Syllabus: GS2/IR
Context
- Israel and Hamas have agreed to a ceasefire and hostage release deal, potentially ending the two-year-long conflict in Gaza.
- The agreement could reopen the Red Sea shipping route, which had been disrupted by Houthi attacks on vessels, believed to be backed by Iran.
Freight Rates and Global Trade
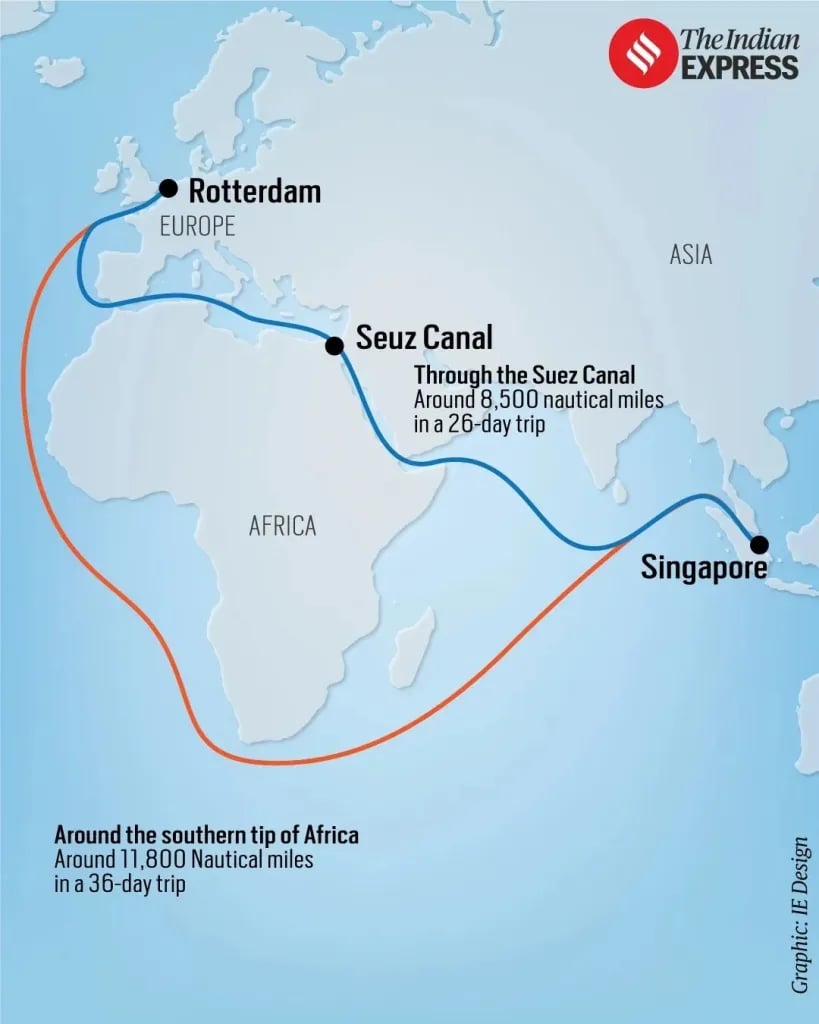
- Since late 2023, freight rates surged nearly threefold due to the need to reroute vessels around the Cape of Good Hope.
- Shorter Suez Canal routes were blocked, increasing transit time, shipping costs, and profits for companies.
- India’s trade was particularly affected, as 90–95% of it depends on foreign carriers, mainly through the Suez Canal.
Impact on India
- Export Challenges: Longer routes raised costs and transit time, affecting profit margins, especially for low-margin, labour-intensive goods.
- Transport Costs: Indian exporters faced higher remittances to foreign shipping lines, exceeding $100 billion annually, even before the Red Sea crisis.
- Strategic Projects at Risk: India–Middle East–Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) could be delayed.
- IMEC aims to provide alternative routes to Europe via rail, ship-rail networks, and road, reducing reliance on the Suez Canal and offering up to 40% faster transit.
- Policy Response: The crisis highlighted India’s dependence on foreign shipping and the strategic dominance of China in shipbuilding.
- Union Cabinet approval (Rs 69,725 crore package) aims to revitalize India’s shipbuilding sector.
- Shipbuilding Financial Assistance Scheme (SBFAS) extended to 2036 with Rs 24,736 crore.
- National Shipbuilding Mission to oversee initiatives.
| Major Choke Points in International Trade Sea Route – Strait of Hormuz: Located between the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, the Strait of Hormuz is a crucial passage for oil shipments from the Middle East. 1. A significant portion of the world’s oil supply passes through this choke point. – Malacca Strait: Situated between the Malay Peninsula and the Indonesian island of Sumatra, the Malacca Strait is one of the busiest waterways globally. 1. It connects the Indian Ocean to the South China Sea and the Pacific Ocean, making it a key route for trade between Europe, the Middle East, and East Asia. – Panama Canal: Linking the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, the Panama Canal is crucial for maritime trade between the Americas, Europe, and Asia. 1. It allows ships to bypass the lengthy and treacherous journey around the southern tip of South America. – Taiwan Strait: Separating Taiwan from mainland China, the Taiwan Strait is essential for shipping in the East Asian region. It is a heavily trafficked waterway for goods moving between China, Taiwan, Japan, and other Asian nations. |
Key Expected Outcomes
- The ceasefire may ease freight rates and improve global trade, particularly India-Europe exports.
- The long-term impact depends on Houthi compliance and security along the Red Sea route.
- With freight rates now expected to ease India’s exports of low-margin products such as agricultural goods, textiles, footwear, and marine products could find easier transit to Europe.
- India relies heavily on the Suez Canal route for its trade with Europe, the US, Africa, and West Asia.
- India is now prioritizing self-reliance in maritime logistics, including shipbuilding, to reduce strategic vulnerability.
Source: IE
Previous article
Foreign Minister of Afghanistan Visited India