Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
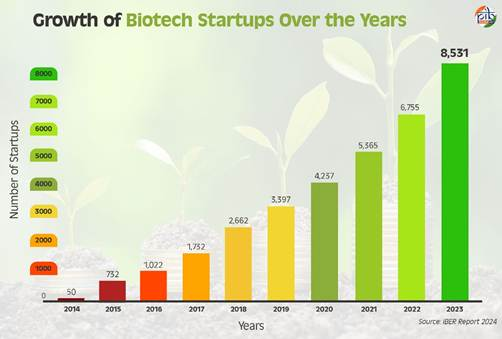
- India’s biotech sector has surged in the past several years, from a modest count of roughly 500 startups in 2018, the number has soared to over 10,000 in 2025.
What is Bioeconomy?
- The bioeconomy is the use of renewable biological resources to produce food, energy and industrial goods, which supports sustainability and economic growth.
- Innovations like gene editing and bioprinting are driving progress, while integration across sectors strengthens long-term impact.
- By aligning biotechnology with digital tools and circular economy principles, the bioeconomy offers sustainable solutions to environmental challenges and promotes overall societal well-being.
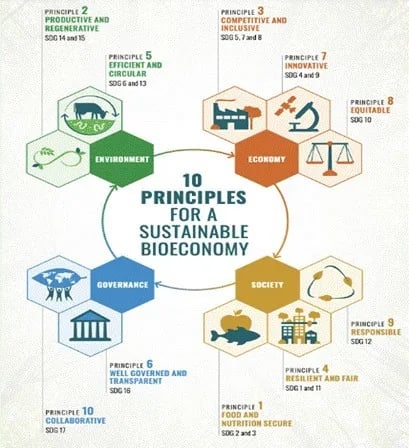
India’s Bioeconomy
- India is among the Top 12 destinations for biotechnology worldwide and 3rd largest destination for biotechnology in Asia Pacific.
- India’s bioeconomy has grown sixteen-fold from $10 billion in 2014 to an impressive $165.7 billion in 2024.
- Contributing 4.25% to the national GDP, the sector has demonstrated a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.9% over the past four years.
- India’s Biotechnology sector is categorised into Biopharmaceuticals, Bio agriculture, Bio IT and Bio Services.
- Future Goals: Target of achieving a $300 billion bioeconomy by 2030.
- India also seeks to lead globally in bio-pharma, including vaccines, diagnostics, and therapeutics.
Concerns
- Fragmentation of Infrastructure: India hosts over 70 incubators, but few have end-to-end facilities such as pilot-scale purification systems, fill-and-finish suites, regulatory affairs support.
- This forces entrepreneurs to operate across cities, duplicating costs and processes.
- Regulatory Complexities: Outdated frameworks for clinical trials, patent laws and product approval.
- Lag behind modern demands (AI, biologics, genomics), delaying market entry and deterring investment.
Government Initiatives and Key Programmes
- BioE3 Policy (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment): It was approved by the Union Cabinet in 2024, has an ambitious vision to create a $300-billion bioeconomy by 2030.
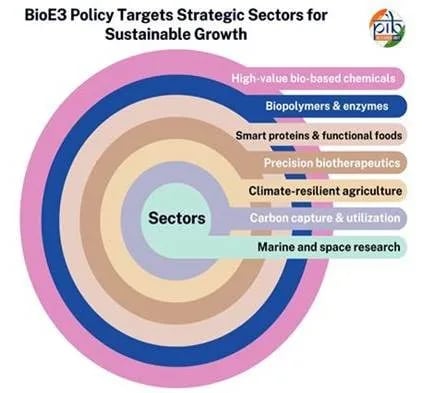
- National Biopharma Mission: It is a government-approved initiative led by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) and implemented by BIRAC.
- Aim: To boost India’s capabilities in biopharmaceuticals, vaccines, biosimilars, medical devices, and diagnostics by fostering collaboration between industry and academia.
- Bio-agriculture: Agricultural biotechnology in India is advancing rapidly through innovations in genomics, transgenics, and gene editing under the Department of Biotechnology’s Agriculture Biotechnology programme.
- Climate-Smart Crops: A drought-tolerant, high-yielding chickpea variety SAATVIK (NC 9) has been approved for cultivation.
- Genome-Edited Rice: Loss-of-function mutations in yield-limiting genes have led to improved rice lines like DEP1-edited MTU-1010, showing higher yields.
- Genotyping Arrays: India’s first 90K SNP arrays—IndRA for rice and IndCA for chickpea—enable DNA fingerprinting and variety identification.
- Amaranth Resources: A genomic database, NIRS techniques, and a 64K SNP chip aid nutritional screening and development of anti-obesity amaranth varieties.
- Biocontrol: A nano-formulation from Myrothecium verrucaria offers eco-friendly control of powdery mildew in tomato and grape.
- Kisan-Kavach: An anti-pesticide protective suit enhances farmer safety from toxic exposure.
- Biotech-KISAN (Biotech-Krishi Innovation Science Application Network): Biotech-KISAN is a scientist-farmer partnership programme launched to empower farmers through agricultural innovation and scientific interventions.
- Bioenergy: Ethanol blending has seen a significant rise—from 1.53% in 2014 to 15% in 2024, with a target of 20% blending by 2025.
- Boosting Biotech Innovation Through BIRAC Initiatives: The Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC), established by the Department of Biotechnology in 2012, plays a pivotal role in nurturing India’s biotech startup ecosystem.
- With 95 bio-incubation centres set up nationwide, BIRAC supports startups through funding, infrastructure, and mentorship.
Way Ahead
- India’s bioeconomy stands at a defining moment, with its integrated approach to innovation, sustainability, and inclusive development setting a global benchmark.
- The convergence of bio-manufacturing, bio-agriculture, and bioenergy not only strengthens national resilience but also signals India’s strategic intent to lead in the emerging global bioeconomy.
Source: TH
Previous article
Fiscal Challenges of Indian Municipalities
Next article
RBI Supervision for EPFO, Post Office Bank