Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context
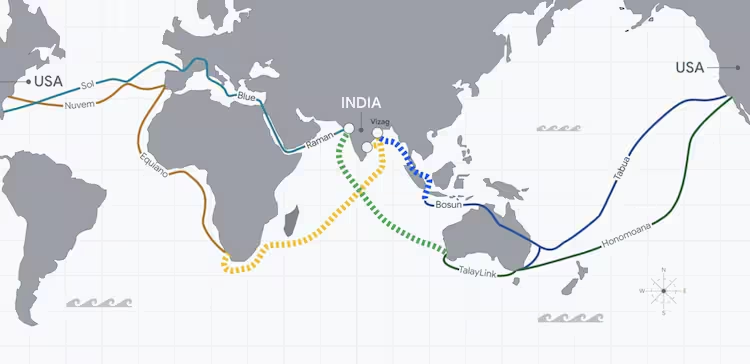
- At India AI Impact Summit, Google has announced that it will connect India with the US through new subsea cables as part of a 15 billion dollar investment spread over five years.
About
- Google announced the collaborative infrastructure initiative named America-India Connect.
- A new international subsea gateway will be established in Vizag.
- It will house a gigawatt-scale compute facility and an international subsea cable gateway.
- Three new subsea paths connecting India to Singapore, South Africa, and Australia.
- Four strategic fibre-optic routes will also be established that will link the India, U.S. and Southern Hemisphere.
- Google pledged $30 million to improve public services with AI and another $30 million for scientific research.
- Google DeepMind is also launching a new partnership with the Indian government to deploy its frontier AI for Science models locally.
- Google also unveiled major skilling programs in India including:
- the Google AI Professional Certificate for students and early-career professionals,
- partnerships with Karma Yogi Bharat to train 20 million public servants,
- and generative AI support for over 10,000 Atal Tinkering Labs reaching 11 million students.
Significance
- The new infrastructure is expected to support rising demand for cloud computing and AI services in India, while also strengthening connections with Africa, Australia and parts of Southeast Asia.
- More subsea capacity typically means cheaper, faster internet which feeds into productivity and economic growth at scale.
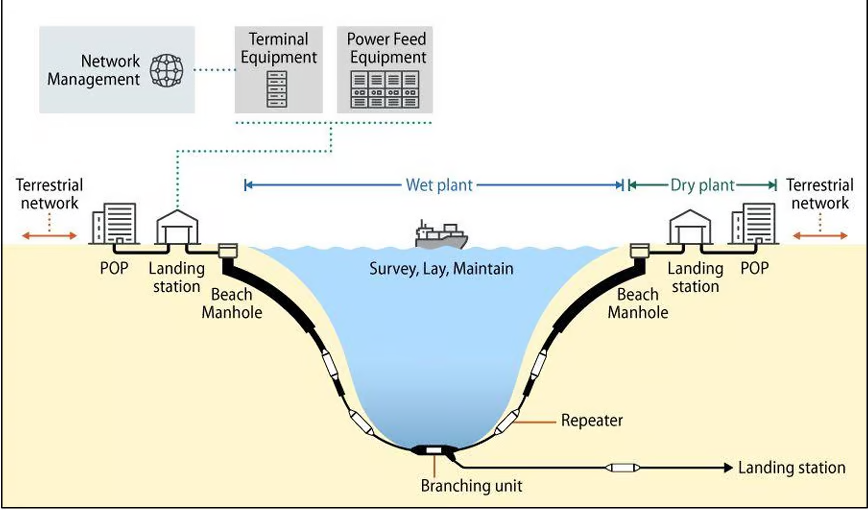
What Are Undersea Cables?
- Undersea cables connect global internet networks, providing vast data transfer capacity via fiber optic strands.
- These cables land at designated points and are linked to terrestrial networks.
- They connect internet service providers and telecom operators everywhere with those in other countries.
- These cables are a few inches thick and are heavily padded to withstand the hostile environment of the sea floor.
- Importance of Undersea Cables: About 90% of global data, 80% of world trade, and key financial and government transactions rely on undersea cables.
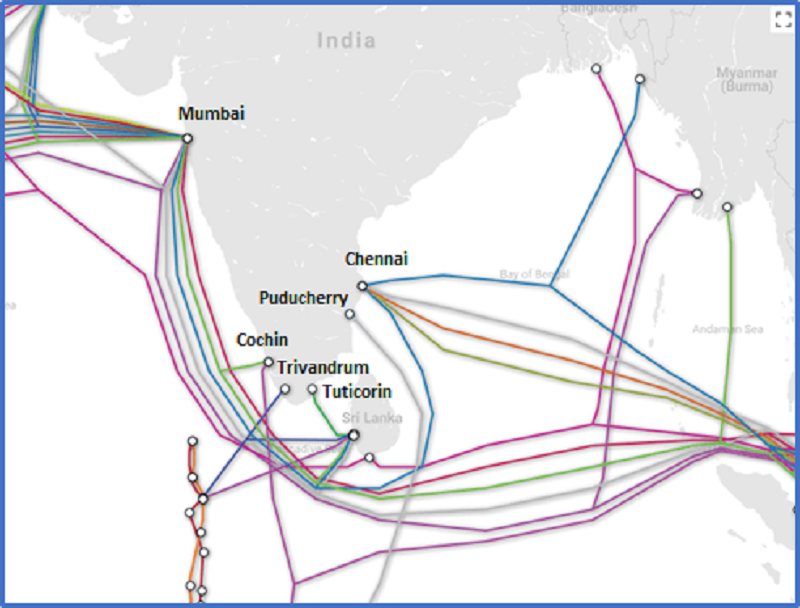
India’s Cable Infrastructure
- India has two main cable hubs, Mumbai and Chennai, with 17 cable systems landing there.
- India also has two domestic cable systems — the Chennai Andaman and Nicobar Islands (CANI) cable to provide high-speed connectivity to the islands, and the Kochi Lakshadweep Islands project.
International Advisory Body for Submarine Cable Resilience
- The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) and the International Cable Protection Committee (ICPC) jointly launched the International Advisory Body for Submarine Cable Resilience in 2024.
- This initiative aims to strengthen the resilience of submarine cables.
- The Advisory Body provides strategic guidance to address challenges related to increasing traffic, aging infrastructure, and growing environmental threats to submarine cables.
International Cable Protection Committee (ICPC)
- ICPC, founded in 1958, is a global forum for governments and commercial entities involved in the submarine cable industry.
- Its primary mission is to enhance the security of undersea cables by providing a platform for exchanging technical, legal, and environmental information.
Source: AIR
Previous article
News In Short 19-02-2026