Bagurumba Dance
Syllabus: GS1/Culture
Context
- The Prime Minister visited Assam and attended the Bagurumba Dwhou 2026.
About
- Bagurumba, often referred to as the “butterfly dance”, is one of the most significant and graceful folk dances of Assam.
- It is a mass folk dance of the Bodo community.
- It was traditionally performed by young women, the dance symbolises harmony with nature, celebrating themes of fertility, peace and joy.
- The fluid hand movements and gentle footwork mirror the flight of butterflies, reflecting the community’s close bond with the natural world.
- The dance is closely associated with the Bwisagu festival, which marks the Bodo New Year and the advent of spring.
- Its music, led by the bamboo flute-like Sifung, the rhythmic Kham drum and the resonant Serja, adds depth and emotion to the performance.
Source: TH
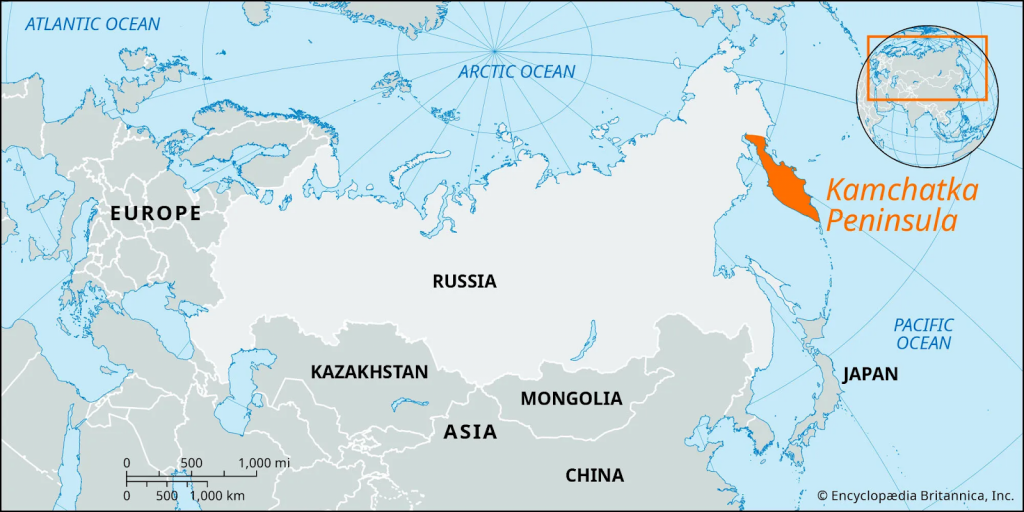
Kamchatka Peninsula
Syllabus: GS1/ Physical Geography
In News
- A severe winter storm has brought life to a standstill across the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia’s Far East, with heavy snowfall burying streets and homes.
About
- Kamchatka forms part of Russia’s Far Eastern Federal District and constitutes Kamchatka Krai, with a sparse population of about 322,000.
- It is 1,250-km-long peninsula located between the Sea of Okhotsk (west), Pacific Ocean, and Bering Sea (east), featuring the Sredinny (Central) and Vostochny (Eastern) Ranges with 29 active volcanoes in the UNESCO-listed Volcanoes of Kamchatka.
- The Kamchatka River flows through a central valley.
Source: TH
Responsible Nations Index (RNI)
Syllabus: GS2/ Governance
In News
- India has recently introduced the Responsible Nations Index (RNI)
About
- The Responsible Nations Index (RNI) is a global benchmarking framework that shifts the focus from mere economic power to ethical governance, sustainability, and global responsibility in assessing national performance.
- The index evaluates countries across four core dimensions ethical governance, social well-being, environmental stewardship & global responsibility
- It is developed by World Intellectual Foundation (WIF) in collaboration with Jawaharlal Nehru University (JNU) & Indian Institute of Management Mumbai.
- Singapore, Switzerland & Denmark topped the list & India ranks 16th globally.
Source: PIB
Social Commerce
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- In India, despite strong potential, social commerce contributes only 1–2% of total e-commerce revenue, compared to 30–40% in China and 20–25% in Indonesia.
