Kalaripayattu
Syllabus: GS 1/Culture
In News
- Kalaripayattu has been relegated to the demonstration section for the 38th National Games in Uttarakhand, scheduled to begin on January 28.
Kalaripayattu
- It is an ancient martial art originating from Kerala, India, but practiced worldwide.
- The term “Kalari” in Malayalam refers to a traditional gymnasium where this martial art, known as Payattu, is taught.
- Mythological Belief: Some believe Kalaripayattu was introduced by Lord Parasurama, the sixth incarnation of Lord Vishnu, after reclaiming Kerala from the sea.
- However, historians date its origin between 200 BCE and 600 CE, with its peak popularity between the 14th and 16th centuries.

- Stages of Kalaripayattu:
- Maippayattu: Body conditioning phase, preparing the body for combat.
- Kolthari: Training with wooden weapons (short and long sticks) for attack and self-defense.
- Angathari: Training with sharp metal weapons after overcoming fear of wooden weapons.
- Verumkai: Bare-hand fighting, with a focus on body anatomy and target points for strikes.
- Significance : It has been widely admired for its complex techniques, graceful movements, and the impressive flexibility of its practitioners, as recorded by chroniclers and poets over time
| National Games 2025 – Uttarakhand will host the National Games 2025 from January 28 to February 14, 2025. – Over 10,000 athletes, officials, and coaches will participate in 38 sports. – The mascot for the Games is “Mauli”, inspired by the Monal (Uttarakhand’s state bird). – The Games tagline is: “Sankalp Se Shikhar Tak” (From Resolve to Zenith). |
Source :IE
BRICS
Syllabus: GS2/ International Organisations
In News
- Nigeria becomes the ninth partner country of BRICS, joining Belarus, Bolivia, Cuba, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Thailand, Uganda, and Uzbekistan.
About BRICS
- Definition: BRICS is an intergovernmental informal grouping of emerging economies aimed at fostering cooperation and enhancing their global influence.
- Members: Brazil, Russia, India, China (these are founding members); South Africa joined in 2010; Iran, UAE, Egypt, Ethiopia, Saudi Arabia joined in 2024, Indonesia joined in 2025.
- Argentina was initially expected to join in 2024 but later opted out.
- Background: The first BRIC Summit was held in Russia in 2009.
- Importance: The BRICS grouping represents approximately 40% of the global population, making it one of the largest demographic blocs in the world.
- It also accounts for an estimated 37.3% of global GDP, highlighting its significant contribution to the global economy.
Source: TOI
Securities Transaction Tax
Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- The Securities Transaction Tax (STT) collection has surged by over 75%, reaching Rs 44,538 crore as of January 2025, compared to Rs 25,415 crore during the same period in 2024.
What is Securities Transaction Tax (STT)?
- STT is a type of tax that is charged on the purchase and sale of securities like stocks, mutual funds, and derivatives on recognized stock exchanges in India.
- It is a direct tax, meaning that it is levied directly on the transaction value of securities.
- The STT was introduced in India in 2004 to replace the earlier system of imposing a tax on securities transactions called the “stamp duty.”
- The 2024 budget has increased the securities transaction tax (STT) on Futures & Options (F&O) of securities to 0.02 percent and 0.1 percent respectively.
Source: IE
Nord Stream Pipeline
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
In News
- The Nord Stream subsea pipeline leaks released an estimated 465 ± 20 thousand metric tons of methane into the atmosphere.
About Nord Stream Pipeline
- About: The Nord Stream is a major subsea gas pipeline system spanning 1,200 km under the Baltic Sea, designed to transport natural gas from Russia to Europe.
- Key Features: Gas originates from the Bovanenkovo oil and gas condensate deposit in Western Siberia, Russia.
- Components: Nord Stream 1 completed in 2011 ( Route from Vyborg in Leningrad Oblast, Russia, to Lubmin, Germany.)
- Nord Stream 2 completed in 2021 ( Route from Ust-Luga in Leningrad Oblast, Russia, to Lubmin, Germany.)
Significance
- The Nord Stream pipelines are among the largest subsea gas pipelines in the world.
- They are central to Europe’s energy strategy but have also been at the center of geopolitical and environmental debates, particularly amid strained relations between Russia and Western nations.
Source: Nature
Dark Oxygen
Syllabus: GS3/ S&T
In News
- The recent discovery of “dark oxygen” production in the Clarion-Clipperton Zone challenges conventional understanding of oxygen generation, which has long been tied to photosynthesis requiring sunlight.
Key Findings
- Metallic nodules found 4,000 meters beneath the Pacific Ocean’s surface generate oxygen through electrolysis.
- This process does not depend on sunlight, marking a paradigm shift in the understanding of oxygen generation.
