Syllabus: GS2/Health
Context
- The Meghalaya government is pushing for a TB-free State by re-skilling TB survivors and bringing them back into control programmes as ‘TB champions’.
TB Champions
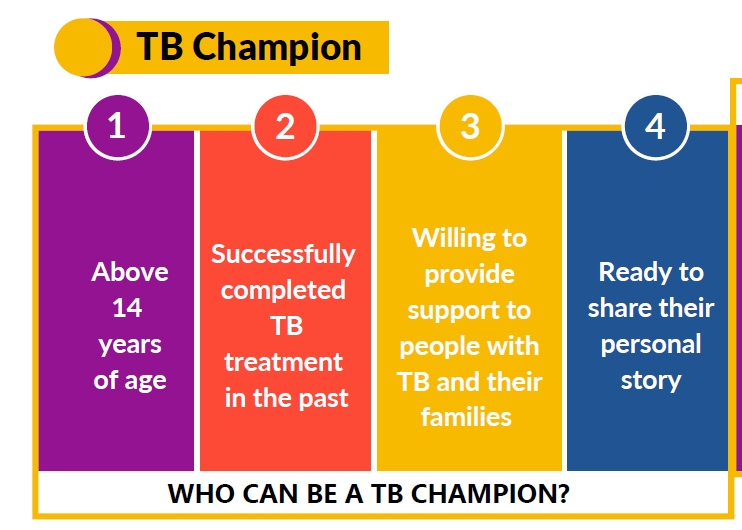
- A TB Champion is a person who has been affected by TB and successfully completed the treatment.
- As survivors, they can provide valuable support to those with TB and their families.
- NTEP has designed a standard sensitization and training curriculum for empowering TB survivors as TB Champions.
- TB survivors themselves can access the self-learning modules available online.
- Districts can coordinate with NTEP partners or local NGOs to conduct the training.
What is Tuberculosis?
- Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease that most often affects the lungs and is caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- It spreads through the air when infected people cough, sneeze or spit.
- Symptoms: prolonged cough (sometimes with blood), chest pain, weakness, fatigue, weight loss, fever, night sweats.
- While TB usually affects the lungs, it also affects the kidneys, brain, spine and skin.
- Treatment: It is preventable and curable with antibiotics.
- TB Vaccine: The Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine remains the only licensed vaccine against TB; it provides moderate protection against severe forms of TB (TB meningitis) in infants and young children.
TB in India
- TB as a global health challenge: India has the highest TB burden in the world, contributing to 26% of the global burden and 29% of global TB-related deaths.
- India is followed by Indonesia (10%), China (6.8%), the Philippines (6.8%), and Pakistan (6.3%).
- Multidrug-Resistant TB: India represents 27% of the world’s multi-drug-resistant TB cases, underscoring the need for specialized treatment approaches.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has recognised India’s progress, with a 17.7% decline in TB incidence from 2015 to 2023, a rate more than double the global decline of 8.3%.
- India’s goal is to eliminate tuberculosis (TB) by 2025, five years ahead of the global target of 2030.
Challenges Faced by India in Eliminating TB
- Drug-resistant TB cases: India has a significant burden of drug-resistant TB, including multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB).
- This type of TB is much harder to treat and requires more expensive, specialised drugs and a longer duration of treatment.
- Diagnostics and Case Detection: The accurate and timely diagnosis of TB remains a challenge.
- Some areas lack access to modern diagnostic tools, leading to reliance on older methods with limitations.
- Poor primary health-care and infrastructure: In many parts of India, especially in rural and remote areas, there is limited access to healthcare facilities.
- This can result in delayed diagnosis and treatment, allowing TB to spread within communities.
- Stigma and Awareness: Stigma associated with TB lead to delays in seeking healthcare, and lack of awareness about the disease contribute to its persistence.
- Private Sector Engagement: A significant portion of healthcare services in India is provided by the private sector.
- Coordinating efforts between the public and private sectors and ensuring standardized treatment protocols are crucial for effective TB control.
- Treatment Adherence: TB treatment requires a prolonged course of antibiotics, and ensuring patient adherence to the full course is challenging.
- Vulnerable Populations: Certain populations, such as migrant workers, urban slum dwellers, and those living in crowded conditions, are at higher risk of TB.
Steps Taken by Government of India to Eliminate TB
- Revised National Tuberculosis Control Program (RNTCP): The RNTCP, launched in 1997, was the flagship program to control TB in India.
- The program has been continuously revised and strengthened over the years.
- National Tuberculosis Elimination Program (NTEP): The Government of India has developed a National Strategic Plan (2017-25) for Ending TB in the country by 2025.
- Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (PMTBMBA): Launched in 2022 for community support to TB patients with the objective to provide nutritional, diagnostic and vocational support.
- Universal Drug Susceptibility Testing (DST): The government has scaled up efforts to provide universal access to drug susceptibility testing, helping to identify drug-resistant strains of TB early and tailor treatment accordingly.
- Earlier, the patients were started on first line treatment and were tested for drug resistance only if the therapy did not work.
- Ni-kshay portal: An online Ni-kshay portal has been set up to track the notified TB cases.
- New Drugs: Newer drugs such as Bedaquiline and Delamanid for the treatment of drug-resistant TB have been included in the government’s basket of drugs provided free TB patients.
- R&D for Treatment: Researchers have been studying shorter three- and four-month courses of anti-tubercular drugs, instead of the existing six-month therapy.
- Vaccine Development: Trials are underway to test the effectiveness of a vaccine called Immuvac, which was initially developed to prevent leprosy, in preventing TB.
- Researchers are also testing VPM1002, which is a recombinant form of the BCG vaccine modified to express the TB antigens better.
| World Tuberculosis Day 2025 – Commemorates: Dr. Robert Koch’s discovery of Mycobacterium tuberculosis on 24th March 1882. – Objective: Raise awareness about the health, social, and economic impact of TB globally. – 2025 Theme: “Yes! We Can End TB: Commit, Invest, Deliver.” – Focuses on renewed global commitment, financing, and action-oriented delivery to end TB by 2030 (as per SDG targets). |
Source: TH
Previous article
Seabed Warfare in a New Era of Geotech Conflicts
Next article
Under-funding of Nutrient Subsidy Schemes