What is Social Commerce?
- Social commerce refers to the buying and selling of goods directly through social media platforms.
- Consumers discover products while browsing social media and complete the purchase without shifting to traditional e-commerce platforms.
- It combines social interaction (influencers, live videos, community groups) with online shopping.
- Influencer-led selling: Products are promoted by creators whom consumers trust.
- Live-stream shopping: Sellers demonstrate products in real time and interact with buyers.
- Community-based selling: Products are sold through WhatsApp groups, Facebook pages, or regional social networks.
Difference Between E-commerce and Social Commerce
- Traditional e-commerce is search-driven and platform-centric, whereas social commerce is discovery-driven and trust-centric.
- E-commerce involves planned purchases, whereas social commerce encourages impulse buying.
Key Challenges Hindering Growth in India
- Weak authenticity checks in India’s influencer ecosystem, unlike China’s strict credibility norms, undermine consumer trust.
- High dependence on cash on delivery strains platform finances.
- Weak logistics and digital infrastructure restrict scale and speed.
- Fragmented retail market and low order values reduce profitability.
Source: LM
India’s First Open-Sea Marine Fish Farming Project
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy/ Environment
Context
- India’s first open-sea marine fish farming project was launched at North Bay in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
About
- Objective: The primary goal is to transition towards a commercially viable model for open-sea farming, reduce pressure on traditional coastal fishing, and generate sustainable livelihoods for local fishing communities.
- Target Species: The initiative focuses on cultivating high-value marine finfish species like Cobia (Rachycentron canadum) and Seabass (Lates calcarifer), alongside experimental deep-water seaweed cultivation.
- Implementing Agencies: The project is a collaboration between the Ministry of Earth Sciences, the National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT), and the Andaman & Nicobar Islands administration.
- Technology: The project uses advanced, indigenously developed open-sea cages designed by NIOT to withstand natural oceanic conditions.
About Andaman Sea
- The Andaman Sea, a marginal sea in the northeastern Indian Ocean, holds historical trade significance and strategic value for maritime routes and regional biodiversity.
- It controls key chokepoints like the Ten Degree Channel and Six Degree Channel, vital for 25% of global trade via Malacca Strait.
Source: PIB
New State of matter is a solid-liquid Hybrid
Syllabus: GS3/Science and Technology
Context
- Scientists have reported a new state of matter appears to be a solid-liquid hybrid.
About
- It is a new nanoscale state of matter where a single metal nanoparticle simultaneously exhibits solid-like and liquid-like atomic behaviour, challenging the sharp solid–liquid distinction.
- The nanoparticle displays the properties of solids and liquids both, but also unique behaviours that neither a pure liquid nor a pure solid would display on its own.
- The team used a technique called high-resolution transmission electron (HRTE) microscopy to observe nanoparticles.
- The findings suggest that the boundary between solid and liquid phases at the nanoscale isn’t as distinct as scientists have thought it to be.
- The most significant novel property the nanoparticle exhibited was the ability to remain liquid at temperatures far below the normal freezing point.
- Practical significance: This behaviour could revolutionise heterogeneous catalysts (e.g., platinum-on-carbon), improving durability by preventing particle clumping and poisoning while retaining highly active liquid or amorphous states—vital for fuel cells, hydrogen vehicles, pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals and pollution control.
Source: TH
Environmental Protection Fund
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
In News
- The Union Government has formally notified comprehensive rules governing the administration and utilisation of the Environmental (Protection) Fund.
About Environmental (Protection) Fund
- The Environmental (Protection) Fund is a statutory, dedicated fund under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, meant to channel monetary penalties from environmental violations into pollution control, restoration, monitoring, research, and capacity building.
- Is is administered by the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) or any body notified by the Central Government
- 75% of penalty proceeds transferred to the Consolidated Fund of the State/UT, 25% retained by the Centre.
- The Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) to audit the Fund.
Source: TOI
Previous article
RBI Strengthens Priority Sector Lending (PSL) Oversight