Syllabus: GS3/ Science and Technology
Context
- IIT Madras has completed a 410-meter Hyperloop test track, marking a milestone in futuristic transportation.
- The Mumbai-Pune corridor will be the first full-scale Hyperloop project in India.
What is Hyperloop technology?
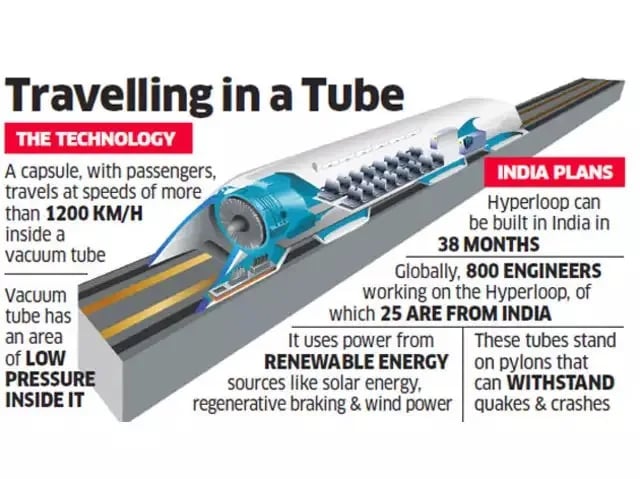
- A Hyperloop is a high-speed transportation system where pods, functioning as pressurized vehicles, move at extraordinary speeds through low-pressure tubes.
- Key Features;
- Speed: Hyperloop pods can reach up to 1200 km/h with an operational speed of around 360 km/h.
- Frictionless System: Operates within a vacuum-sealed environment, minimizing resistance and energy consumption.
- Efficiency: Provides direct, point-to-point travel without intermediate stops.
Benefits
- Energy Efficiency: Due to reduced air resistance and friction, Hyperloop systems are expected to be highly energy-efficient.
- Sustainability: Many Hyperloop concepts are designed to be powered by renewable energy sources like solar power, making them environmentally friendly.
- Reduced Travel Time: Hyperloop could drastically reduce travel times between cities, making long-distance commutes more feasible.
Challenges
- Infrastructure Costs: Building the necessary infrastructure, including tubes, stations, and supporting systems, is extremely expensive.
- Land Acquisition: Acquiring the land needed for Hyperloop routes can be challenging, especially in densely populated areas.
- Technological Hurdles: Developing and perfecting the technology, including maglev systems, vacuum seals, and safety mechanisms, requires significant research and development.
Source: ET
Previous article
Bharat 6G Vision Document