Syllabus: GS3/Sustainable Development
Context
- India has, for the first time, secured a position among the top 100 countries in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Index.
About
- The Sustainable Development Report (SDR) reviews progress made each year on the Sustainable Development Goals since their adoption by the 193 UN Member States in 2015.
- This edition also includes for the first time an assessment of which countries have made the most progress on the SDGs using a headline SDG Index (SDGi).
Major Highlights
- Global Commitment through Voluntary National Reviews (VNRs): 190 out of 193 UN member states have participated in the VNR process since the adoption of Agenda 2030.
- Regional Trends in SDG Progress: East and South Asia is the fastest progressing region since 2015.
- Drivers of progress: Rapid improvements in socioeconomic indicators.
- Top Performers in SDG Index: Finland, Sweden and Denmark hold the top three positions.
- 19 out of the top 20 performers are European countries.
- Challenges remain even for top countries — particularly in climate action and biodiversity goals.
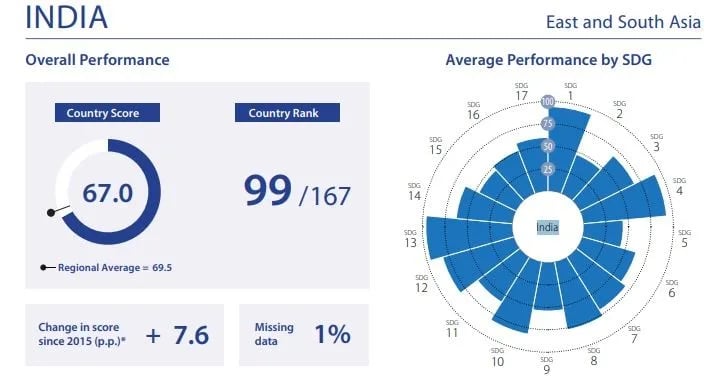
- India ranked 99th out of 167 nations.
- It places India with a score of 67 on the SDG Index, a significant improvement from its 109th rank in 2024.
- Since the adoption of the SDGs, India has steadily improved its standing: it ranked 112th in 2023, 121st in 2022, and 120th in 2021.
- Among India’s neighbours, China ranks 49th (74.4), Bhutan ranks 74th (70.5), Nepal 85th (68.6), Bangladesh 114th (63.9), and Pakistan 140th (57).
- Maritime neighbours Maldives and Sri Lanka stand at 53rd and 93rd places respectively.
- Global SDG Progress Remains Off-Track: None of the 17 SDGs are currently on track to be achieved globally by 2030.
- Only 17% of SDG targets are on track worldwide.
- Major obstacles: Conflicts, structural vulnerabilities, limited fiscal space.
- Notable progress seen in: SDG 3 (Health): Under-5 and neonatal mortality.
- SDG 7: Access to electricity.
- SDG 9: Mobile broadband use and internet access.
- It identified five areas of significant regression since 2015: obesity rates (SDG 2), press freedom (SDG 16), sustainable nitrogen management (SDG 2), the Red List Index measuring biodiversity loss (SDG 15), and the Corruption Perceptions Index (SDG 16).
- UN-Based Multilateralism Index (UN-Mi): Barbados ranks 1st – most committed to UN-based multilateralism.
- The United States ranks last, following the withdrawal from Paris Climate Agreement (2025), Exit from World Health Organization (WHO) and Formal opposition to SDGs and Agenda 2030.
- Fiscal Constraints in Developing Countries: Around 50% of the global population lives in countries lacking fiscal capacity to invest in sustainable development.
- Global public goods (like climate protection, global health, peace) remain underfunded.
Recommendations
- Need for Reform in Global Financial Architecture (GFA) as the current GFA favors wealthy nations with easier capital access.
- Proposes practical reforms to boost and align global financing toward SDGs and public goods.
| Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) – Adoption: The United Nations General Assembly, during its 70th Session in 2015, adopted the document titled “Transforming our World: The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.” 1. This document outlines 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and 169 associated targets. – The SDGs, also known as the Global Goals, came into force with effect from 1st January 2016. – Aim: The SDGs serve as a comprehensive blueprint aimed at achieving a better and more sustainable future for all. – The goals call for action on addressing global challenges such as poverty, inequality, climate change, environmental degradation, peace and justice. – Applicability: The SDGs are universal, applying to all nations—developed, developing and least developed countries. 1. Countries are primarily responsible for following up and reviewing the progress made in implementing the goals and targets at the national level until 2030. – Legality: The SDGs are not legally binding, but they have effectively become international obligations and have the potential to reorient domestic spending priorities in countries. 1. Countries are expected to take ownership and develop a national framework to monitor these goals. |
Source: TH
Previous article
RBI and Banks to Launch Digital Payment Intelligence Platform (DPIP)
Next article
Climate Finance