Potential Applications
- This phenomenon could provide insights into life in extreme environments on Earth and other planets.
- Understanding “dark oxygen” production could assist in the search for extraterrestrial life by expanding the criteria for habitability.
Source: NDTV
India’s First Indigenous Surgical Tele-robotic System
Syllabus :GS3/Science and Technology
In News
- India’s first indigenous surgical tele-robotic system, SSI Mantra, was used to perform two complex heart surgeries remotely, with the surgeon in Gurugram and the patient in Jaipur.
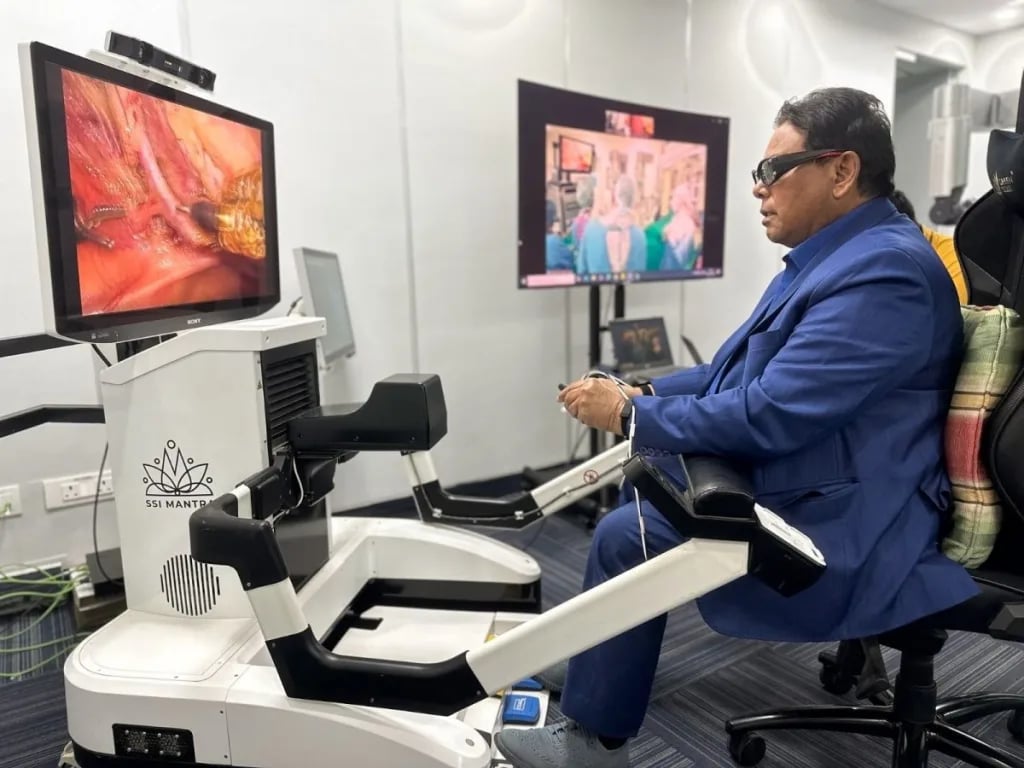
About SSI Mantra
- SSI Mantra is a robotic system that performs complex surgical procedures in Genito-Uro-Oncology cases.
- It is developed by SSI Ltd and it is the only robotic system worldwide to receive regulatory approval for telesurgery and tele-proctoring.
- Its recent approval by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) paves the way for remote surgeries and medical education, allowing healthcare professionals to collaborate across distances.
- Benefits: Reduced operation time, better precision, minimal trauma, lower blood loss, faster recovery, and reduced infection risk.
- The technology aims to bridge geographical gaps in surgical care, making tele-surgery accessible globally.
- Challenges to Wider Adoption: High costs of robotic surgeries, which are currently more available in metro and tier-1 cities.
- Other Challenges included latency time, requiring good connectivity, and addressing potential technical problems.
Source :TH
DDT-Infused Soil
Syllabus: GS3/ Agriculture
Context
- Researchers from Sweden have discovered a method to reclaim infertile soil contaminated with DDT (Dichloro-Diphenyl-Trichloroethane) by mixing it with biochar.
About
- Biochar is an environmentally friendly material, akin to charcoal, that has the ability to bind contaminants such as DDT.
- This binding prevents the toxin from being absorbed by soil organisms, thus limiting its harmful impact.
- When mixed with soil, biochar improves soil fertility and helps mitigate the effects of pollution.
What is DDT?
- DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) is a chemical, first synthesized in 1874 and its insecticidal properties were discovered in 1939.
- Though initially hailed as an effective pest control tool, its long-term use has resulted in serious environmental and health concerns.
- Harmful effects: DDT tends to accumulate in the fatty tissues of both humans and animals, leading to long-term exposure. DDT is a persistent organic pollutant (POP).
