to erupt (e.g., Deccan Traps in India).
Volcanoes in India
- Active: Barren Island (Andaman & Nicobar Islands) – India’s only active volcano.
- Dormant: Narcondam Island (Andamans).
- Extinct: Deccan Plateau (remnant of massive volcanic activity ~65 million years ago).
Source: AIR
Shipki-La
Syllabus :GS1/Places
In News
- China has agreed in principle to resume trade through the Shipki-La pass in Himachal Pradesh’s Kinnaur district
Shipki-La pass
- It is situated in Himachal Pradesh’s Kinnaur district and the Sutlej River (known as Langqen Zangbo in Tibet) enters India through this pass.
- It is a historic trade route between India and Tibet, active since at least the 15th century and rooted in deep cultural ties symbolised by a traditional oath of continuity.
- However, trade through the pass ceased due to geopolitical tensions, beginning with the 1962 Sino-India war and later affected by the Doklam standoff and the COVID-19 pandemic.
Source :TH
India Launches Rs. 25,000 Crore Export Promotion Mission
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- The Commerce and Industry Ministry has designed the Export Promotion Mission (EPM) with a total outlay of Rs. 25,000 crore (US$ 2.85 billion) for six years.
Strategic Objectives Export Promotion Mission
- To mitigate risks from tariffs, trade wars, and global demand slowdown.
- To diversify export markets and the export basket, reducing overdependence on a few sectors and destinations.
- To enhance the exportability of Indian products through branding, compliance, and quality upgradation.
- To focus on small exporters, easing their access to finance and markets.
Two pillars of export support
- Niryat Protsahan (Export Encouragement): The overall allocation for this component is expected to be Rs 10,000 crore.
- Components: Interest equalisation support of over Rs. 5,000 crore, Export factoring and export credit insurance, Collateral-free loans and innovative financing tools for small exporters, Six new credit support schemes under consideration.
- Niryat Disha (export Direction): The allocation for this component is Rs 14,500 crore. It includes multiple sub-schemes aimed at addressing quality, logistics, and global integration challenges.
- Export quality compliance: Approx. Rs. 4,000 crore.
- Overseas market development: Approx. Rs. 4,000 crore.
- Branding and international positioning of Indian products.
- Export warehousing and logistics support.
- Capacity building: Integrating MSMEs into global value chains.
Source: FE
Famine in Gaza
Syllabus: GS3/ Sustainable Development Goals
Context
- According to a new Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) analysis, More than half a million people in Gaza are trapped in famine.
What is the Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) ?
- IPC is an independent body funded by Western countries and widely recognised as the main global system for measuring the severity of hunger crises.
- It was set up to sound the alarm so that famine and mass starvation could be prevented and to help organisations respond.
- At the global level, the IPC partnership includes 21 organizations and intergovernmental institutions
- The IPC itself does not formally declare famine. It provides scientific analysis, which is reviewed by a Famine Review Committee (FRC) of independent experts. Governments or UN bodies issue the official declaration.
How famine is determined?
- The IPC system charts acute food insecurity on a five-phase scale. Its most extreme warning is Phase 5, which has two levels, catastrophe and famine.
- If the IPC or one of its partners finds that at least one area is in famine, a famine review committee, led by up to six experts, is activated.
- For an area to be classified as in famine, at least 20% of people must be suffering extreme food shortages, with one in three children acutely malnourished and two people out of every 10,000 dying daily from starvation or malnutrition and disease.
What are the Precedents?
- This is the fifth time in the past 14 years that a famine has been determined by the IPC, and the first time it has confirmed famine outside Africa.
- Somalia (2011): Over 250,000 deaths.
- South Sudan (2017 & 2020): Prolonged civil conflict and displacement.
- Sudan (2024): War-induced collapse of food systems.
- Gaza (2025): First famine outside Africa, amidst conflict and blockade.
Source: IE
NASA’s CHAPEA Project
Syllabus: GS3/Space
Context
- NASA has unveiled the second Crew Health and Performance Exploration Analog (CHAPEA) habitat, designed for a series of analogue missions simulating year-long stays on the surface of Mars.
About
- The mission consists of four crew members living in the CHAPEA habitat, an isolated 1,700 square foot, 3D-printed structure.
- The CHAPEA mission is part of NASA’s ongoing efforts to prepare for future manned missions to Mars.
- Objective: Study physical and psychological effects of long-duration space missions.
