UNESCO ‘Creative City of Gastronomy’
Syllabus: GS1/ Culture
Context
- A proposal for Creative City Lucknow under the category Gastronomy for Awadhi Cuisine has been submitted to the World Heritage Centre recently.
UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN)
- The UNESCO Creative Cities Network (UCCN) is a global network of cities that recognize culture and creativity as drivers of sustainable urban development.
- UCCN was created in 2004.
- The network focuses on seven creative fields: Crafts and Folk Art, Design, Film, Gastronomy, Literature, Media Arts, and Music.
Indian cities in UCCN
- India has several cities recognized by UNESCO as part of the Creative Cities Network.
- The network currently includes;
- Jaipur and Srinagar (Crafts and Folk Arts),
- Varanasi, Chennai and Gwalior (Music),
- Mumbai (Film),
- Hyderabad (Gastronomy),
- Kozhikode (Literature).
Source: HT
Shipki La
Syllabus: GS1/ Geography and GS3/ Internal Security
Context
- Recently, the Chief Minister of Himachal Pradesh launched border tourism activities at Shipki-La.
About Shipki La
- Location: A high-altitude motorable mountain pass (3,930 m) in Kinnaur district, Himachal Pradesh, on the India-China border.
- Strategic & Cultural Significance:
- Situated on the ancient Silk Route, blending geopolitical importance, cultural heritage, and Himalayan landscapes.
- Historically served as a trade route between India and Tibet, until it was closed for trade in 2020.
- The Sutlej River (Tibetan name: Langqen Zangbo) enters India through this pass.
- Kailash Mansarovar Yatra Potential: Shipki La has been proposed by the Himachal Pradesh government as the easiest route for the Kailash Mansarovar Yatra, pending approval from the Centre.
Source: TH
Lokpal
Syllabus: GS2/ Polity
In News
- The Full Bench of Lokpal of India has adopted a new motto “Empower Citizens, Expose Corruption”.

Lokpal
- About: It is an anti-corruption authority or ombudsman in India that was established to address grievances regarding corruption in public offices.
- Legal Status: The Lokpal is not a constitutional body but a statutory body created through legislation Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act 2013.
- Chairperson: Retired Chief Justice of India or a Supreme Court judge.
- Appointment of Lokpal: Appointed by a selection committee consisting of Prime Minister, Chief Justice of India (CJI), Leader of the Opposition (LoP) in Lok Sabha & One Eminent Jurist (appointed by the above members).
- Tenure: The Lokpal is appointed for a 5-year term or until they attain the age of 70 years.
- Powers and Functions: To investigate and prosecute corruption cases against public servants, including government officials, ministers, and the Prime Minister (except on matters related to national security).
- The Lokpal has supervision over CBI’s investigations in corruption cases.
Source: AIR
Malta’s Golden Passport Scheme
Syllabus: GS2/ International Relations
Context
- The European Court of Justice ruled that Malta may no longer sell citizenship through its ‘golden passports’ scheme, as it is contrary to European law.
About
- Launched in 2014, Malta’s Individual Investor Programme (IIP), known as the Golden Passport scheme, allowed wealthy foreigners to acquire Maltese citizenship, and by extension EU citizenship, through financial contributions.
- Applicants were required to:
- Contribute €600,000–€750,000 to Malta’s national development fund.
- Purchase or lease real estate in Malta.
- Make a €10,000 donation to a registered NGO.
- It attracted investors from Russia, China, the Middle East, and others, including politically exposed persons and celebrities.
Why the Scheme Was Controversial
- Security concerns: Citizenship grants included access to the EU’s visa-free Schengen Area, raising risks of money laundering and infiltration by criminal networks.
- Lack of transparency: Many successful applicants remained unnamed.
Source: BS
Hortoki-Sairang line
Syllabus: GS3/Infrastructure
In News
- The Commission of Railway Safety (CRS) has approved the Hortoki-Sairang line .
Hortoki-Sairang line
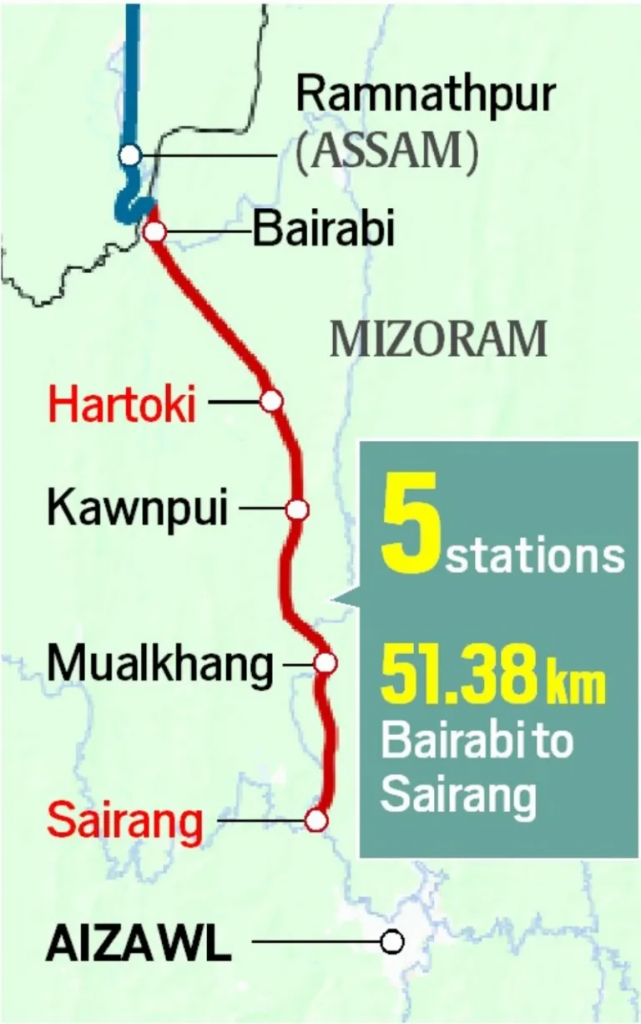
- It is the final leg of the Bairabi-Sairang railway project in Mizoram.
