Syllabus: GS3/ Economy
Context
- As India targets 500 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2030 and net-zero emissions by 2070, securing access to critical minerals has become a national priority.
What are Critical Minerals?
- These are minerals that are essential for economic development and national security.
- The lack of availability of these minerals or the concentration of extraction or processing in a few geographical locations could potentially lead to “supply chain vulnerabilities and even disruption of supplies”.
List of Critical Minerals
- Different countries have their own unique lists of critical minerals based on their specific circumstances and priorities.
- A total of 30 minerals were found to be most critical for India, out of which two are critical as fertilizer minerals: Antimony, Beryllium, Bismuth, Cobalt, Copper, Gallium, Germanium, Graphite, Hafnium, Indium, Lithium, Molybdenum, Niobium, Nickel, PGE, Phosphorous, Potash, Rare Earth Elements (REEs), Rhenium, Silicon, Strontium, Tantalum, Tellurium, Tin, Titanium, Tungsten, Vanadium, Zirconium, Selenium and Cadmium.
Critical Minerals in India’s Green Transition
- Significance: Critical minerals are essential for technologies powering electric vehicles (EVs), solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage systems.
- Lithium and cobalt form the core of EV batteries, while REEs are vital for high-performance magnets in wind turbines and electronics.
- Market Outlook: India’s EV market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 49% (2023–2030) under initiatives like the Electric Mobility Promotion Scheme (EMPS) 2024.
- The battery storage market, valued at $2.8 billion in 2023, is set to expand rapidly with renewable energy integration.
- Import Dependence: India imports nearly 100% of its lithium, cobalt, and nickel, and over 90% of its REEs, leaving it vulnerable to supply disruptions.
- China currently dominates 60% of global REE production and 85% of processing capacity, heightening strategic risks.
India’s Policy Push for Mineral Exploration
- Domestic Reserves: India has vast untapped mineral potential, with lithium in Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) and Rajasthan, and REEs in Odisha and Andhra Pradesh.
- In 2023, the Geological Survey of India (GSI) identified 5.9 million tonnes of inferred lithium resources in J&K.
- Policy Initiatives: National Mineral Exploration Policy (NMEP), 2016 and Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 2021 have accelerated exploration through private participation and advanced surveys.
- KABIL (Khanij Bidesh India Ltd) is acquiring overseas mineral assets to ensure supply security.
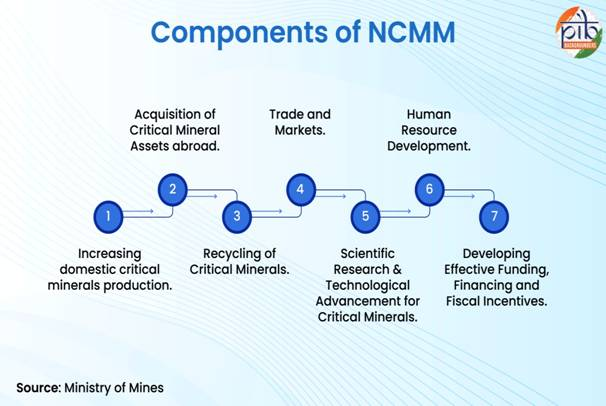
- The National Critical Mineral Mission (NCMM) with a ₹34,300 crore plan aims to strengthen the value chain from exploration to recovery.
What are the challenges?
- Environmental Concerns: Mining and extraction pose ecological and social challenges.
- Limited Processing and Refining Capacity: India lacks sufficient domestic facilities for advanced processing and refining of critical minerals like lithium, cobalt, and REEs.
- Low Domestic Production: Despite having significant untapped reserves, India contributes less than 1% of global Rare Earth Element (REE) production, limiting its influence in global critical mineral markets and creating supply vulnerabilities.
Way Ahead
- Policy Incentives: Strong fiscal measures such as subsidies, tax incentives, production-linked schemes, and dedicated R&D funding are essential to make domestic exploration and processing economically viable.
- Speedy operationalisation of approved mining leases and fast-tracked exploration in mineral-rich regions like Chhattisgarh, Rajasthan, and Jammu & Kashmir will help boost supply security.
- Upgrading to mechanised mining equipment, automated processing plants, and sustainable waste management systems will improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
- Promoting a Circular Economy: With India generating nearly four million metric tonnes of e-waste annually, enhancing recycling and recovery of critical minerals from used batteries and electronic waste can significantly reduce import dependence.
Source: TH
Previous article
SAIME model (Aquaculture model) of Sundarbans wins FAO recognition
Next article
News in Short – 16 October, 2025