The Tea Horse Road
Syllabus: GS1/History
In News
- China’s Ambassador to India, Xu Feihong, recently highlighted the historical significance of the Tea Horse Road, emphasizing its role in facilitating India-China trade through Tibet.
What is Tea Horse Road?
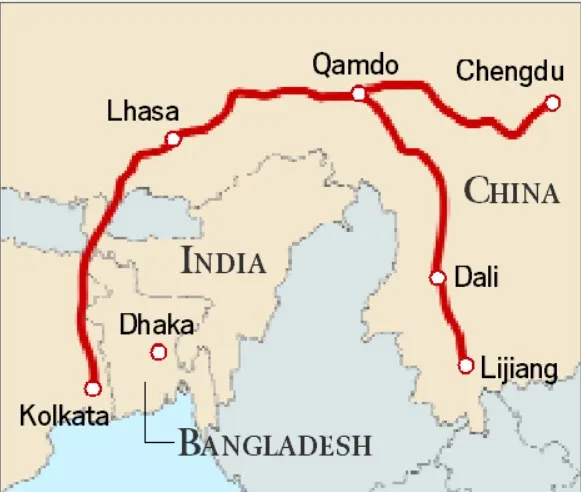
- The Tea Horse Road was an ancient trade route connecting China, Tibet, and India. It was primarily used for trading tea from China in exchange for horses from Tibet, forming an essential commercial network in the region.
- It had two main pathways passing through cities like Dali and Lijiang in Yunnan province. The routes reached Lhasa in Tibet before branching into India, Nepal, and Bangladesh.
- It originated during the Tang dynasty (618-907 CE) in China.
- Buddhist monk Yijing (635-713 CE) described goods like sugar, textiles, and rice noodles being transported from southwestern China to Tibet and India, while horses, leather, Tibetan gold, saffron, and medicinal herbs were sent to China.
Significance of the Tea Horse Road
- Strengthened India-China trade ties through Tibet.
- Facilitated cultural exchange, influencing cuisine, textiles, and Buddhism.
- Boosted economic interdependence by linking China’s tea-producing regions with India’s trading hubs.
Source: IE
Pagri Sambhal Jatta Movement
Syllabus: GS 1/History
In News
- Farmers protesting at the Punjab and Haryana borders observed February 23 as Pagri Sambhal Diwas, in honour of Ajit Singh.
Pagri Sambhal Jatta Movement
- “Pagri Sambhal Jatta” means “take care of your turban, o farmer,” symbolizing self-respect and honor.
- It was launched by Ajit Singh in 1907 to protest against three oppressive British agricultural laws.
- The movement opposed the following British laws
- Punjab Land Alienation Act, 1900 restricted farmers’ rights to sell or mortgage land.
- Punjab Land Colonisation Act, 1906 gave British control over land in the Chenab Colony.
- Doab Bari Act, 1907 reduced farmers to contract workers.
- Farmers were also burdened by higher taxes on land and irrigation.
Impact of the Movement:
- The movement was one of the first major farmer protests against British rule.
- It led to mass protests, civil disobedience, and public pressure.
- The British government repealed some oppressive clauses due to the protests.
- It inspired future movements like the Ghadar Movement and Bhagat Singh’s activities.
| Ajit Singh – Born on February 23, 1881, in Khatkar Kalan village, Punjab. He was a prominent freedom fighter, revolutionary, and nationalist leader. – He worked with other revolutionaries in Europe, including Lala Hardayal and Madame Cama. – He played a key role in inspiring his nephew, Bhagat Singh. – He exiled from 1909 to 1947 due to his opposition to British colonial rule. – He died on August 15, 1947, the day India gained independence. |
Source: IE
Advocate-on-Record
Syllabus :GS 2/Governance
In News
- The Supreme Court questioned how Advocates-on-Record (AoRs) can authorize non-AoRs to appear in cases on their behalf.
Advocate-on-Record
- An Advocate on Record (AOR) is an advocate authorised under the Supreme Court Rules to act, plead, and file cases directly on behalf of a client in the Supreme Court.
- It was introduced by the Supreme Court under Article 145(1) of the Indian Constitution, which grants the Court the power to regulate its practices and procedures.
- The Supreme Court Rules, 2013 lays down the requirements to be fulfilled to become an advocate on record.
Source :Livelaw
National Commission for Indian System of Medicine (NCISM)
Syllabus: GS2/ Health
Context
- The National Commission for Indian System of Medicine (NCISM) has issued a stern warning to Ayurveda, Siddha, and Unani medical colleges across the country.
About
- The National Commission For Indian System Of Medicine is the statutory body constituted under NCISM Act, 2020.
- This commission is working under the Ministry of Ayush and governs the Board of Ayurveda and Unani and the Board of Unani, Siddha and Sowarigpa.
- Objectives:
- To ensure availability of adequate and high-quality medical professionals of Indian System of Medicine (ISM);
- Adoption of the latest medical research by medical professionals of Indian System of Medicine; and
- Periodic assessment of ISM medical institutions.
Source: FPJ
Previous article
Supreme Court Emphasized Segregation of Waste at Source
Next article
Delimitation Debate: Why Are Southern States Wary?