- It enables the first-ever rail connection to the state capital, Aizawl, via the 33.86-km Hortoki–Sairang section.
- It lies in hilly terrain and includes 32 tunnels and 35 major bridges.
- Sairang is a satellite town of Aizawl, around 20 km from the city.
- Bairabi in Kolasib district, near the border with Assam, has so far been the only railhead in Mizoram.
- Sairang is a satellite town of Aizawl, around 20 km from the city.
Importance
- The Bairabi-Sairang project is part of a broader push by the Ministry of Railways to connect all northeast state capitals by rail.
- This involves numerous new line and doubling projects across Assam, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Manipur and Tripura.
- It is a key infrastructure initiative under the Centre’s Act East Policy to enhance connectivity and economic integration in the northeast region.
Source :IE
Symposium on ‘Discovery and Development of Monoclonal Antibody Therapeutics’
Syllabus: GS3/ Science & Technology
Context
- The Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI) hosted a national symposium on the Discovery and Development of Monoclonal Antibody (mAb) Therapeutics, to foster collaboration in advancing India’s Biopharmaceutical sector.
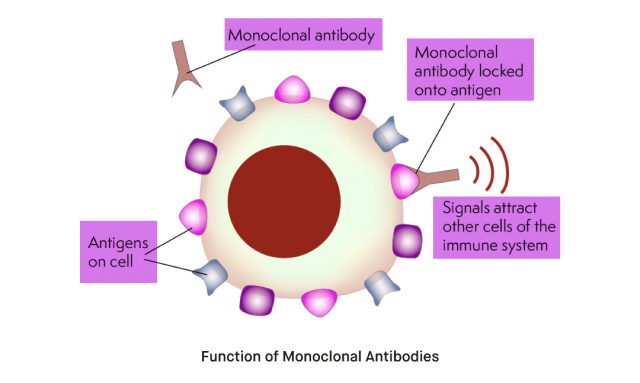
What are Monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs)?
- Monoclonal antibodies are lab-engineered proteins designed to target specific antigens (foreign substances like viruses, bacteria, or cancer cells).
- They are derived from a single clone of a B-cell and hence are identical in structure and specificity.
- mAbs mimic the natural immune response but are highly specific, making them powerful tools in treating diseases.
Applications of mAbs
- Healthcare and Medicine:
- Infectious diseases (e.g., mAbs used for COVID-19 therapy like Casirivimab and Imdevimab).
- Organ transplantation (preventing rejection).
- Diagnostics: Used in pregnancy tests, ELISA kits, and disease markers.
Source: PIB
International Organisation of Aids to Marine Navigation (IALA)
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
In News
- India, as the Vice President of the International Organization for Marine Aids to Navigation (IALA), actively participated in the 2nd Session of the IALA Council, held in Nice, France.
About IALA
- Established: In 1957, originally as the International Association of Marine Aids to Navigation and Lighthouse Authorities (IALA).
- Headquarters: Based in Saint-Germain-en-Laye, near Paris, France.
- Members: IALA currently has 39 members.
- Status: Transitioned from a Non-Governmental Organisation (NGO) to an Intergovernmental Organisation (IGO) in August 2024, following ratification by 30 states through a Convention.
- Objective: IALA aims to improve safety at sea, reduce marine accidents, and protect the marine environment by developing common practices, technical standards, and recommendations for maritime navigation.
Source: AIR
Eco-Sensitive Zone (BESZ)
Syllabus: GS3/ Environment
Context
- A municipal solid-waste incinerator set up in Gangotri (Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand) within the Bhagirathi Eco-Sensitive Zone (BESZ) has triggered criticism among environmental activists.
What are Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs)?
- Eco-Sensitive Zones (ESZs) are areas notified by the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEFCC) under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- ESZs are designated areas around protected areas like national parks and wildlife sanctuaries.
- Their primary purpose is to protect the fragile ecosystems of these protected areas by regulating human activities in the surrounding areas.
- The extent of ESZ can go up to 10 km around the protected area. In exceptional cases, even beyond 10 km.
- Activities in ESZs are classified as:
- Prohibited: commercial mining, setting up of major hydroelectric projects, setting up of polluting industries (red category).
- Regulated: construction, tourism, tree felling, vehicular traffic.
- Permitted: agriculture, organic farming, local community use.
- In June 2022, the Supreme Court of India mandated that all national parks and wildlife sanctuaries within protected forests must have a minimum Eco-Sensitive Zone (ESZ) of 1 km.
Source: TH
Exercise ‘Khaan Quest’
Syllabus: GS3/Defence
In News
- The Indian Army contingent arrived in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia to participate in the multinational military Exercise Khaan Quest.
Exercise ‘Khaan Quest’
- It began as a bilateral initiative between the United States and the Mongolian Armed Forces in 2003, evolved into a multinational peacekeeping endeavour from 2006 onwards.
- It is an annual exercise that brings together military forces from across the globe to collaborate and enhance their peacekeeping capabilities.
- It will enable the participating countries to share their best practices in Tactics, Techniques and Procedures for conduct of joint operations.
- It aims to prepare the Indian armed forces for peacekeeping operations in a multinational setting, thereby “increasing interoperability and military readiness in peace support operations under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter.”
Source :TH
| Read this in Hindi: संक्षिप्त समाचार 12-06-2025 |
Previous article
50 Years of Emergency
Next article
Air India Plane Crash in Ahmedabad