Syllabus: GS1/ Geography
Context
- Recently, a climate study found that if the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) collapses, Europe could face a dramatic and prolonged winter freeze, even in a world warmed by greenhouse gas emissions.
About Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)
- It is one of the most powerful and complex systems driving Earth’s climate.
- It is often likened to a giant conveyor belt that transports warm surface waters from the tropics northward and returns cold, dense water southward at depth.
- It regulates temperatures across the Atlantic basin and plays a vital role in global climate stability, sea-level patterns, and marine ecosystems.
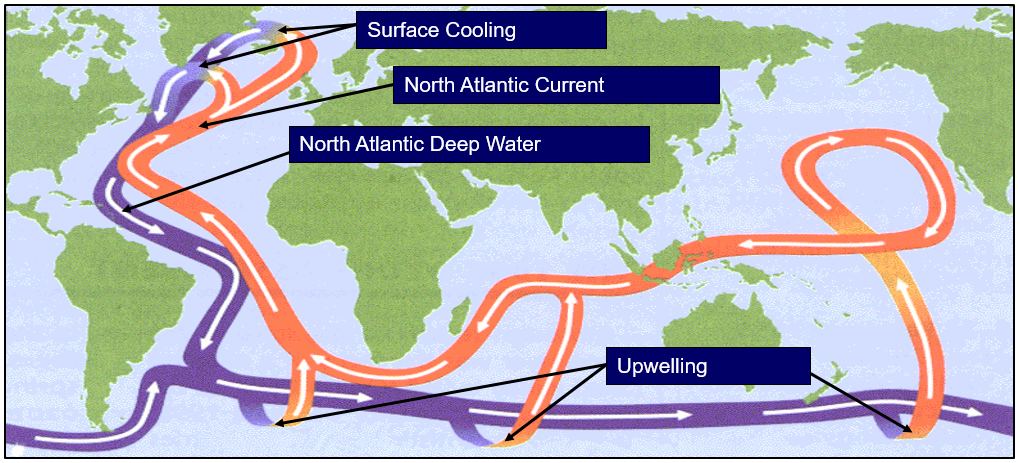
Working of AMOC
- The AMOC is a key component of the global thermohaline circulation.
- Warm, salty water flows northward via currents like the Gulf Stream. As it reaches higher latitudes, it cools and becomes denser, sinking into the deep ocean and flowing back south.
- It helps distribute heat and nutrients across the globe, influencing weather patterns from the Amazon to the Arctic.
Slowing of AMOC and the Tipping Point
- Recent studies suggest that the AMOC has weakened significantly since the mid-20th century, and is expected to slow by 18–43% by 2100.
- It is primarily driven by climate change, particularly the influx of freshwater from melting Greenland ice, which disrupts the salinity and density gradients that power the current.
- AMOC may be approaching a tipping point, beyond which its collapse could trigger abrupt and irreversible climate shifts.
- AMOC has two potential tipping points — one linked to salt transport feedback and another to deep ocean convection.
| Climate Tipping Points – These are critical thresholds in Earth’s systems—once crossed, they can trigger self-reinforcing feedback loops that lead to abrupt, irreversible, and potentially catastrophic changes. – They occur when a small change in temperature or pressure pushes a system — like an ice sheet, rainforest, or ocean current — into a radically different state. Key Tipping Elements at Risk – Recent assessments have identified at least 16 major Earth system components that are vulnerable to tipping, including: 1. Greenland and West Antarctic Ice Sheets; 2. Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC); 3. Amazon Rainforest Dieback; 4. Arctic Permafrost Thaw;Coral Reef Collapse; |
Potential Consequences
- Europe may face colder winters despite global warming, as warm currents fail to reach its shores.
- West Africa could see disrupted monsoon patterns, affecting agriculture and water security.
- Eastern North America might experience accelerated sea-level rise.
- The Amazon and South Asia could suffer from altered rainfall patterns, increasing drought risk.
| Ocean Currents – Horizontal and vertical components of the circulation system of ocean waters. Types – Surface Currents: Surface Circulation – Deep Water Currents: Thermohaline Circulation Forces – Primary: Solar Heating, Winds, Gravity, Coriolis force – Secondary: Temperature, Salinity & Density Difference |
Previous article
Magna Carta
Next article
Increase in Oil Prices Amidst Iran-Israel Tensions