- Activities: Scientific tasks, growing vegetables, maintaining habitat, simulated “Marswalks.”
Mars
- Mars is the fourth planet from the sun and has a distinct rusty red appearance and two unusual moons.
- Phobos: ~6000 km above Mars; Deimos: ~20 000 km above Mars.
- Mars also has the largest volcanoes in the solar system, Olympus Mons being one of them.
- Atmosphere: The temperature on Mars ranges between 20 degrees Celsius and -153 degrees Celsius.
- The planet has a rocky surface with canyons, volcanoes, dry lake beds, and craters, all covered in red dust.
- It has about one-third the gravity of Earth and the atmosphere is much thinner than Earth’s, containing more than 95% carbon dioxide and less than 1% oxygen.
- The planet turns on its axis more slowly than Earth, and being farther from the Sun, takes longer to revolve around the Sun.
- A day on Mars is 24.6 hours and a year is 687 Earth days long.
Challenges in Mars Mission
- The biggest challenge is the long duration of a Mars mission because even a one-way trip would take six to nine months.
- Other challenges include logistics for life support, and maintaining supplies and crew health.
- Mars’s thin atmosphere also makes it difficult to slow down a spacecraft for a safe and precise landing.
- Given the distance, communications from and to Earth could have as much as a 20-minute lag, which would be too long in case of real-time help during emergencies.
Source: TH
ISRO holds Air-drop Test for Gaganyaan Mission
Syllabus: GS3/Space
Context
- ISRO has successfully accomplished the first Integrated Air Drop Test (IADT-01) for end to end demonstration of parachute-based deceleration system for Gaganyaan missions.
- The test marks a critical milestone in validating safety mechanisms to ensure the secure return of astronauts to Earth.
Gaganyaan
- Gaganyaan is India’s first human spaceflight mission, undertaken by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO).
- Aim: To demonstrate India’s capability to send humans to space, ensure safe return, and establish long-term capacity for human space exploration.
- Objectives:
- Human Spaceflight: Send a crew of 2–3 astronauts to low-earth orbit (LEO) at an altitude of ~400 km.
- Mission Duration: Around 3 days in orbit before safe return to Earth.
- India plans its first crewed Gaganyaan flight in 2027, followed by Chandrayaan-4 in 2028, a Venus mission, and the proposed Bharat Antariksh Station by 2035.
Source: AIR
Indigenous Integrated Air Defence Weapon System (IADWD)
Syllabus: GS3/ Defence
Context
- India has successfully conducted the maiden flight-tests of the Integrated Air Defence Weapon System (IADWS) off the coast of Odisha.
What is the IADWS?
- The Integrated Air Defence Weapon System (IADWS) is a multi-layered air defence system developed indigenously. It integrates three advanced components:
- Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile (QRSAM)
- Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS)
- Laser-based Directed Energy Weapon (DEW)
- It is operated and coordinated through a Centralised Command and Control Centre, developed by the Defence Research and Development Laboratory (DRDL), Hyderabad.
Defence Layers
- Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile (QRSAM): Range: 25–30 km.
- Role: Engages fast-moving, high-altitude threats like fighter jets, helicopters, and cruise missiles at the outermost defence layer.
- Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS): Developed by Research Centre Imarat (RCI), Hyderabad.
- A fourth-generation MANPAD for Army, Navy, and Air Force use.
- Neutralises targets such as drones and helicopters in the 300 m–6 km range.
- Portable, miniaturised, and capable of engaging low-altitude threats.
- Directed Energy Weapon (DEW): Developed by Centre for High Energy Systems and Sciences (CHESS), Hyderabad.
- Vehicle-mounted Laser DEW MK-II(A) demonstrated earlier this year, defeating UAVs and swarm drones.
- Range: less than 3 km.
- Places India among the few nations with operational directed energy weapon technology.
Strategic Significance
- IADWS strengthens India’s multi-layered air defence capability, covering aerial threats within a 30 km radius — from high-speed jets to slow-moving drones. Key points of significance include:
- Indigenous technology: All components, including command and control, are fully homegrown.
- Seamless integration: Missiles and directed energy weapons operate in coordination.
- Reduced foreign dependence: Enhances self-reliance in advanced defence systems.
- Future scope: The successful test is seen as a step towards Mission Sudarshan Chakra, announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, aimed at developing a comprehensive national air defence shield.
Previous article
Cost of Dealing with Invasive Species