
Syllabus: GS3/Environment & Biodiversity
Context
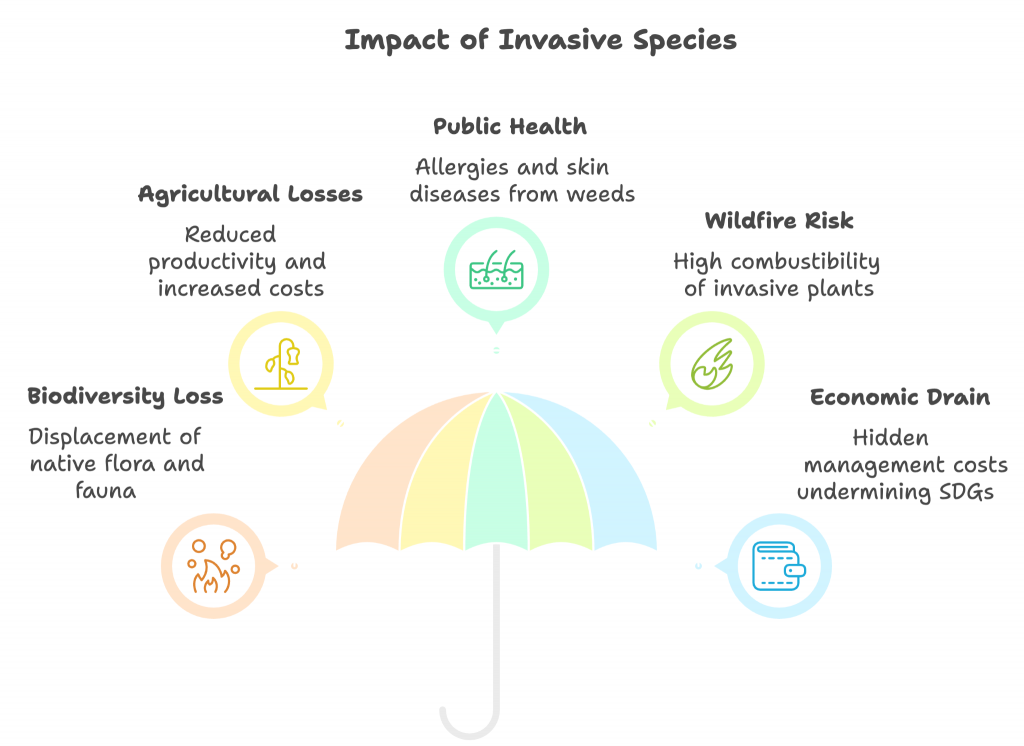
- According to a recent study published in Nature Ecology & Evolution, invasive non-native plants and animals have inflicted more than $2.2 trillion in damages worldwide since 1960, and found that the true costs may be 16 times higher than previously estimated.
Invasive Alien Species (IAS)
- Invasive Species are non-native flora and fauna that disrupt local ecosystems, including the environment, economy, or human health.
- Globally, plants were the most damaging invasive group, causing $926.38 billion in costs, followed by:
- Arthropods: $830.29 billion
- Mammals: $263.35 billion
- Researchers emphasize that trade and travel are the main vectors for their spread.
Common invasive species in India
- Among the most costly to manage are Japanese knotweed (Reynoutria japonica) and common lantana (Lantana camara).
- In India, the MoEFCC recognizes over 154 invasive faunal species, spanning terrestrial, freshwater, and marine ecosystems.
- Invasive plants like Lantana camara and Senna spectabilis have colonized vast swathes of the Western Ghats, including critical tiger and elephant habitats.
- Lantana alone has invaded over 40% of India’s tiger habitats, threatening prey availability and altering forest dynamics.
Why the Underreporting?
- Study points to several systemic issues:
- Lack of centralized data systems;
- Limited inter-agency coordination;
- Language barriers in global databases;
- Competing conservation priorities.
Global Policy Responses
- Several international agreements aim to curb biological invasions:
- Ballast Water Management Convention: Prevents aquatic species spread via ships.
- Convention on Biological Diversity: Obligates countries to prevent, control, or eradicate alien species threatening ecosystems.
- These frameworks highlight a growing recognition of invasive species as a global ecological and economic threat.
India’s Efforts to Curb Biological Invasions
- National Biodiversity Strategy and Action Plan (NBSAP): It aligns with the Kunming-Montreal Global Biodiversity Framework and includes invasive species management as a key priority. It adopts a ‘Whole-of-Government and Whole-of-Society’ approach, involving multiple union ministries and stakeholders. It emphasizes:
- Restoration of degraded ecosystems;
- Protection of terrestrial and marine areas;
- Pollution control and invasive species mitigation;
- Community participation in biodiversity governance.
- Scientific Research and Documentation: The Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) published a comprehensive Handbook on Invasive Species.
What Needs to Change?
- To address this growing threat, India needs to:
- Develop a national database for invasive species costs and management;
- Invest in early detection and rapid response systems;
- Promote interdisciplinary research and community engagement;
- Integrate invasive species control into climate and biodiversity policies.
Previous article
No Riverbed Mining Nod Without Sand Replenishment Study: SC
Next article
News In Short 25-August-2025