Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
In News/Context
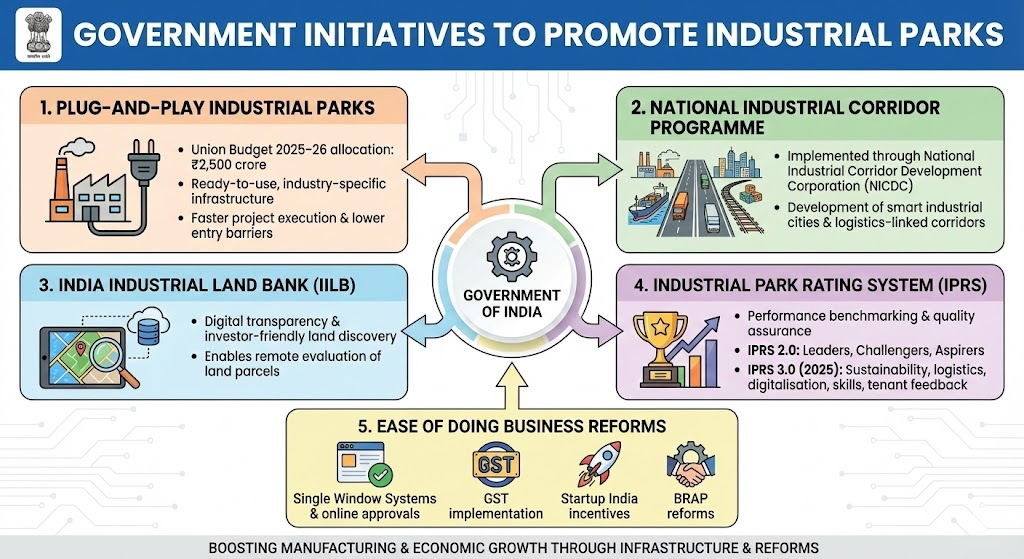
- Industrial parks have emerged as a core instrument of India’s industrial and innovation strategy, enabling faster manufacturing growth, higher investment, job creation and sustainable development.
What is an Industrial Park?
- An industrial park is a planned and demarcated area developed specifically for industrial use, with common facilities like power, water, internal roads, waste management, testing labs, logistics services and security.
- These parks are usually managed by a dedicated authority or developer responsible for allotment of plots, maintenance of infrastructure, regulatory compliances and long‑term development of the industrial ecosystem.
Status of Industrial Parks in India
- The IILB, a GIS‑enabled platform developed by DPIIT, has mapped around 4,500+ industrial parks across India, covering several lakh hectares, with substantial land still vacant for new investments.
- Under Industrial Park Rating System (IPRS) 3.0, parks are classified as “Leaders”, “Challengers” and “Aspirers” based on infrastructure quality, connectivity, services and industrial activity, giving a national snapshot of park performance.
Significance of Industrial Parks
- They reduce entry barriers and transaction costs by providing ready‑to‑use land, common infrastructure and streamlined clearances, thereby improving ease of doing business and attracting both domestic and foreign investors.
- Parks create clusters that promote economies of scale, supply‑chain integration, innovation spillovers and MSME participation, strengthening India’s manufacturing base and export potential.
- With growing emphasis on green infrastructure and resource efficiency, industrial parks are also becoming instruments for environmentally responsible industrialisation and inclusive, job‑rich growth.
Key Challenges
- Uneven quality across parks: Many parks suffer from poor last‑mile connectivity, unreliable utilities, and inadequate social infrastructure compared to “Leader” parks under IPRS 3.0.
- Land and governance issues: Delays in land acquisition, fragmented ownership, weak park‑level management and coordination with urban/local bodies constrain optimal utilisation of existing parks.
- Environmental and social concerns: Non‑compliance with pollution norms, inadequate common effluent treatment, and limited worker housing, safety and gender‑sensitive facilities can trigger local resistance.
Way Ahead
- Upgrade lagging parks by using IPRS 3.0 ratings to prioritise investments in connectivity, utilities, digital systems and green infrastructure, especially in “Challenger” and “Aspirer” parks.
- Deepen integration with skill ecosystems, R&D institutions and startup clusters so that industrial parks become hubs of innovation, not just land banks for factories.
- Strengthen governance through professional park management authorities, transparent user‑charge frameworks, and stronger environmental and social safeguards to ensure sustainable, inclusive industrialisation.
Source: PIB
Previous article
News In Short 23-12-2025