Syllabus: GS1/ Geography
Context
- Recently, a cloudburst event in the Ramban tehsil of Jammu and Kashmir led to torrential rains, hailstorms, and winds, causing widespread destruction.
About
- A cloudburst is a localized event with intense rainfall activity. The phenomenon is most common in hilly regions, however it can occur in plains also.
- The rainfall of 10 cm or more in an hour over a roughly 10 km x 10 km area is classified as a cloudburst event.
- Also 5 cm of rainfall in a half-hour period over the same area would also be categorized as a cloudburst.
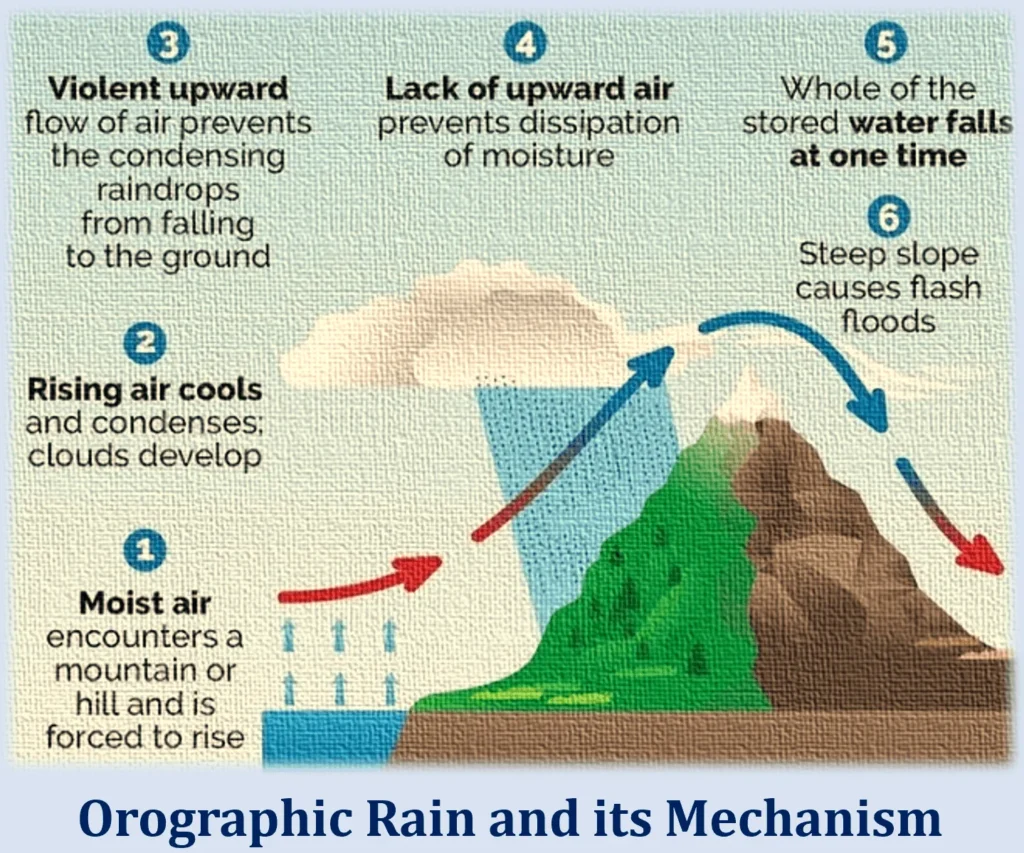
Mechanism of Cloudbursts
- Cloudbursts are more common in hilly areas because of a phenomenon called ‘orographic lift’. When moist, warm air masses approach a mountain range, they are forced to ascend along the slope.
- As the air rises, it encounters lower atmospheric pressure, causing it to expand and cool.
- The cooling leads to condensation of water vapor, forming dense clouds and typically causing rainfall.
Impact of Cloudbursts
- Flash Flood: A flash flood happens quickly, when a lot of rain suddenly enters into the drainage systems (waterbodies, drains), and water overflows.
- Flash floods are more common in hills, because rocky terrain does not absorb water very well.
- Example: The 2013 Kedarnath Disaster involved a cloudburst followed by massive flash floods.
- Landslide: Landslides are a geological phenomenon that involves the sudden and rapid movement of a mass of rock, soil, or debris down a slope under the influence of gravity.
- Loss of Life and Livelihood: Sudden nature of cloudbursts leaves little time for evacuation. Destruction of homes, agricultural fields, and livestock affects livelihoods, especially in rural and tribal communities.
- Damage to Infrastructure: Roads, bridges, power lines, and communication networks are often washed away.
- Social Impact: Frequent disasters create trauma, displacement, and migration pressures. Affects education, healthcare, and access to essential services in remote regions.
Measures taken in India
- The Disaster Management Act, of 2005 provides a comprehensive legal and institutional framework for the management of various disasters in India.
- The National Institute of Disaster Management (NIDM) has been providing capacity building and other support to various national and state-level disaster management authorities.
- Early Warning system:
- India Meteorological Department (IMD), implements the Ensemble Prediction System (EPS), which uses multiple models to improve the accuracy of rainfall predictions.
- Doppler Weather Radars (DWRs): Installed in hilly and vulnerable regions to detect intense rainfall events in real-time.
- Flash Flood Guidance System (FFGS): Developed with WMO support to provide early warning for flash floods across South Asia, including India.
- Mobile-based Alert Systems: IMD and NDMA use SMS and app-based alerts to inform people in real-time.
Way Ahead
- To effectively mitigate the impact of cloudbursts, India must adopt a comprehensive and proactive approach that combines scientific forecasting, infrastructural resilience, and community-based preparedness.
- Land use planning and zoning regulations must be strictly enforced to prevent construction in high-risk zones.
- Urban and rural infrastructure should be designed to handle sudden surges in water flow, with emphasis on stormwater drainage systems, slope stabilization, and rainwater harvesting.
- Also there is a need to integrate climate change adaptation into disaster management planning as intensity of such extreme weather events has increased.
Source: IE
Previous article
News In Short-19-04-2025