Cash Plus Model Pushes Up Early Breastfeeding Rate in Rajasthan
Syllabus: GS1/ Issues Related to Women and Children, GS2/ Governance
Context
- Rajasthan’s Cash Plus Model, the first in India to combine Direct Benefit Transfers (DBT) with Social and Behaviour Change Communication (SBCC), has led to a 49% rise in early breastfeeding.
About the Cash Plus Model
- Complementary to PMMVY: The model builds on the existing Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana, which provides financial assistance to women during their first pregnancy.
- The Cash Plus model extends these benefits to second-time mothers, filling a major policy gap.
- Integrated Behavioural Change Strategy: It combines cash transfers with home-based counselling, nutrition education, community engagements, and digital outreach to promote healthy practices.
- Phased Implementation: Launched in 2020 as a pilot in five tribal districts, the scheme was scaled up state-wide in 2022.
- Financial Commitment: The annual budget for the scaled-up version is ₹210 crore, targeting around 3.5 lakh second-time pregnant women every year.
Source: TH
Vietnam officially Joins BRICS As ‘Partner Country’
Syllabus: GS2/IR
Context
- Vietnam has officially joined BRICS as a partner country.
About
- Vietnam has now become the 10th BRICS partner.
- The partner country category was created at the 2024 BRICS Summit in Kazan, Russia.
- The current list of partners includes Vietnam, Belarus, Bolivia, Kazakhstan, Cuba, Malaysia, Nigeria, Thailand, Uganda, and Uzbekistan.
About BRICS
- BRICS is an acronym that refers to a group of five major emergingnational economies:Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
- Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates have joined BRICS as new full members .
- The term ‘BRIC’ was originally coined by economist Jim O’Neill in 2001.
- Origin: As a formal grouping, BRIC started after the meeting of the Leaders of Russia, India and China in St. Petersburg on the margins of the G8 Outreach Summit in 2006.
- The grouping was formalized during the 1st meeting of BRIC Foreign Ministers on the margins of UNGA in New York in 2006.
- Initially, the grouping was termed BRIC as South Africa was inducted in 2010 and from there on it has been referred to as BRICS.
- Summits: The governments of the BRICS states have met annually at formal summits since 2009.
- BRICS countries have come together to deliberate on important issues under the three pillars of:
- political and security,
- economic and financial and
- cultural and people-to-people exchanges.
- New Development Bank: Formerly referred to as the BRICS Development Bank, is a multilateral development bank established by the BRICS states.
- The Bank shall support public or private projects through loans, guarantees, equity participation and other financial instruments.
Source: AIR
Step-and-shoot spot-scanning proton arc therapy (SPArc)
Syllabus :GS3/Science and Tech
In News
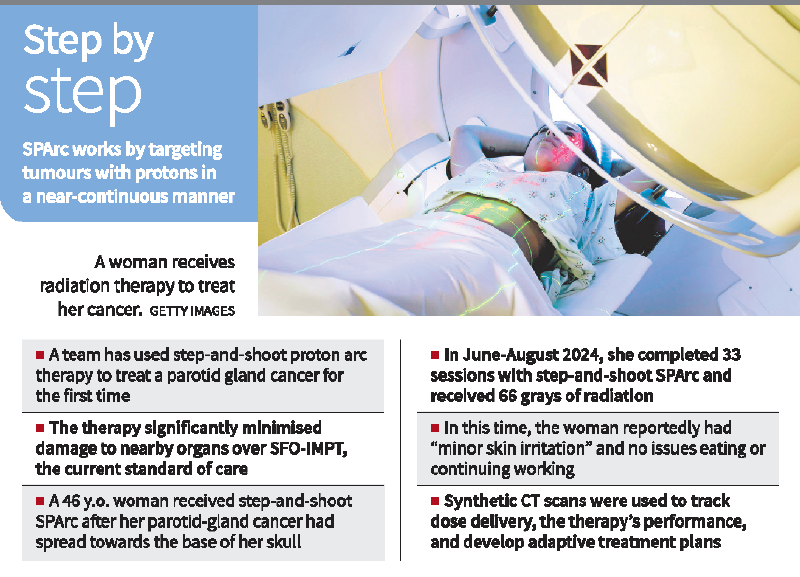
- A team at Corewell Health William Beaumont University Hospital in the U.S. for the first time successfully used step-and-shoot spot-scanning proton arc therapy (SPArc) to treat Adenoid cystic carcinoma.
| Adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) – It is a rare cancer that typically begins in salivary glands but can also occur in areas like the respiratory tract and tear glands. – It grows slowly but can spread to nearby nerves and other body parts. – Symptoms vary by tumour location and may include swelling, pain, and difficulty swallowing or breathing. – It is difficult to treat due to its nerve invasion and high chance of recurrence. |
About the Threapy
- Step-and-shoot spot-scanning proton arc therapy (SPArc) reduced radiation exposure to vital organs like the brainstem, optical chiasm, and spinal canal significantly compared to standard SFO-IMPT therapy.
- It uses proton beams with varying energy layers to precisely ‘paint’ the tumour while machine learning tools ensure accurate dose delivery despite changes like weight loss.
Relevance
- SPArc holds great potential for treating tumours in complex anatomical areas, though concerns remain about its high cost and the risk of under-treating due to tumour movement or shrinkage during therapy.
- Although fully dynamic SPArc showed slightly better results, it is still in development.
Source: TH
Rubber Board
Syllabus :GS3/Economy
In News
- The Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry approved the appointment of staff members to the Rubber Board to several long-pending vacancies.
Rubber Board
- It is a statutory organization constituted under Section (4) of the Rubber Act, 1947 and functions under the administrative control of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- It is headed by a Chairman appointed by the Central Government and has 28 members representing various interests of the natural rubber industry.
