Syllabus: GS3/Economy
Context
- The government has proposed a new bill to repeal and replace the 60-year-old Income-tax Act, 1961, with a simpler and more efficient tax framework.
About
- Income Tax Bill 2025 aims to simplify Income Tax Act 1961. The new bill reduces chapters and words for enhanced clarity.
- It aims to reduce litigation and enhance compliance. Once passed, the proposed legislation will be called the Income Tax Act, 2025, and is expected to take effect in April 2026.
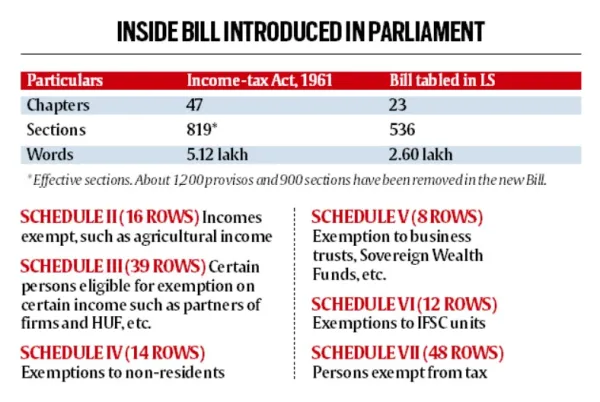
Key Features
- Qualitative Improvements
- Simplified language, making the law more accessible.
- Consolidation of amendments, reducing fragmentation.
- Removal of obsolete and redundant provisions for greater clarity.
- Structural rationalization through tables and formulae for improved readability.
- Preservation of existing taxation principles, ensuring continuity while enhancing usability.
- Crypto as Property: Virtual digital assets such as cryptocurrencies have been included in the definition of property to be counted as a capital asset.
- Dispute Resolution: It provides the points of determination, decision, and the reasons behind it, marking a shift from the earlier section, which lacked clarity on the manner of issuing DRP directions.
- Capital Gain Exemptions: Section 54E of the Act, which details exemptions for capital gains on transfer of capital assets prior to April 1992 has been removed.
- Tax Year: The Bill introduces the concept of “tax year”, which has been defined as the 12-month period beginning April 1.
Conclusion
- Once the Bill is passed in the Parliament, it will be sent to a Parliamentary Standing Committee on Finance for reviewing.
- After a call is taken on including any proposed amendments, the government will decide the date for rolling out the new income tax law.
Source: PIB
Previous article
Freeze on USAID by United States
Next article
News In Short 14-2-2025