- It was banned in the United States in 1972.
- Some countries, primarily in Africa, still use DDT to control malaria and other insect-borne diseases.
- Indian scenario: India continues to produce and use DDT, primarily for controlling vector-borne diseases like malaria and dengue.
- Hindustan Insecticides Limited (HIL) is the sole manufacturer of DDT in India.
Source: DTE
Central Reserve Police Force
Syllabus: GS3/Internal Security, Security agencies
Context
- Assam police chief Gyanendra Pratap Singh has been appointed Director General of the Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF).
Central Reserve Police Force
- About: The CRPF is the premier central police force of the Union of India entrusted with maintaining internal security.
- Origin: Established originally as the Crown Representative’s Police in 1939, it stands as one of the oldest central paramilitary forces.
- In response to escalating political turmoil and unrest within the princely state of India.
- Ministry: Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Key roles of CRPF:
- Law and Order: Assists in maintaining peace during protests, riots, and elections.
- Counter-Insurgency Operations: Engages in operations against armed insurgents, terrorists, and extremist groups, especially in areas like Jammu & Kashmir and the Northeast.
- Disaster Response: Provides aid during natural disasters.
- Specialized Units of the CRPF: Commando Battalion for Resolute Action (CoBRA), specializes in jungle warfare and counterinsurgency operations, particularly in Naxal-affected areas.
- Rapid Action Force (RAF): Focuses on controlling riots and handling public unrest.
Source: TH
Water Hyacinth
Syllabus: GS3/Species in News
Context
- Recently, a group of fishermen were said to be stranded on Kenya’s Lake Naivasha due to water hyacinth that has taken over large parts of it.
About
- Scientific Name: eichhornia crassipes
- It is native to South America and was introduced to Kenya in the 1980s as an ornamental plant.
- It is an aquatic weed common in waterbodies across South Asia, including India.
- It was introduced to India during the British colonial rule as an ornamental aquatic plant.
- It is considered the most invasive aquatic plant species in the world.
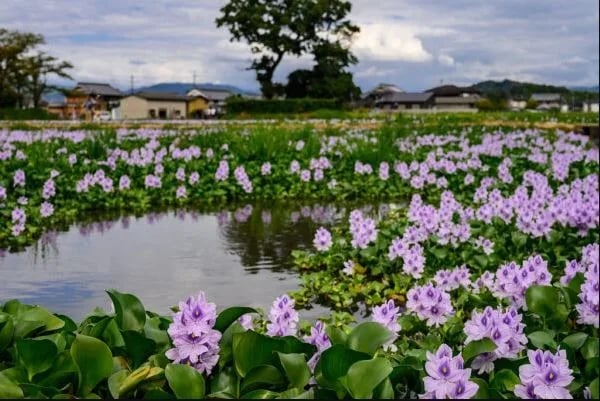

- Concerns:
- Clogging Waterways: It grows rapidly, often forming dense mats that block rivers, lakes, and canals, disrupting water transport and irrigation.
- Disrupting Ecosystems: It reduces oxygen levels in water, harms aquatic life, and hinders sunlight from reaching underwater plants.
- Economic Impact: The clogging can affect fishing, water quality, and recreational activities, leading to significant financial losses.
- Efforts to control water hyacinth include physical removal, biological control (using insects or other species), and chemical treatments.
Source: TH
NDRF Raising Day
Syllabus :GS3/Disaster Management
In News
- The Prime Minister salutes the brave personnel of the National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) on its Raising Day.
About National Disaster Response Force (NDRF)
- It was established in 2006 under theDisaster Management Act 2005 to specialize in disaster response.
- It initially focused on law and order, later becoming dedicated to disaster response.
- Its Motto is “आपदा सेवा सदैव सर्वत्र”.
- Organizational Structure: It comprises 16 Battalions drawn from various CAPF forces (BSF, CISF, CRPF, ITBP, SSB, and Assam Rifles).
- Each Battalion consists of 18 specialized search and rescue teams, with 47 members each (engineers, technicians, paramedics, canine units).
- The total strength of the force is 1,149 personnel per Battalion.
- It operates under the unified command of the Director General, NDRF.
- Key Milestones : The NDRF’s proactive and strategic deployment has effectively mitigated damages from various calamities, such as the Kosi floods (2008), Jammu and Kashmir floods (2014), and the Nepal earthquake (2015).
- The NDRF has also handled Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear (CBRN) challenges and has been involved in international rescue operations, such as in Turkiye and Syria after the 2023 earthquake.
- Noteworthy domestic operations include responses to the Balasore train accident, the Uttarkashi tunnel collapse, and numerous other disasters.
Source :PIB
Previous article
Outward Foreign Direct Investment