- The Board’s headquarters is located at Kottayam in Kerala.
Functions
- The Board is responsible for the development of the rubber industry in the country by assisting and encouraging research, development, extension and training activities related to rubber.
- It also maintains statistical data of rubber, takes steps to promote marketing of rubber and undertake labour welfare activities.
Source :TH
Flue Gas Desulphurisation
Syllabus: GS3/Environment
Context
- A committee chaired by Principal Scientific Advisor (PSA) Ajay Sood, has recommended that India do away with mandating Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD) units in all coal-fired thermal power plants (TPPs).
About
- In 2015, the Union Environment Ministry issued a policy that mandated all 537 coal-fired TPPs in India to install FGD units to reduce SO2 emissions.
- In 2025, a study commissioned by the PSA’s office concluded that the Environment Ministry should roll back its 2015 policy mandating all of India’s TPPs to install FGD units.
- Installing FGD units is a costly affair. According to the Central Electricity Authority, FGD costs approximately ₹1.2 crore per MW to install.
Flue Gas Desulphurisation (FGD)
- Flue gas is emitted as a byproduct of combustion of fossil fuels. It mainly contains pollutants such as carbon dioxide (CO2), sulphur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, etc.
- FGD units specifically target the SO2 emissions in flue gas.
- SO2 is an acidic gas, and is usually treated with a basic compound in the FGD unit to neutralise the pollutant.
- It is one of the major greenhouse gases that cause global warming, and can cause respiratory problems in humans.
- There are three common types of FGD systems around the world — dry sorbent injection, wet limestone treatment, and using sea water to remove SO2.
- The dry sorbent injection method involves adding a powdered sorbent like limestone to the flue gas, where it reacts with SO2.
- The wet limestone treatment method also uses limestone to remove SO2, but instead of using it in a powdered form, it uses a limestone slurry.
- Passing SO2 through this slurry results in the formation of gypsum, which is a stable compound and has wide applications in industries like construction.
- This is the commonly used technology, and has very high efficiency.
- Sea water treatment is used in plants located near coastal areas.
- Sea water first absorbs SO2 from flue gas, and then the water is treated to make it suitable to be discharged back into the sea.
Source: TH
UN’s ICAO Rated India Above Global Average
Syllabus: GS3/Disaster Management
Context
- India was rated well above the global average in terms of its operations and airworthiness by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO).
About
- The Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) was last audited in November 2022.
- The overall Effective Implementation score rose to 85.65% from 69.95% in 2018, indicating an improvement in the country’s aviation safety ranking.
- India scored higher than the global average in all eight categories under ICAO’s Universal Safety Oversight Audit Programme (USOAP).
- In the operations category, India scored 94.02%, significantly higher than the global average of 72.28%, and even surpassed countries like the United States (86.51%) and China (90%).
- In terms of airworthiness, India achieved a score of 97.06%, again outperforming the US (89.13%) and China (94.83%).
- Although India was audited in 2022, while the US and China were audited in 2024.
| Do you know? – India is currently the third-largest domestic aviation market in the world, after the United States and China. – It is also recognized as the fastest-growing major aviation market, reflecting the increasing demand and expansion in civil aviation infrastructure. |
About ICAO and Safety Audits
- ICAO is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for establishing global standards and regulations for civil aviation safety and operations.
- ICAO conducts the Universal Safety Oversight Audit Programme (USOAP) to assess the ability of member states to ensure effective safety oversight in civil aviation.
- The USOAP evaluates eight critical areas: legislation, organisation, licensing, operations, airworthiness, accident investigation, air navigation services, and aerodromes.
FAA’s Safety Assessment of India
- The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) of the United States conducts the International Aviation Safety Assessment (IASA) to determine if a country’s civil aviation authority complies with ICAO standards.
- In 2021, the DGCA of India was audited by the FAA, based on the positive findings, in 2023, the FAA reaffirmed India’s status as Category 1 under the IASA programme, indicating full compliance with ICAO safety oversight standards.
- A Category 1 rating allows Indian airlines to operate and expand flights to the United States and to code-share with US carriers.
Source: IE
New Species of Jumping Spider Discovered
Syllabus :GS3/Environment
In News
- Researchers in southern India have discovered a new species of jumping spider, Spartaeus karigiri, marking the first time the genera Spartaeus and Sonoita.
Jumping spiders
- They belong to the Salticidae family which is the largest spider family with over 5,000 species.
- They are small to medium-sized spiders known for their dense iridescent scales and large front median eyes.
- They inhabit diverse environments, from vegetation and rocky areas to buildings, and are active daytime hunters relying on their keen eyesight to catch prey like ants and fruit flies.
- They occur worldwide, except for Greenland and Antarctica.
- Unlike many spiders, they don’t spin webs for trapping prey but use silk as an anchor line and create silken retreats for molting or resting.
New species : Spartaeus karigiri
- The study found male spiders hiding in rocky crevices in Karnataka’s Karigiri region and females guarding eggs, with additional specimens spotted in Tamil Nadu.
- It marks the first time that the genera Spartaeus and Sonoita (specific groups within a subfamily)have been found in India.
- It was previously known only from Southeast Asia and Africa.
- These findings increase India’s Spartaeinae spider count to 15 species across 10 genera, highlighting the country’s rich but still largely unexplored spider biodiversity.
| Do you know ? – The research also identified Sonoita cf. lightfooti in Karnataka, raising questions about its origin. – Additionally, the study clarified that Marpissa gangasagarensis is the same species as Phaeacius fimbriatus, resolving a longstanding taxonomic confusion. |
Source :TH
| Read this in Hindi: संक्षिप्त समाचार 16-06-2025 |
Previous article
How DNA Identification Works?